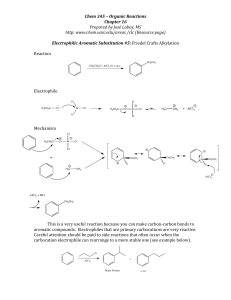
Exam 2 Review A
... three things: 1. React with nucleophiles, 2. -eliminate (lose H+) to form an alkene, 3. undergo skeletal rearrangements via 1,2-hydride shifts or 1,2-methanide shifts. [we will defer discussion of #3 until Chapter 7]. Remember, carbocation stability plays a role in analyzing transition states, whic ...
... three things: 1. React with nucleophiles, 2. -eliminate (lose H+) to form an alkene, 3. undergo skeletal rearrangements via 1,2-hydride shifts or 1,2-methanide shifts. [we will defer discussion of #3 until Chapter 7]. Remember, carbocation stability plays a role in analyzing transition states, whic ...
Quarter 3: Post Test Review
... 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. define the relationship between electrons in these two types of bonds c. a _______ bond is between a metal and a non-metal d. a ________ bond is between two non-metals 46. What are the main differences bet ...
... 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. define the relationship between electrons in these two types of bonds c. a _______ bond is between a metal and a non-metal d. a ________ bond is between two non-metals 46. What are the main differences bet ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry Soaps
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? ...
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? ...
اســـم المـــدرس: د
... 2) Write the chemical and the reaction mechanism for the reaction of benzaldehyde with excess methanol and acid catalyst. ...
... 2) Write the chemical and the reaction mechanism for the reaction of benzaldehyde with excess methanol and acid catalyst. ...
Name - Clark College
... Please work and place your answers in the spaces provided. Show your work for maximum credit! The last page may be torn off and used for scratch paper. Do not write on the IR/NMR sheet. Bring all material up when you are finished. 1. Provide the reagents for the following 2-step transformation. [6] ...
... Please work and place your answers in the spaces provided. Show your work for maximum credit! The last page may be torn off and used for scratch paper. Do not write on the IR/NMR sheet. Bring all material up when you are finished. 1. Provide the reagents for the following 2-step transformation. [6] ...
Chemistry 218, Winter 2007 Exam 2 Name: 1.
... ester protecting group is to treat it with sodium methoxide (followed by an acidic quench). (14 pts) O R ...
... ester protecting group is to treat it with sodium methoxide (followed by an acidic quench). (14 pts) O R ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... v. Formation of alkoxide ion by reaction of alcohols with Na° or K° 2. Preparation of Alcohols a. 1° alcohols from 1° Alkyl Halides with hydroxide (SN2, review) b. Vicinal Diols from anti-addition of water to Epoxides under acidic or basic conditions (review) or from oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 ( ...
... v. Formation of alkoxide ion by reaction of alcohols with Na° or K° 2. Preparation of Alcohols a. 1° alcohols from 1° Alkyl Halides with hydroxide (SN2, review) b. Vicinal Diols from anti-addition of water to Epoxides under acidic or basic conditions (review) or from oxidation of alkenes with OsO4 ( ...
Soaps, Fragrances and Skin Care 1. In which line of the table are fat
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? 4. A student carried out four tests on ethanol and ethanoic acids to compare the properties of the two homologous series, alcohols and carboxylic acids. a. Choose one test in which ethanol and ethanoic acid will give different results a ...
... What term can be applied to aspirin but not oil of wintergreen? 4. A student carried out four tests on ethanol and ethanoic acids to compare the properties of the two homologous series, alcohols and carboxylic acids. a. Choose one test in which ethanol and ethanoic acid will give different results a ...
study note 3 33
... broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are types of addition reactions. Oxidation and hydrolysis are, in some cases ...
... broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are types of addition reactions. Oxidation and hydrolysis are, in some cases ...
Unit 3 Goals - kimscience.com
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
Lecture 28 - The Cook Group @ NDSU
... The substitution of an alcohol functional group with a halogen can be carried out on tertiary alcohols with mineral acids. This reaction only works with 3° alcohols as the mechanism involves the loss of water to form a carbocation and subsequent addition of halide. H OH ...
... The substitution of an alcohol functional group with a halogen can be carried out on tertiary alcohols with mineral acids. This reaction only works with 3° alcohols as the mechanism involves the loss of water to form a carbocation and subsequent addition of halide. H OH ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... 23.) If 20 mL of 0.010 M H3PO4 solution is completely neutralized by 60.0 mL of Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
... 23.) If 20 mL of 0.010 M H3PO4 solution is completely neutralized by 60.0 mL of Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
Senior Science topics Programme
... The programme consists of five parts: 1. Hydrogenation of alkenes This part introduces to students the characteristic reaction of alkenes, addition reaction, as exemplified by the hydrogenation of ethene. The process in which the reaction is speeded up by the presence of a catalyst is illustrated by ...
