* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WM5 The synthesis of salicylic acid and aspirin
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Sulfuric acid wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
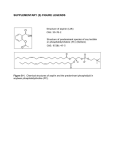
WM5 The synthesis of salicylic acid and aspirin Synthesis is better than harvesting Chemists can synthesise (artificially produce) compounds once the structure is known; Phenol’s germicidal properties were well known by the end of 19th Century; Phenol (a product from heating coal) was readily available; 2-hydroxybenzoic acid has 1 extra functional group compared to phenol; How is phenol converted into 2hydroxybenzoic acid? Draw the structures of phenol and 2hydroxybenzoic acid; What extra atoms need to be added to phenol? What conditions and reagents are needed? (research this); Kolbe –Schmitt synthesis Kolbe (1874) produced salicylic acid from dry sodium phenoxide in a stream of carbon dioxide at 150 – 160 °C. He found that the yield was only 50%. Schmitt (1884) increased the yield to 90% by increasing the pressure to 5 bar (7atm) until no more CO2 was taken up. On an industrial scale… Felix Hoffmann developed the process for the Bayer company; Unpleasant side-effects on mouth, gullet and stomach; Hoffmann modified the structure and tested products on his rheumatic father! 1898: 2-ethanoylhydroxybenzoic acid (a.k.a acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin) produced Aspirin: made by esterification You can read about esters and esterification in CI 13.4. Aspirin is an ester O Functional group R-C-O-R’ Alcohol + acid ester Aspirin is not very soluble in water so it became the first medicine to be sold as tablets;