Handout 3
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
advanced placement chemistry workbook and note set
... use the ideal gas equation and perform gas stoichiometry ...
... use the ideal gas equation and perform gas stoichiometry ...
Lecture - Ch 17
... – 3˚ alcohols react with HCl or HBr by SN1 through carbocation intermediate – 1˚ and 2˚ alcohols are converted into halides by treatment with SOCl2 or PBr3 via SN2 mechanism ...
... – 3˚ alcohols react with HCl or HBr by SN1 through carbocation intermediate – 1˚ and 2˚ alcohols are converted into halides by treatment with SOCl2 or PBr3 via SN2 mechanism ...
Packet 1 - Kentucky Community and Technical College System
... of two ionic compounds are mixed Step 1 Write the reactants as they actually exist before any reaction occurs (the complete ionic equation). Remember that when a salt dissolves, its ions completely separate. Step 2 Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anio ...
... of two ionic compounds are mixed Step 1 Write the reactants as they actually exist before any reaction occurs (the complete ionic equation). Remember that when a salt dissolves, its ions completely separate. Step 2 Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anio ...
doc - Dartmouth College
... (a) The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16 g mol–1. Calculate the maximum mass of aspirin the student could synthesize. (b) The student collected and purified her aspirin product and wanted to calculate the yield of the reaction. Unfortunately her balance was broken, but her pH meter was in worki ...
... (a) The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16 g mol–1. Calculate the maximum mass of aspirin the student could synthesize. (b) The student collected and purified her aspirin product and wanted to calculate the yield of the reaction. Unfortunately her balance was broken, but her pH meter was in worki ...
$doc.title
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel addi1ve, ...
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel addi1ve, ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... (H) bonded to a primary chain carbon. 4. Alkane: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2, where all the carboncarbon bonds are single bonds. 5. Alkene: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n, where only one of the carbon-carbon bonds is a double bond. 6. Alkyl Group: An alkane fragment ...
... (H) bonded to a primary chain carbon. 4. Alkane: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2, where all the carboncarbon bonds are single bonds. 5. Alkene: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n, where only one of the carbon-carbon bonds is a double bond. 6. Alkyl Group: An alkane fragment ...
19 Amines and Amides Study Goals
... derivatives. Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary and named according to IUPAC and common naming systems. Heterocyclic amines are introduced and their role in alkaloids and other physiological amines is described. Demonstration: Amines and Amides Amines and amides are introduced ...
... derivatives. Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary and named according to IUPAC and common naming systems. Heterocyclic amines are introduced and their role in alkaloids and other physiological amines is described. Demonstration: Amines and Amides Amines and amides are introduced ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... In other words, particle size distribution narrows, independently on the initial distribution while all particles grow and no additional nucleation appears. This selfregulating mechanism of size distribution is often called “focusing effect” [29]. On the whole, particle growth is controlled by compe ...
... In other words, particle size distribution narrows, independently on the initial distribution while all particles grow and no additional nucleation appears. This selfregulating mechanism of size distribution is often called “focusing effect” [29]. On the whole, particle growth is controlled by compe ...
Document
... • Compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, where as those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be meaningful ...
... • Compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, where as those that do not are said to be insoluble NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water the degree of solubility depends on the temperature even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be meaningful ...
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates - Angelo State University
... Biochemistry • Biochemistry is the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and living organisms. • In organic chemistry, we organized our study of carbon-containing molecules by functional group (alcohol, alkene, ketone, carboxylic acid, etc.). • In the first five chapters, we will take a look at sev ...
... Biochemistry • Biochemistry is the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and living organisms. • In organic chemistry, we organized our study of carbon-containing molecules by functional group (alcohol, alkene, ketone, carboxylic acid, etc.). • In the first five chapters, we will take a look at sev ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... (H) bonded to a primary chain carbon. 4. Alkane: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2, where all the carboncarbon bonds are single bonds. 5. Alkene: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n, where only one of the carbon-carbon bonds is a double bond. 6. Alkyl Group: An alkane fragment ...
... (H) bonded to a primary chain carbon. 4. Alkane: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2, where all the carboncarbon bonds are single bonds. 5. Alkene: A hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n, where only one of the carbon-carbon bonds is a double bond. 6. Alkyl Group: An alkane fragment ...
Chemical Equilibria - Beck-Shop
... increase and deplete the amount of products present, which in turn cause the backward rate to decrease? A: There is a fallacy here. As more products form, the rate of the backward reaction does increase. But this increase does not deplete the concentration of the products because the rate of the for ...
