File
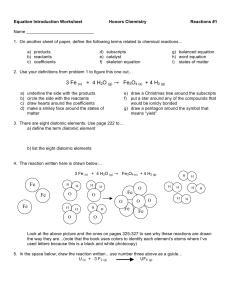
... 5. Elimination reactions of alcohols are generally slow and require an acid catalyst and heating. i) Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 1-propanol to form propene and water. ii) Write a word equation using IUPAC names for the elimination reaction (in the presence of concentrated H ...
... 5. Elimination reactions of alcohols are generally slow and require an acid catalyst and heating. i) Draw structural diagrams to represent the reaction of 1-propanol to form propene and water. ii) Write a word equation using IUPAC names for the elimination reaction (in the presence of concentrated H ...
1 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (Conjugate Addition) If we look
... reaction are slightly different. In essence, the product of an aldol-type reaction between two esters is almost always a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound. In its simplest form: ...
... reaction are slightly different. In essence, the product of an aldol-type reaction between two esters is almost always a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound. In its simplest form: ...
ch-22 HW answers - HCC Learning Web
... A) organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. B) organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. C) organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. D) organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. E) None of the above. ...
... A) organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. B) organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. C) organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. D) organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. E) None of the above. ...
Additional file 1
... 1-Acenaphthen-5-yl-ethanone (3): Pyridinium dichromate (3.0 g, 9.0 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, t ...
... 1-Acenaphthen-5-yl-ethanone (3): Pyridinium dichromate (3.0 g, 9.0 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, t ...
Weekly Review Lecture
... e. Friedel-Crafts alkylation (used for tert-butyl or isopropyl only!) 2) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution a. Addition-Elimination (through EWG-stabilized anionic intermediate) used to add –OR or –SR group b. Elimination-Addition (through benzyne intermediate) used to add –NH2 group 3) Reaction ...
... e. Friedel-Crafts alkylation (used for tert-butyl or isopropyl only!) 2) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution a. Addition-Elimination (through EWG-stabilized anionic intermediate) used to add –OR or –SR group b. Elimination-Addition (through benzyne intermediate) used to add –NH2 group 3) Reaction ...
Slide 1
... • In these polymers, two different functional groups are required and for each new bond between the monomer units (shown coloured below), a small molecule (often water) is produced. • Each monomer must also have two functional groups. • This can involve two different functional groups on the same mo ...
... • In these polymers, two different functional groups are required and for each new bond between the monomer units (shown coloured below), a small molecule (often water) is produced. • Each monomer must also have two functional groups. • This can involve two different functional groups on the same mo ...
Slide 1
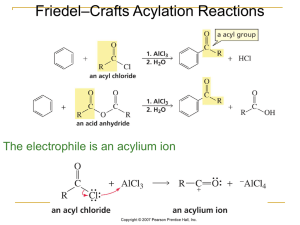
... It is not possible to obtain a good yield of an alkylbenzene containing a straight-chain group via Friedel–Crafts alkylation due to carbocation ...
... It is not possible to obtain a good yield of an alkylbenzene containing a straight-chain group via Friedel–Crafts alkylation due to carbocation ...
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... so that some of the liquid vaporizes, rises part-way up the condenser, and then condenses and falls back down into the reaction flask. This process allows the reaction to be heated over a period of time, without evaporating away the solvent or reactants. At the end of the reaction your product will ...
... so that some of the liquid vaporizes, rises part-way up the condenser, and then condenses and falls back down into the reaction flask. This process allows the reaction to be heated over a period of time, without evaporating away the solvent or reactants. At the end of the reaction your product will ...
11. Oxidation of alcohols, hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes and
... Structural formula: CH3CH(OH)CH3 ...
... Structural formula: CH3CH(OH)CH3 ...
WM5 The synthesis of salicylic acid and aspirin
... Chemists can synthesise (artificially produce) compounds once the structure is known; Phenol’s germicidal properties were well known by the end of 19th Century; Phenol (a product from heating coal) was readily available; 2-hydroxybenzoic acid has 1 extra functional group compared to phenol; ...