... The programme consists of five parts: 1. Hydrogenation of alkenes This part introduces to students the characteristic reaction of alkenes, addition reaction, as exemplified by the hydrogenation of ethene. The process in which the reaction is speeded up by the presence of a catalyst is illustrated by ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... • Sometimes called the Hofmann hypobromite reaction • Cl2 is sometimes used in place of Br2 • A primary amide is the required starting compound ...
... • Sometimes called the Hofmann hypobromite reaction • Cl2 is sometimes used in place of Br2 • A primary amide is the required starting compound ...
Exam 1
... different physical properties. Boiling points are 35oC, 36oC, and 117oC, respectively. Their respective solubilities in water are 7.5g/100mL, insoluble, and 9g/100mL. (i) Draw structures for each of these compounds. (ii) Justify the observed boiling points and their solubilities. ...
... different physical properties. Boiling points are 35oC, 36oC, and 117oC, respectively. Their respective solubilities in water are 7.5g/100mL, insoluble, and 9g/100mL. (i) Draw structures for each of these compounds. (ii) Justify the observed boiling points and their solubilities. ...
Oxacyclopropane (Epoxide) Synthesis: Epoxidation by
... The mildest reagent capable of breaking both the and bonds in a double bond is ozone, O3. This process is known as “ozonolysis.” Ozone is produced by an electrical discharge in dry oxygen in a instrument called an ozonator. The initial product of the reaction of ozone with an alkene is an ozonid ...
... The mildest reagent capable of breaking both the and bonds in a double bond is ozone, O3. This process is known as “ozonolysis.” Ozone is produced by an electrical discharge in dry oxygen in a instrument called an ozonator. The initial product of the reaction of ozone with an alkene is an ozonid ...
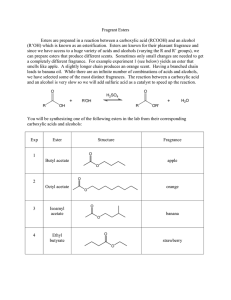
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... Esters are prepared in a reaction between a carboxylic acid (RCOOH) and an alcohol (R’OH) which is known as an esterification. Esters are known for their pleasant fragrance and since we have access to a huge variety of acids and alcohols (varying the R and R’ groups), we can prepare esters that prod ...
... Esters are prepared in a reaction between a carboxylic acid (RCOOH) and an alcohol (R’OH) which is known as an esterification. Esters are known for their pleasant fragrance and since we have access to a huge variety of acids and alcohols (varying the R and R’ groups), we can prepare esters that prod ...
CH 3502 4500
... 16. Discuss the mechanism of cleavage of ethers by HI. 17. Explain Williamson’s synthesis of ethers. 18. Discuss Norrish type-I reaction. 19. Discuss the mechanism of Wittig reaction and its uses in organic synthesis. 20. Explain Wolf-Kishner reduction with its mechanism. 21. Give any two methods o ...
... 16. Discuss the mechanism of cleavage of ethers by HI. 17. Explain Williamson’s synthesis of ethers. 18. Discuss Norrish type-I reaction. 19. Discuss the mechanism of Wittig reaction and its uses in organic synthesis. 20. Explain Wolf-Kishner reduction with its mechanism. 21. Give any two methods o ...
organic quiz 2
... the following will be the product(s)? a) 1-chlorohexane only b) 2-chlorohexane only c) 3-chlorohexane only d) both (b) and (c) 18) DNA is a natural polymer composed of a) glucose monomers b) nucleotide monomers c) amino acid monomers d) cellulose monomers 19) The process in which large organic molec ...
... the following will be the product(s)? a) 1-chlorohexane only b) 2-chlorohexane only c) 3-chlorohexane only d) both (b) and (c) 18) DNA is a natural polymer composed of a) glucose monomers b) nucleotide monomers c) amino acid monomers d) cellulose monomers 19) The process in which large organic molec ...
doc CHEM 222 Lab exam with Answers
... temperature and then allowing them to come back out of solution. 2.__T___ The purpose of refluxing is to carry out a reaction at the boiling point of the solvent. 3.__F___ All chemical reactions must take place in solution. 4.__T___ When a carbene is formed in the presence of an alkene, a cyclopropa ...
... temperature and then allowing them to come back out of solution. 2.__T___ The purpose of refluxing is to carry out a reaction at the boiling point of the solvent. 3.__F___ All chemical reactions must take place in solution. 4.__T___ When a carbene is formed in the presence of an alkene, a cyclopropa ...
CHE 322
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.