Homework Solutions Week 6
... When silver sulfate starts to precipitate, 97% of the calcium has precipitated. And when calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the river ...
... When silver sulfate starts to precipitate, 97% of the calcium has precipitated. And when calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the river ...
Chemistry 30 – Organic Chemistry
... • Alcohols undergo elimination to produce water and an alkene • Alkyl halides can undergo elimination to produce alkene and hydrogen halide ...
... • Alcohols undergo elimination to produce water and an alkene • Alkyl halides can undergo elimination to produce alkene and hydrogen halide ...
EXPERIMENT 2 Properties of Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alcohols
... Reactivity with 3 M NaOH(aq). Use the general procedure for solubility tests to test only those compounds that did not dissolve in water. Use 3 M NaOH(aq) as the solvent. Watch carefully for any sign of reaction as discussed in the background. Reactivity with 3 M HCl(aq). Use the general procedure f ...
... Reactivity with 3 M NaOH(aq). Use the general procedure for solubility tests to test only those compounds that did not dissolve in water. Use 3 M NaOH(aq) as the solvent. Watch carefully for any sign of reaction as discussed in the background. Reactivity with 3 M HCl(aq). Use the general procedure f ...
The Organic Chemistry of Drug Design and Drug Action
... Site of Reactions Catalyzed by P450 Part of molecule undergoing reaction is determined by: 1. topography of the active site of the isozyme 2. degree of steric hindrance of the heme iron-oxo species to the site of reaction 3. ease of H atom abstraction or electron transfer from the ...
... Site of Reactions Catalyzed by P450 Part of molecule undergoing reaction is determined by: 1. topography of the active site of the isozyme 2. degree of steric hindrance of the heme iron-oxo species to the site of reaction 3. ease of H atom abstraction or electron transfer from the ...
Part A Completion
... ________ 10. The oxidation number of each oxygen atom in most compounds is !2. ________ 11. The oxidation number of Cl in KClO3 is !1. ________ 12. The oxidation number of each hydrogen atom in most compounds is !1. ________ 13. The oxidation number for copper in a copper penny is "2. ...
... ________ 10. The oxidation number of each oxygen atom in most compounds is !2. ________ 11. The oxidation number of Cl in KClO3 is !1. ________ 12. The oxidation number of each hydrogen atom in most compounds is !1. ________ 13. The oxidation number for copper in a copper penny is "2. ...
Chem. 31 – 9/15 Lecture
... – In HPLC, the derivatives make weak to moderately absorbing carbonyl compounds strongly absorbing ...
... – In HPLC, the derivatives make weak to moderately absorbing carbonyl compounds strongly absorbing ...
Document
... • Problem: draw condensed structural formulas for the two aldehydes of molecular formula C4H8O • Solution: • first draw the functional group of an aldehyde and add the remaining three carbons; these may be bonded in two ways. • then add the seven hydrogens necessary to complete the four bonds of eac ...
... • Problem: draw condensed structural formulas for the two aldehydes of molecular formula C4H8O • Solution: • first draw the functional group of an aldehyde and add the remaining three carbons; these may be bonded in two ways. • then add the seven hydrogens necessary to complete the four bonds of eac ...
PPT - Gmu
... (stable), but can be attacked by strong Electrophiles. The stability of the aromatic ring ( bond structure) results in substitution as opposed to addition of the Electrophile as seen in the bond structure of Alkenes and Alkynes. ...
... (stable), but can be attacked by strong Electrophiles. The stability of the aromatic ring ( bond structure) results in substitution as opposed to addition of the Electrophile as seen in the bond structure of Alkenes and Alkynes. ...
Unit 5 2 Thermodynamics Enthalpy
... D) Hess’s law: (really a very sweet concept) When a reaction occurs in a series of steps, ∆H (the change in enthalpy, a.k.a., the heat of reaction) for the overall reaction should equal the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. That is: When a reaction is the sum of two or more other ...
... D) Hess’s law: (really a very sweet concept) When a reaction occurs in a series of steps, ∆H (the change in enthalpy, a.k.a., the heat of reaction) for the overall reaction should equal the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. That is: When a reaction is the sum of two or more other ...
Class Notes
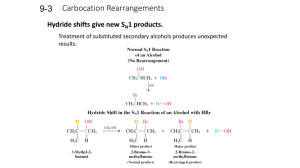
... a. The carbanion is added first, at one point in time, under strongly anionic conditions o The first three steps all occur under these anionic conditions b. Acid is only added much later, in a second laboratory step. This gives a cationic environment. c. Why don’t you just protonate after the first ...
... a. The carbanion is added first, at one point in time, under strongly anionic conditions o The first three steps all occur under these anionic conditions b. Acid is only added much later, in a second laboratory step. This gives a cationic environment. c. Why don’t you just protonate after the first ...
ALcohols CPP
... the acidified K2Cr2O7 is dripped into the warm alcohol aldehydes have low boiling points - no hydrogen bonding - they distil off immediately if it didn’t distil off it would be oxidised to the equivalent carboxylic acid to oxidise an alcohol straight to the acid, reflux the mixture ...
... the acidified K2Cr2O7 is dripped into the warm alcohol aldehydes have low boiling points - no hydrogen bonding - they distil off immediately if it didn’t distil off it would be oxidised to the equivalent carboxylic acid to oxidise an alcohol straight to the acid, reflux the mixture ...
Aromatic Compounds
... Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds Heterocyclic compounds have an element other than carbon as a member of the ring Example of aromatic heterocyclic compounds are shown below ...
... Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds Heterocyclic compounds have an element other than carbon as a member of the ring Example of aromatic heterocyclic compounds are shown below ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when we express the rate of a chemical reaction, what we really measure in the laboratory is an average rate over some observation period. The reaction has an instantaneous rate at each point in tim ...
... going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when we express the rate of a chemical reaction, what we really measure in the laboratory is an average rate over some observation period. The reaction has an instantaneous rate at each point in tim ...
Novel Transition Metal-Catalysed Syntheses of Carboxylic Acid
... In an extension of this concept, it was shown that these complexes also act as precatalysts for both the oxidation of alcohols and the reduction of ketones via transfer hydrogenation. Addition of base and a suitable hydrogen donor (2-propanol) led to reduction of ketones, or a suitable acceptor (3-p ...
... In an extension of this concept, it was shown that these complexes also act as precatalysts for both the oxidation of alcohols and the reduction of ketones via transfer hydrogenation. Addition of base and a suitable hydrogen donor (2-propanol) led to reduction of ketones, or a suitable acceptor (3-p ...
Syllabus - Chemistry
... The Chemistry of Excited State Molecules: Photochemical laws & quantum yield. Kinetics & quantum yield of photo-physical (radiative) and photo-chemical processes. Photochemical processes: primary, secondary, adiabatic & non- adiabatic. Properties of thexi states; Determination of dipole moments & ac ...
... The Chemistry of Excited State Molecules: Photochemical laws & quantum yield. Kinetics & quantum yield of photo-physical (radiative) and photo-chemical processes. Photochemical processes: primary, secondary, adiabatic & non- adiabatic. Properties of thexi states; Determination of dipole moments & ac ...
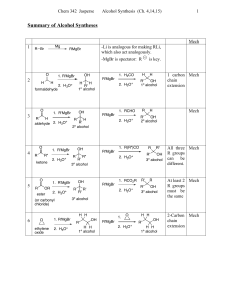
Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents
... Retrosynthetic analysis is the process by which we plan a synthesis by reasoning backward from the desired product (the "target molecule"). ...
... Retrosynthetic analysis is the process by which we plan a synthesis by reasoning backward from the desired product (the "target molecule"). ...
Chemistry Unit 1
... Urea was the first organic compound synthesized in the laboratory. The synthesis of urea by Friedrich Wöhler and subsequent synthesis of other organic compounds marked the downfall of the ‘life force’ theory. How do you explain organic compounds at present and define organic chemistry? The common fe ...
... Urea was the first organic compound synthesized in the laboratory. The synthesis of urea by Friedrich Wöhler and subsequent synthesis of other organic compounds marked the downfall of the ‘life force’ theory. How do you explain organic compounds at present and define organic chemistry? The common fe ...
Answers - University of Waterloo
... *E chromium, Cr 10 Sacrificial anodes are attached to the hulls of ships to protect the iron (Fe) in the hull from corrosion. Which of the following metals could be used as a sacrificial anode for protecting the iron hull of a ship? A ...
... *E chromium, Cr 10 Sacrificial anodes are attached to the hulls of ships to protect the iron (Fe) in the hull from corrosion. Which of the following metals could be used as a sacrificial anode for protecting the iron hull of a ship? A ...
Chapter 12 Carboxylic Acids
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water, and the lower molecular-weight carboxylic acids (up through four carbon atoms) are miscible with water. As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, water solubility decreases until acids with more than 10 carbon atoms are essentially insoluble i ...
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water, and the lower molecular-weight carboxylic acids (up through four carbon atoms) are miscible with water. As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, water solubility decreases until acids with more than 10 carbon atoms are essentially insoluble i ...
Task 4 6 points - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... One of the spices used in the recipe consists of 80-90% of substance X. A combustion analysis of 2.9644g of substance X results in 8.8020g CO2 and 2.1624g H2O. The molar mass of substance X is M < 200g∙mol-1. ...
... One of the spices used in the recipe consists of 80-90% of substance X. A combustion analysis of 2.9644g of substance X results in 8.8020g CO2 and 2.1624g H2O. The molar mass of substance X is M < 200g∙mol-1. ...
UILChemistryProblemsPart2
... 28. It required 25.0 mL of 0.333 M sodium hydroxide solution to completely neutralize 15.0 mL of sulfuric acid solution. What was the molarity of the sulfuric acid solution? Calculate the number moles of NaOH used. 2. Write the balanced reaction. 3. Convert moles NaOH to moles H2SO4 using the coeffi ...
... 28. It required 25.0 mL of 0.333 M sodium hydroxide solution to completely neutralize 15.0 mL of sulfuric acid solution. What was the molarity of the sulfuric acid solution? Calculate the number moles of NaOH used. 2. Write the balanced reaction. 3. Convert moles NaOH to moles H2SO4 using the coeffi ...
Document
... 5. Copper reacts with nitric acid to produce copper(II) nitrate, nitrogen dioxide gas, and water. If you have 0.500 moles of Cu, ________. Cu(s) + 4 HNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO2(g) + 2 H2O() a) you need at least 0.125 moles of HNO3 to produce 0.500 moles of Cu(NO3)2. b) you need at least 0.250 m ...
... 5. Copper reacts with nitric acid to produce copper(II) nitrate, nitrogen dioxide gas, and water. If you have 0.500 moles of Cu, ________. Cu(s) + 4 HNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO2(g) + 2 H2O() a) you need at least 0.125 moles of HNO3 to produce 0.500 moles of Cu(NO3)2. b) you need at least 0.250 m ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.