Lecture 10 Carbon-Nitrogen Bonds Formation I
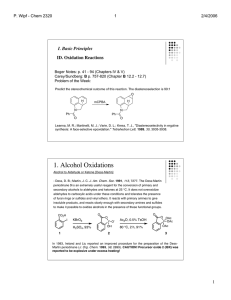
... 4.1 Principles The methods for the formation of bonds between nitrogen and aliphatic carbon can be broadly divided into two categories: (i) reaction of nucleophilic nitrogen with electrophilic carbon, and (ii) reaction of electrophilic nitrogen with nucleophilic carbon. In this section, we will try ...
... 4.1 Principles The methods for the formation of bonds between nitrogen and aliphatic carbon can be broadly divided into two categories: (i) reaction of nucleophilic nitrogen with electrophilic carbon, and (ii) reaction of electrophilic nitrogen with nucleophilic carbon. In this section, we will try ...
IB2 Revision Topic 7
... The amount of SO3 and the value of the equilibrium constant both increase. The amount of SO3 and the value of the equilibrium constant both decrease. The amount of SO3 increases but the value of the equilibrium constant decreases. The amount of SO3 increases but the value of the equilibrium constant ...
... The amount of SO3 and the value of the equilibrium constant both increase. The amount of SO3 and the value of the equilibrium constant both decrease. The amount of SO3 increases but the value of the equilibrium constant decreases. The amount of SO3 increases but the value of the equilibrium constant ...
Study Guide 2 - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols produces aldehydes and ketones respectively. Both aldehydes and ketones are examples of carbonyl compounds, both of them containing the carbonyl group, C=O. This activity considers the structures and systematic names of the alkanal series of aldehydes and ...
... Oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols produces aldehydes and ketones respectively. Both aldehydes and ketones are examples of carbonyl compounds, both of them containing the carbonyl group, C=O. This activity considers the structures and systematic names of the alkanal series of aldehydes and ...
ch15[1].
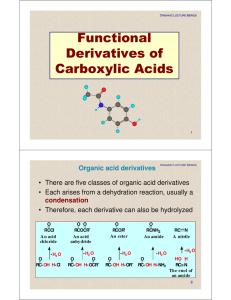
... Reaction with NH 3 and Amines • Acid anhydrides react with ammonia, and with 1° and 2° amines to form amides. • 2 moles of ammonia or amine are required; one to form the amide and one to neutralize the carboxylic acid ...
... Reaction with NH 3 and Amines • Acid anhydrides react with ammonia, and with 1° and 2° amines to form amides. • 2 moles of ammonia or amine are required; one to form the amide and one to neutralize the carboxylic acid ...
CHAPTER 3 STRUCTURES OF METAL COMPLEXES
... Application of molecular orbital theory to octahedral complexes requires the construction of seven-centered molecular orbitals. In the case of both tetrahedral and square-planar complexes, five-centered molecular orbitals are involved. It must be noted that the linear combination of atomic orbitals ...
... Application of molecular orbital theory to octahedral complexes requires the construction of seven-centered molecular orbitals. In the case of both tetrahedral and square-planar complexes, five-centered molecular orbitals are involved. It must be noted that the linear combination of atomic orbitals ...
Learning Outcomes Leaving Certificate Chemistry
... using the Balmer series in the emission spectrum as an example describe and explain the absorption spectrum use flame tests to provide evidence that energy is absorbed or released in discrete units when electrons move from one energy level to another explain how flame tests provide evidence that ene ...
... using the Balmer series in the emission spectrum as an example describe and explain the absorption spectrum use flame tests to provide evidence that energy is absorbed or released in discrete units when electrons move from one energy level to another explain how flame tests provide evidence that ene ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... yielding a great deal of information on “intrinsic” properties, such as kinetics, thermochemistry, and reaction mechanisms in the absence of solvation and counterion effects.1 The reactions with simple hydrocarbons have been particularly important, because they are closely related to solution organo ...
... yielding a great deal of information on “intrinsic” properties, such as kinetics, thermochemistry, and reaction mechanisms in the absence of solvation and counterion effects.1 The reactions with simple hydrocarbons have been particularly important, because they are closely related to solution organo ...
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... the cephalosporins are also β-lactam antibiotics The cephalosporins d iffer in the group bonded to the acyl carbon an d the s ide chain of the thiazin e rin g O NH2 ...
... the cephalosporins are also β-lactam antibiotics The cephalosporins d iffer in the group bonded to the acyl carbon an d the s ide chain of the thiazin e rin g O NH2 ...
