Electrochemistry
... 1. A substance that has the element that has been ________ (LOST electrons) will have an oxidation number that becomes more ________. 2. A substance that has the element that has been ________ (GAINED electrons) will have an oxidation number that becomes more ________. B. ___________ are produced in ...
... 1. A substance that has the element that has been ________ (LOST electrons) will have an oxidation number that becomes more ________. 2. A substance that has the element that has been ________ (GAINED electrons) will have an oxidation number that becomes more ________. B. ___________ are produced in ...
Balancing Redox Equations
... Oxidation Number - The charge that an atom would have if the compound in which it were found were ionic. The rules: 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a molecule must be equal to the overall charge on the molecule. 2) To assign a number to a transition metal ion (not listed in the t ...
... Oxidation Number - The charge that an atom would have if the compound in which it were found were ionic. The rules: 1) The sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a molecule must be equal to the overall charge on the molecule. 2) To assign a number to a transition metal ion (not listed in the t ...
Preparation of spherical DDNP study Liu off on a journey
... Influence of ammonia salt crystals diazotization due in ammonia salt filtration process Amount drained liquor, ammonium salt crystals when stout, filtration fast, do not And then washed with water. Because the sodium picramate reduction is an exothermic reaction, the addition point may be scattered ...
... Influence of ammonia salt crystals diazotization due in ammonia salt filtration process Amount drained liquor, ammonium salt crystals when stout, filtration fast, do not And then washed with water. Because the sodium picramate reduction is an exothermic reaction, the addition point may be scattered ...
Chapter_Sixteen_lecture
... reaction. Reversal requires an acid catalyst and a large quantity of water. Hydrolysis: A reaction in which a bond or bonds are broken and the -H and -OH of water add to the atoms of the broken bond or bonds. ...
... reaction. Reversal requires an acid catalyst and a large quantity of water. Hydrolysis: A reaction in which a bond or bonds are broken and the -H and -OH of water add to the atoms of the broken bond or bonds. ...
V a.) \
... ammonium salt, cetyltrimethylamrnonium chloride, is found in mouthwashes and is used as a germicide for sterilizing medical instruments. ...
... ammonium salt, cetyltrimethylamrnonium chloride, is found in mouthwashes and is used as a germicide for sterilizing medical instruments. ...
ACP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam - Doc-U-Ment
... A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name for aqueous HBr. A) bromic acid B) bromo ...
... A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name for aqueous HBr. A) bromic acid B) bromo ...
Chem 400 Review Chem 350 JJ.S17
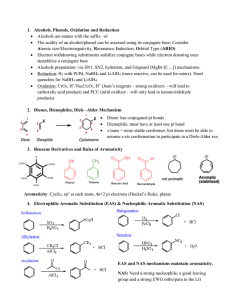
... Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with Pt/Pd, NaBH4 and LiAlH4 (more reactive, can be used for esters). Need quen ...
... Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with Pt/Pd, NaBH4 and LiAlH4 (more reactive, can be used for esters). Need quen ...
INTRODUCING ALCOHOLS
... Concentrated sulphuric acid produces messy results. Not only is it an acid, but it is also a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises some of the alcohol to carbon dioxide and at the same time is reduced itself to sulphur dioxide. Both of these gases have to be removed from the alkene. The dehydration of ...
... Concentrated sulphuric acid produces messy results. Not only is it an acid, but it is also a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises some of the alcohol to carbon dioxide and at the same time is reduced itself to sulphur dioxide. Both of these gases have to be removed from the alkene. The dehydration of ...
Organic Chemistry III Laboratory
... In 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone there is not the same conformational flexibility as in 2-methylcyclohexanone. The tert-butyl group is too large to occupy the axial position in a cyclohexane ring. Therefore, the compound is conformationally locked with the tert-butyl group in the equatorial position. Th ...
... In 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone there is not the same conformational flexibility as in 2-methylcyclohexanone. The tert-butyl group is too large to occupy the axial position in a cyclohexane ring. Therefore, the compound is conformationally locked with the tert-butyl group in the equatorial position. Th ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
std 8 9 reviewanswers
... 9. A catalyst can speed up the rate of a given chemical reaction by A increasing the equilibrium constant in favor of products. B lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. C raising the temperature at which the reaction occurs. D increasing the pressure of reactants, thus fa ...
