CHEM 494 Lecture 8 - UIC Department of Chemistry
... When elimination can occur in more than one direction, the major alkene is the one formed by loss of a H atom from the β carbon having the fewest hydrogens ...
... When elimination can occur in more than one direction, the major alkene is the one formed by loss of a H atom from the β carbon having the fewest hydrogens ...
the chemistry of smell
... Mix the solution with a wooden stick until the solid dissolves. Leave the stick in the test tube (even during heating). Repeat this process with your other assigned ester making sure to label the test tube. 4. Place the test tubes in the 80-85C water bath, using test tube holders to keep the tubes ...
... Mix the solution with a wooden stick until the solid dissolves. Leave the stick in the test tube (even during heating). Repeat this process with your other assigned ester making sure to label the test tube. 4. Place the test tubes in the 80-85C water bath, using test tube holders to keep the tubes ...
Fatty Acids and Alcohols Composition of Brazilian Sugarcane Waxes
... Improved knowledge of the properties, composition, and analysis of sugarcane wax would assist in efforts for its industrial application. Waxes can be applied in food and cosmetic industries. Sugarcane wax also can be applied in pharmaceutics, due to the presence of long chain aliphatic alcohol (poli ...
... Improved knowledge of the properties, composition, and analysis of sugarcane wax would assist in efforts for its industrial application. Waxes can be applied in food and cosmetic industries. Sugarcane wax also can be applied in pharmaceutics, due to the presence of long chain aliphatic alcohol (poli ...
1 of 11 Chem 481 Chapter 6 Answers to the Sixth Assignment Topic
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
The intersecting-state model: a link between
... The classical rate constants calculated by our formalism are in good agreement with the experimental data collected in the 300±1000 K temperature range. This is illustrated in Fig. 2 using the CH3 1 C2H6 ! CH4 1 C2H5 reaction, which has been the subject of numerous experimental studies [10]. It is e ...
... The classical rate constants calculated by our formalism are in good agreement with the experimental data collected in the 300±1000 K temperature range. This is illustrated in Fig. 2 using the CH3 1 C2H6 ! CH4 1 C2H5 reaction, which has been the subject of numerous experimental studies [10]. It is e ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
... • Alcohols can readily be oxidised to the carbonyl moiety • This is an incredibly important reaction - you should realise that the carbonyl group is one of the cornerstones of C–C bond formation (organometallics, neutral nucleophiles, aldol, Julia, Peterson & Wittig reactions) R1 = H OH ...
... • Alcohols can readily be oxidised to the carbonyl moiety • This is an incredibly important reaction - you should realise that the carbonyl group is one of the cornerstones of C–C bond formation (organometallics, neutral nucleophiles, aldol, Julia, Peterson & Wittig reactions) R1 = H OH ...
Preparation and Characterization of Di-, Tri
... Copyright © 2013 A. J. Abdulghani and A. M. N. Khaleel. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. A series of new di-, tri-, an ...
... Copyright © 2013 A. J. Abdulghani and A. M. N. Khaleel. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. A series of new di-, tri-, an ...
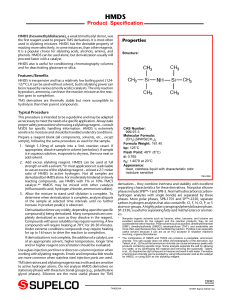
HMDS - Sigma
... phases include SPB™-1 and SPB-5. Normal hydrocarbons (carbonhydrogen analytes with single bonds) are separated by these phases. More polar phases, SPB-1701 and SP™-2250, separate carbon-hydrogen analytes that also contain Br, Cl, F, N, O, P, or S atoms or groups. A highly polar cyanopropylphenylsilo ...
... phases include SPB™-1 and SPB-5. Normal hydrocarbons (carbonhydrogen analytes with single bonds) are separated by these phases. More polar phases, SPB-1701 and SP™-2250, separate carbon-hydrogen analytes that also contain Br, Cl, F, N, O, P, or S atoms or groups. A highly polar cyanopropylphenylsilo ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... 11. A student found that orange IV indicator turned yellow and methyl orange turned red in samples of an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecul ...