Metal-ligand bond lengths and strengths
... notable that the keto oxygen of the COOH group, that is also apically coordinated and subject to Jahn-Teller distortion, see Fig. 5, has a shorter Cu––O bond at 2.338 Å. It is not surprising that only a handful of OH-coordinated carboxylic acid complex are found, as the keto-oxygen is the more basi ...
... notable that the keto oxygen of the COOH group, that is also apically coordinated and subject to Jahn-Teller distortion, see Fig. 5, has a shorter Cu––O bond at 2.338 Å. It is not surprising that only a handful of OH-coordinated carboxylic acid complex are found, as the keto-oxygen is the more basi ...
Aromatic Compounds
... • Electrophilic substitutions are favored by electrondonating substituents which stabilize the carbocation intermediate • Nucleophilic substitutions are favored by electronwithdrawing substituents which stabilize a carbanion intermediate • Electron-withdrawing groups that deactivate rings for electr ...
... • Electrophilic substitutions are favored by electrondonating substituents which stabilize the carbocation intermediate • Nucleophilic substitutions are favored by electronwithdrawing substituents which stabilize a carbanion intermediate • Electron-withdrawing groups that deactivate rings for electr ...
SECONDARY METABOLISM: THE BUILDING BLOCKS AND
... atoms can be introduced and removed by a variety of processes, and so are not considered in the initial analysis, except as a pointer to an acetate (see page 62) or shikimate (see page 123) origin. The structural features of these building blocks are shown in Figure 2.2. • C1 : The simplest of the b ...
... atoms can be introduced and removed by a variety of processes, and so are not considered in the initial analysis, except as a pointer to an acetate (see page 62) or shikimate (see page 123) origin. The structural features of these building blocks are shown in Figure 2.2. • C1 : The simplest of the b ...
Meeting Agenda - Kubiak Research Group
... to Energy-Dense Liquids Monday, December 9, 2013 NSB Auditorium ...
... to Energy-Dense Liquids Monday, December 9, 2013 NSB Auditorium ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... The amide group (–NHCOCH3) is a strong activating and directing group because the nitrogen atom with its nonbonding pair of electrons is bonded to the aromatic ring. The amide group is a stronger director than the chlorine atom, and substitution occurs mostly at the positions ortho to the amide. Lik ...
... The amide group (–NHCOCH3) is a strong activating and directing group because the nitrogen atom with its nonbonding pair of electrons is bonded to the aromatic ring. The amide group is a stronger director than the chlorine atom, and substitution occurs mostly at the positions ortho to the amide. Lik ...
Si(OR - am Lehrstuhl für Bauchemie
... alkanes. The first silicon hydrides were made in 1857 by Friedrich Wöhler and Heinrich Buff who reacted Al/Si alloys with aqueous HCl. The compounds prepared were analysed by Charls Friedel and Albert Landenburg in 1867 shown to be SiH4 and SiHCl3. The first homologue, Si2H6, was prepared by Henri M ...
... alkanes. The first silicon hydrides were made in 1857 by Friedrich Wöhler and Heinrich Buff who reacted Al/Si alloys with aqueous HCl. The compounds prepared were analysed by Charls Friedel and Albert Landenburg in 1867 shown to be SiH4 and SiHCl3. The first homologue, Si2H6, was prepared by Henri M ...
PPT
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
Paper I
... John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. KEYWORDS: Cr–oxide catalyst; silica; ethane; CH-activation; dehydrogenation; reaction mechanism; DFT; QMMM; ...
... John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. KEYWORDS: Cr–oxide catalyst; silica; ethane; CH-activation; dehydrogenation; reaction mechanism; DFT; QMMM; ...
Ch 10 - Enrico Fermi High School
... In an experiment involving the determination of the equilibrium constant for a reaction, 10.0 mL of 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe+3 (aq) was mixed with 20.0 mL of 4.00 x 10-3 M SCN-(aq). The number of moles of FeSCN2+(aq) that was formed after the reaction of Fe+3 (aq) and SCN-(aq) came to equilibrium was 3.50 x ...
... In an experiment involving the determination of the equilibrium constant for a reaction, 10.0 mL of 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe+3 (aq) was mixed with 20.0 mL of 4.00 x 10-3 M SCN-(aq). The number of moles of FeSCN2+(aq) that was formed after the reaction of Fe+3 (aq) and SCN-(aq) came to equilibrium was 3.50 x ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.






![ch15[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194241_2-0a33cfb98ac502873dac865380b726e0-300x300.png)