Functional Groups PP
... only)? Which is an alkene (double bond)? An alkyne (triple bond)? 1. C2H6 2. C2H4 3. C2H2 ...
... only)? Which is an alkene (double bond)? An alkyne (triple bond)? 1. C2H6 2. C2H4 3. C2H2 ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... ii. reaction with Ketones and Aldehydes iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduc ...
... ii. reaction with Ketones and Aldehydes iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduc ...
R-c-H+H-oH:n-J-u oo o il o o o I o
... 14. \tVhichof the following compounds contains a diether linkage? (a) a hemiacetal (b) chloral hydrate (c) aketal (d) camphor 15. \tVhichof the following substancesis used as a preservative of biological specimens? (a) paraldehyde (b) formalin (c) methyl ethyl ketone (d) cinnamaldehyde 16. \Mhich of ...
... 14. \tVhichof the following compounds contains a diether linkage? (a) a hemiacetal (b) chloral hydrate (c) aketal (d) camphor 15. \tVhichof the following substancesis used as a preservative of biological specimens? (a) paraldehyde (b) formalin (c) methyl ethyl ketone (d) cinnamaldehyde 16. \Mhich of ...
Microsoft Word
... deprotected in compound 18 by using 60% aqueous aceticacid gave diol 19. Primary alcoholic group was selectively protected by using TBDMS chloride to give compound 20. Alcohol 20 was esterified with acidchloride 15 in presence of Zinc to afford ester 21. After successful formation of ester 21, our e ...
... deprotected in compound 18 by using 60% aqueous aceticacid gave diol 19. Primary alcoholic group was selectively protected by using TBDMS chloride to give compound 20. Alcohol 20 was esterified with acidchloride 15 in presence of Zinc to afford ester 21. After successful formation of ester 21, our e ...
Organic Chemistry Practice Test
... A. Cellulose and Starch B. Polyethylene and Nylon C. Protein and Starch D. Protein and Nylon ...
... A. Cellulose and Starch B. Polyethylene and Nylon C. Protein and Starch D. Protein and Nylon ...
Chem 130 Fall 2004 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 8.1
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
Combustion, Addition and Elimination Objective Combustion Example
... combustion of 2-methypentane. ...
... combustion of 2-methypentane. ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... alcohol (12.1) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an alkyl group. carbinol carbon (12.4) in an alcohol, the carbon to which the hydroxyl group is attached. dehydration (of alcohols) (12.5) a reaction that involves the loss of a water molecule; e.g., the loss of wate ...
... alcohol (12.1) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an alkyl group. carbinol carbon (12.4) in an alcohol, the carbon to which the hydroxyl group is attached. dehydration (of alcohols) (12.5) a reaction that involves the loss of a water molecule; e.g., the loss of wate ...
Asymmetric Organocatalysis
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
슬라이드 1
... The main advantage of nickel is that it reacts more readily with arylchlorides and methanesulfonates than does the Pd system. These reactants may be more economical than iodides or triflates in large-scale synthesis. ...
... The main advantage of nickel is that it reacts more readily with arylchlorides and methanesulfonates than does the Pd system. These reactants may be more economical than iodides or triflates in large-scale synthesis. ...
Formative 3.5 2014
... Any ester with 6 carbons. Any 6 carbon carboxylic acid. (c) (i) Butan-1-ol reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to form but-1-ene and water. This is an elimination reaction. Since this is a primary alcohol with the –OH group at the end of the carbon chain there is only one possible product. Butan-2-ol is ...
... Any ester with 6 carbons. Any 6 carbon carboxylic acid. (c) (i) Butan-1-ol reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to form but-1-ene and water. This is an elimination reaction. Since this is a primary alcohol with the –OH group at the end of the carbon chain there is only one possible product. Butan-2-ol is ...
chapter 8 part 2
... Show how you would use solvomercuration-demercuration to prepare tert-butyl methyl ether Why would one use Hg(OCCF3)2 instead of Hg(Oac)2 ...
... Show how you would use solvomercuration-demercuration to prepare tert-butyl methyl ether Why would one use Hg(OCCF3)2 instead of Hg(Oac)2 ...
Organic Chemistry –Syllabus- one Semester Sackler faculty of
... Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cyclohexane, Combustion of alkanes, Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry, Halogenation of alkanes. Stereochemistry Classification of Isomers, Chirality, Enantiomers, Achiral molecules, ch ...
... Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cyclohexane, Combustion of alkanes, Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry, Halogenation of alkanes. Stereochemistry Classification of Isomers, Chirality, Enantiomers, Achiral molecules, ch ...
Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry Chemistry
... takes place when methane reacts with chlorine. A chlorine atom has replaced a hydrogen atom in a molecule of methane. This is known as halogenation of alkanes or more specifically the chlorination of methane is referred to as a free radical substitution reaction and it involves four steps: initiatio ...
... takes place when methane reacts with chlorine. A chlorine atom has replaced a hydrogen atom in a molecule of methane. This is known as halogenation of alkanes or more specifically the chlorination of methane is referred to as a free radical substitution reaction and it involves four steps: initiatio ...
Chemistry 218, Winter 2007 Exam 2 Name: 1.
... 2. In the following reaction, one of the products is formed preferentially over the other one. Circle the product that is more likely to be formed, and explain why using resonance forms. (10 pts) O ...
... 2. In the following reaction, one of the products is formed preferentially over the other one. Circle the product that is more likely to be formed, and explain why using resonance forms. (10 pts) O ...
Types of Chemical Reactions - Celebrity Examples
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
... y Emission of heat and y Giving off light y Formation of a precipitate y Formation of a gas y Color change ...
Topic 3 – Chemical Structure and Bonding
... o Nitration of benzene followed by reduction using Sn/HCl o Substitution of a halogen by CN- to lengthen a carbon chain o Acylation of a benzene ring followed by reduction using LiAlH4 to give an alcohol ...
... o Nitration of benzene followed by reduction using Sn/HCl o Substitution of a halogen by CN- to lengthen a carbon chain o Acylation of a benzene ring followed by reduction using LiAlH4 to give an alcohol ...
CH 3502 4500
... 16. Discuss the mechanism of cleavage of ethers by HI. 17. Explain Williamson’s synthesis of ethers. 18. Discuss Norrish type-I reaction. 19. Discuss the mechanism of Wittig reaction and its uses in organic synthesis. 20. Explain Wolf-Kishner reduction with its mechanism. 21. Give any two methods o ...
... 16. Discuss the mechanism of cleavage of ethers by HI. 17. Explain Williamson’s synthesis of ethers. 18. Discuss Norrish type-I reaction. 19. Discuss the mechanism of Wittig reaction and its uses in organic synthesis. 20. Explain Wolf-Kishner reduction with its mechanism. 21. Give any two methods o ...
投影片 1
... Dissonant pattern: One E class group is bonded to a carbon with a positive charge, whereas the other E class group resides on a carbon with a negative charge. ...
... Dissonant pattern: One E class group is bonded to a carbon with a positive charge, whereas the other E class group resides on a carbon with a negative charge. ...
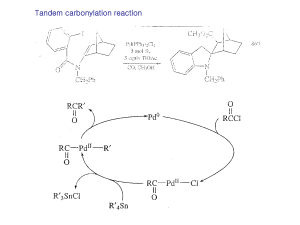
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.