... 11. A student found that orange IV indicator turned yellow and methyl orange turned red in samples of an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecul ...
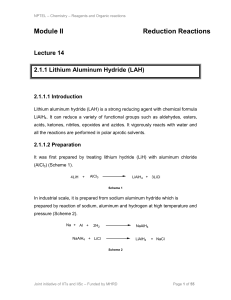
1.1. Storage of hydrogen 1.1.1. Why to store hydrogen? Three
... and the unstable tritium (T). All the isotopes of hydrogen form covalent molecules like H2, D2, and T2, respectively, because of the single electron in the atom. Hydrogen has an ambivalent behaviour towards other elements, occurring as an anion (H+) or cation (H-) in ionic compounds, forming covalen ...
... and the unstable tritium (T). All the isotopes of hydrogen form covalent molecules like H2, D2, and T2, respectively, because of the single electron in the atom. Hydrogen has an ambivalent behaviour towards other elements, occurring as an anion (H+) or cation (H-) in ionic compounds, forming covalen ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Solutions (Chs 4 and 5 in Jespersen, Ch4 in
... Chemical equilibrium - chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates ...
... Chemical equilibrium - chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... applications for modeling bioinorganic systems, catalysis and analytical practice(3). Spontaneous self-assembly reactions have been considered as vehicles for reliable and economical preparation of macrocyclic complexes. Hence these reactions hold a fascination for chemists to mimic anabolic reactio ...
... applications for modeling bioinorganic systems, catalysis and analytical practice(3). Spontaneous self-assembly reactions have been considered as vehicles for reliable and economical preparation of macrocyclic complexes. Hence these reactions hold a fascination for chemists to mimic anabolic reactio ...
Complexes
... temperature dependent EXAFS studies, interesting results obtained are that coordinated or lattice waters are found in these complexes, and that the atomic distances between Ln(III) and coordinated oxygens depend on the coordination number or the Ln(III) ionic radius. The compounds with Ln(III) have ...
... temperature dependent EXAFS studies, interesting results obtained are that coordinated or lattice waters are found in these complexes, and that the atomic distances between Ln(III) and coordinated oxygens depend on the coordination number or the Ln(III) ionic radius. The compounds with Ln(III) have ...
Unit 5 Test Review
... Methane and oxygen are combined in a reaction vessel in amounts of 16 grams and 32 grams respectively. What amounts of reactants and products will be present in the reaction vessel once the reaction is complete? a. 0 grams CH4, 0 grams of O2, 44 grams of CO2, 36 grams of H2O b. 8 grams CH4, 0 grams ...
... Methane and oxygen are combined in a reaction vessel in amounts of 16 grams and 32 grams respectively. What amounts of reactants and products will be present in the reaction vessel once the reaction is complete? a. 0 grams CH4, 0 grams of O2, 44 grams of CO2, 36 grams of H2O b. 8 grams CH4, 0 grams ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
Ch.17
... Polyfunctional acids - contain other functional groups Priority for naming compounds (by functional group) 1. Carboxyl 5. Alkene 2. Carbonyl 6. Alkyne a)Aldehyde 7. Alkoxy (ether) b)Ketone 8. Alkyl 3. Alcohol 9. Halogen 4. Amine* ...
... Polyfunctional acids - contain other functional groups Priority for naming compounds (by functional group) 1. Carboxyl 5. Alkene 2. Carbonyl 6. Alkyne a)Aldehyde 7. Alkoxy (ether) b)Ketone 8. Alkyl 3. Alcohol 9. Halogen 4. Amine* ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
alcohol - Haverford Alchemy
... • Water acting as a Lewis base, can remove an adjacent hydrogen, forming the alkene. • Heating selectively drives off the alkene due to its lower boiling point. • Zaitsev’s Rule states that the more substituted alkene will be favored. This is the result of the equilibrium process that is operating: ...
... • Water acting as a Lewis base, can remove an adjacent hydrogen, forming the alkene. • Heating selectively drives off the alkene due to its lower boiling point. • Zaitsev’s Rule states that the more substituted alkene will be favored. This is the result of the equilibrium process that is operating: ...
Assignment 5 - Answers
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.