... increase and deplete the amount of products present, which in turn cause the backward rate to decrease? A: There is a fallacy here. As more products form, the rate of the backward reaction does increase. But this increase does not deplete the concentration of the products because the rate of the for ...
Richard R. Schrock - Nobel Lecture
... was intrigued by high oxidation state peralkyl complexes and had chosen to explore the organometallic chemistry of tantalum soon after my arrival at DuPont. Little alkyl chemistry was known of the metals in group 5 (V, Nb, Ta) at that time; I chose tantalum because it is next to tungsten in group 6 ...
... was intrigued by high oxidation state peralkyl complexes and had chosen to explore the organometallic chemistry of tantalum soon after my arrival at DuPont. Little alkyl chemistry was known of the metals in group 5 (V, Nb, Ta) at that time; I chose tantalum because it is next to tungsten in group 6 ...
Lesson 19 - WordPress.com
... Tertiary alcohols have the OH group next to two branches of the chain. Attached to the same carbon as the OH is: • 3 alkyl groups • 0 Hydrogens e.g. 2-methylpropan-2-ol ...
... Tertiary alcohols have the OH group next to two branches of the chain. Attached to the same carbon as the OH is: • 3 alkyl groups • 0 Hydrogens e.g. 2-methylpropan-2-ol ...
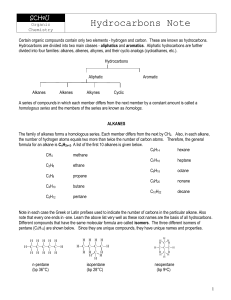
Hydrocarbons Note
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
g - mrnicholsscience
... Write the reaction • Butane gas(C4H10) burns in oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C4H10(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) ...
... Write the reaction • Butane gas(C4H10) burns in oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C4H10(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) ...
File
... 30. Hydrogen reacts with halogens to give __________. (Hydrogen halides, hydrogen hydrides, hydrogen sulphides, All of these) 31. Hydrogen is used in the manufacture of __________. (Fertilizers, CO2, O2, None of these) 32. Hydrogen at the time of its generation during chemical reaction is in the for ...
... 30. Hydrogen reacts with halogens to give __________. (Hydrogen halides, hydrogen hydrides, hydrogen sulphides, All of these) 31. Hydrogen is used in the manufacture of __________. (Fertilizers, CO2, O2, None of these) 32. Hydrogen at the time of its generation during chemical reaction is in the for ...
Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(5)
... Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(19) • Synthesis of Substituted Benzenes • One of the surest ways to learn organic chemistry is to work synthesis problems. The ability to plan a successful multistep synthesis of a complex molecule requires a working knowledge of the uses and ...
... Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(19) • Synthesis of Substituted Benzenes • One of the surest ways to learn organic chemistry is to work synthesis problems. The ability to plan a successful multistep synthesis of a complex molecule requires a working knowledge of the uses and ...
Unit 16: Chemistry for Biology Technicians
... amides; recognition of functional groups in complex molecules, eg carbohydrates, fats, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids Structure: tetrahedral carbon; planar carbon to carbon double bonds; structural isomerism; chain; positional; functional group; geometric; cis and trans; optical (chiral carbon ...
... amides; recognition of functional groups in complex molecules, eg carbohydrates, fats, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids Structure: tetrahedral carbon; planar carbon to carbon double bonds; structural isomerism; chain; positional; functional group; geometric; cis and trans; optical (chiral carbon ...
CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid
... Note that this reaction moves a pair of electrons in a single-step reaction. • A free pair from the hydroxide oxygen forms a dative bond with the hydrogen ion to form water. M&B p.6-7 ...
... Note that this reaction moves a pair of electrons in a single-step reaction. • A free pair from the hydroxide oxygen forms a dative bond with the hydrogen ion to form water. M&B p.6-7 ...
Ans:- (i) Gluconic acid - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2, Kribhco, Surat
... whereas that of electrolyte increases. Q2. How is cell constant calculated from conductance values? Ans. Cell constant = specific conductance/observed conductance. Q3. What is the reference electrode in determining the standard electrode ...
... whereas that of electrolyte increases. Q2. How is cell constant calculated from conductance values? Ans. Cell constant = specific conductance/observed conductance. Q3. What is the reference electrode in determining the standard electrode ...
Polymers: Introduction
... • Below the melting point, the chains can move, but only slowly. Thus the plastic is flexible, but cannot be easily stretched. • Below the glass transition point, the chains become locked and the polymer is rigid ...
... • Below the melting point, the chains can move, but only slowly. Thus the plastic is flexible, but cannot be easily stretched. • Below the glass transition point, the chains become locked and the polymer is rigid ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.