... Chemists can synthesise (artificially produce) compounds once the structure is known; Phenol’s germicidal properties were well known by the end of 19th Century; Phenol (a product from heating coal) was readily available; 2-hydroxybenzoic acid has 1 extra functional group compared to phenol; ...
File
... Cis/trans geometric isomers • In triglycerides fatty acids may contain double bonds, which can be in either the cis or trans configuration . • Fats with at least one double bond between carbon atoms are unsaturated fats. When some of these bonds are in the cis configuration, the molecules cannot pa ...
... Cis/trans geometric isomers • In triglycerides fatty acids may contain double bonds, which can be in either the cis or trans configuration . • Fats with at least one double bond between carbon atoms are unsaturated fats. When some of these bonds are in the cis configuration, the molecules cannot pa ...
CH 12-3 Power Point
... compound (aldehyde, ketone, ester, epoxide) to produce a new C-C bond and an alcohol. ...
... compound (aldehyde, ketone, ester, epoxide) to produce a new C-C bond and an alcohol. ...
Senior Science topics Programme
... understanding of the reactivity of different chemical species with experimental observations to deduce the most likely sequence of elementary steps and thus the mechanism of a particular reaction. Knowledge of reaction mechanisms facilitates scientists to plan for synthesising new compounds from som ...
... understanding of the reactivity of different chemical species with experimental observations to deduce the most likely sequence of elementary steps and thus the mechanism of a particular reaction. Knowledge of reaction mechanisms facilitates scientists to plan for synthesising new compounds from som ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Esters can also react with amines or ammonia to form amides. This reaction doesn't involve acid catalysis, so the first step is nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl carbon. Proton transfer follows and loss of the alcohol portion of the ester. ...
... Esters can also react with amines or ammonia to form amides. This reaction doesn't involve acid catalysis, so the first step is nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl carbon. Proton transfer follows and loss of the alcohol portion of the ester. ...
Review 3 - Bonham Chemistry
... 21. Industrially, we often need ethanoic acid. The starting material for this product is usually ethane. Show below a series of reactions that would transform ethane to ethanoic acid. ...
... 21. Industrially, we often need ethanoic acid. The starting material for this product is usually ethane. Show below a series of reactions that would transform ethane to ethanoic acid. ...
20130409085519
... The R group bonded to the oxygen will have a yl ending and the R group bonded to the C=O will have an oate ending. ...
... The R group bonded to the oxygen will have a yl ending and the R group bonded to the C=O will have an oate ending. ...
Test3
... Acids are defined as compounds that produce H+ ions in water solution. Bases are defined as compounds that produce OH- ions in water solution. Arrhenius theory only applies to reactions in aqueous solution. Acids are defined as compounds that produce OH- ions in water solution. ...
... Acids are defined as compounds that produce H+ ions in water solution. Bases are defined as compounds that produce OH- ions in water solution. Arrhenius theory only applies to reactions in aqueous solution. Acids are defined as compounds that produce OH- ions in water solution. ...
Procedure Notes
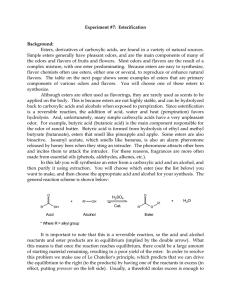
... Procedure Notes • Esters are more commonly used as flavoring rather than scents that are added to the body due to the fact that the reaction is in equilibrium and esters are not very stable. The addition of water and heat from perspiration can cause the reaction to favor the reactants. Carboxylic a ...
... Procedure Notes • Esters are more commonly used as flavoring rather than scents that are added to the body due to the fact that the reaction is in equilibrium and esters are not very stable. The addition of water and heat from perspiration can cause the reaction to favor the reactants. Carboxylic a ...
Chemical Equations
... Assigning Oxidation States (aka Oxidation Number) Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its i ...
... Assigning Oxidation States (aka Oxidation Number) Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its i ...
Section 07 - Section Practice Exam II Solutions
... Problem 5 (based on Problem Set #3, 1999). Provide an efficient synthesis of compound C using starting materials containing no more than four carbon atoms. ...
... Problem 5 (based on Problem Set #3, 1999). Provide an efficient synthesis of compound C using starting materials containing no more than four carbon atoms. ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.