... 9. A catalyst can speed up the rate of a given chemical reaction by A increasing the equilibrium constant in favor of products. B lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. C raising the temperature at which the reaction occurs. D increasing the pressure of reactants, thus fa ...
Arrows - Rutgers Chemistry
... When we discuss the mechanism, we begin by protonating one of the OH groups (step 1). We show this by a double-‐hooked arrow originating at an oxygen lone pair and pointing to the H; a second ...
... When we discuss the mechanism, we begin by protonating one of the OH groups (step 1). We show this by a double-‐hooked arrow originating at an oxygen lone pair and pointing to the H; a second ...
document
... β Hydrogen needs to be oppostie the leaving group Enantiomers will have the same E-Z nomenclature after dehyrdohalogenation reaction Diastereomes will have opposite E-Z nomenclature after dehydrohalogenation reaction ...
... β Hydrogen needs to be oppostie the leaving group Enantiomers will have the same E-Z nomenclature after dehyrdohalogenation reaction Diastereomes will have opposite E-Z nomenclature after dehydrohalogenation reaction ...
ANSWERS: Types of Reactions - Chemical Minds
... 6) Addition – occurs in alkenes because they have double bonds. Ethene is an alkene so will undergo addition reactions. The chlorine (molecule) will add (across the double bond.) CH2 = CH2 + Cl2 → CH2Cl – CH2Cl Substitution occurs in alkanes (because they have single bonds). Ethane is an alkane, so ...
... 6) Addition – occurs in alkenes because they have double bonds. Ethene is an alkene so will undergo addition reactions. The chlorine (molecule) will add (across the double bond.) CH2 = CH2 + Cl2 → CH2Cl – CH2Cl Substitution occurs in alkanes (because they have single bonds). Ethane is an alkane, so ...
Higher Chemistry
... For straight and branch chained aldehydes and ketones systematic names, structural formulae and isomers. c) Oxidation reactions of aldehydes and ketones. d) Effect of heat on proteins, denature of proteins. 4. Oxidation of food a) For branch chained alcohols with no more than eight carbon atoms in t ...
... For straight and branch chained aldehydes and ketones systematic names, structural formulae and isomers. c) Oxidation reactions of aldehydes and ketones. d) Effect of heat on proteins, denature of proteins. 4. Oxidation of food a) For branch chained alcohols with no more than eight carbon atoms in t ...
Document
... free metals that become combined change of oxidation states double replacement reactions are not redox Determine most reactive metal Substance oxidized is higher on the table ...
... free metals that become combined change of oxidation states double replacement reactions are not redox Determine most reactive metal Substance oxidized is higher on the table ...
Name (Last, First)
... Organic acids also react with alcohols (ROH) which are NOT BASES. They have –OH, but it is not ionized. In fact, when an alcohol reacts with an organic acid, the –OH comes off the acid, and the –H comes off the alcohol. Make models to show the reaction between ethanoic acid and ethanol. Write the eq ...
... Organic acids also react with alcohols (ROH) which are NOT BASES. They have –OH, but it is not ionized. In fact, when an alcohol reacts with an organic acid, the –OH comes off the acid, and the –H comes off the alcohol. Make models to show the reaction between ethanoic acid and ethanol. Write the eq ...
ch15 lecture 7e
... • An addition reaction results in more atoms bonded to C. • An elimination reaction results in fewer atoms bonded to C. • If there are the same number of atoms bonded to C, the reaction is a substitution. ...
... • An addition reaction results in more atoms bonded to C. • An elimination reaction results in fewer atoms bonded to C. • If there are the same number of atoms bonded to C, the reaction is a substitution. ...
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
... 5.1 Naming Enantiomers via the -R and -S System 1. Each of the four groups attached to the chirality center is assigned a priority of 1, 2, 3, or 4. Priority is assigned on the basis of the atomic number of the atom that is directly attached to the chirality center. The group with the highest atomic ...
... 5.1 Naming Enantiomers via the -R and -S System 1. Each of the four groups attached to the chirality center is assigned a priority of 1, 2, 3, or 4. Priority is assigned on the basis of the atomic number of the atom that is directly attached to the chirality center. The group with the highest atomic ...
Chapter 8powerp point for chemical reactions
... Solid calcium metal reacts with water to form aqueous calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. ...
... Solid calcium metal reacts with water to form aqueous calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.