Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... that is more deactivating than halogen. • Carbocations rearrange. Reaction of benzene with n-propyl chloride and AlCl3 ...
... that is more deactivating than halogen. • Carbocations rearrange. Reaction of benzene with n-propyl chloride and AlCl3 ...
Esterification of 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid with 2
... reaction with different acids without changing in vinyl double bond. 2-Hydroxy Ethyl methacrylate reaction (HEMA) with different acids such as 5-Aminosalicylic acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, salicylic acid is performed for the esterification of alcoholic group. These acids have medicinal properties. T ...
... reaction with different acids without changing in vinyl double bond. 2-Hydroxy Ethyl methacrylate reaction (HEMA) with different acids such as 5-Aminosalicylic acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, salicylic acid is performed for the esterification of alcoholic group. These acids have medicinal properties. T ...
Activation of Alcohols Toward Nucleophilic Substitution: Conversion
... conditions to be used. For example, the use of phosphorus reagents, e.g., Mitsunobu reagents, is complicated because the resulting reaction mixture contains the product and byproducts (triphenylphosphine oxide and hydrazine dicarboxylate). Purification of the halide product from these byproducts req ...
... conditions to be used. For example, the use of phosphorus reagents, e.g., Mitsunobu reagents, is complicated because the resulting reaction mixture contains the product and byproducts (triphenylphosphine oxide and hydrazine dicarboxylate). Purification of the halide product from these byproducts req ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... In the present study the X-band (9.3GHz) ESR spectra of Au (III) and Ru(III) complexes in DMF were recorded at room temperature and at liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT) on a JES-FA SERIES spectrometer. DPPH radical was used as a field maker Analysis of ATADTC through ESR spectra of Au (III) and Ru ( ...
... In the present study the X-band (9.3GHz) ESR spectra of Au (III) and Ru(III) complexes in DMF were recorded at room temperature and at liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT) on a JES-FA SERIES spectrometer. DPPH radical was used as a field maker Analysis of ATADTC through ESR spectra of Au (III) and Ru ( ...
2H + CO3 H2CO3 H2O + CO2(g) H3N Co H3N NH3 OH2 Cl Cl H3N
... see why the mer isomer is formed. Comment on the reaction that generates gas (carbon dioxide): While Co(III) in acidic conditions can oxidize water to generate O2(g), (a) with the ammine ligands its oxidation potential is lowered so it can't oxidize water, and (b) all the subsequent compounds are Co ...
... see why the mer isomer is formed. Comment on the reaction that generates gas (carbon dioxide): While Co(III) in acidic conditions can oxidize water to generate O2(g), (a) with the ammine ligands its oxidation potential is lowered so it can't oxidize water, and (b) all the subsequent compounds are Co ...
Aldonic acids
... alkaline hypochlorite or hypobromide undergoes the Hofmann degradation via isocaynate and decomposes to a one carbon shorter aldose. The new aldose, however, easily undergoes unwanted oxidation to aldonic acid at the conditions applied (with NaOBr or ...
... alkaline hypochlorite or hypobromide undergoes the Hofmann degradation via isocaynate and decomposes to a one carbon shorter aldose. The new aldose, however, easily undergoes unwanted oxidation to aldonic acid at the conditions applied (with NaOBr or ...
chapter 16
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
Hydrogen-bond supramolecular structure of group 13 Schiff base
... In Schiff base metal complexes, the environment at the coordination center can be modified by attaching different substituents to the ligand, which provides a useful range of steric and electronic properties essential for the fine-tuning of structure and reactivity. Therefore, Schiff base ligands ar ...
... In Schiff base metal complexes, the environment at the coordination center can be modified by attaching different substituents to the ligand, which provides a useful range of steric and electronic properties essential for the fine-tuning of structure and reactivity. Therefore, Schiff base ligands ar ...
Experiment 2
... +3) bonded (coordinated) to a specific number (usually 4 or 6) of electron pair donor groups or ligands (Lewis bases). ...
... +3) bonded (coordinated) to a specific number (usually 4 or 6) of electron pair donor groups or ligands (Lewis bases). ...
chapter 8 - Denton ISD
... reaction has taken place. For example, you can see in Figure 1.1 that the decomposition of ammonium dichromate is accompanied by the evolution of energy as heat and light. And you can see evidence that a chemical reaction occurs between natural gas and oxygen if you burn gas for cooking in your hous ...
... reaction has taken place. For example, you can see in Figure 1.1 that the decomposition of ammonium dichromate is accompanied by the evolution of energy as heat and light. And you can see evidence that a chemical reaction occurs between natural gas and oxygen if you burn gas for cooking in your hous ...
full text pdf
... bimetallic compounds [4-6], (iii) magneto- and non-linear optics [7,8], and (iv) microporous materials [9]. Special attention is dedicated to polyfunctional oxalate bridged materials [1-3,7,10]. The oxalate anion is a very versatile ligand that can adopt many kinds of coordination modes: unidentate, ...
... bimetallic compounds [4-6], (iii) magneto- and non-linear optics [7,8], and (iv) microporous materials [9]. Special attention is dedicated to polyfunctional oxalate bridged materials [1-3,7,10]. The oxalate anion is a very versatile ligand that can adopt many kinds of coordination modes: unidentate, ...
dr. Zdenko Časar - Fakulteta za kemijo in kemijsko tehnologijo
... building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, halo substituted analogues like chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters are even more interesting chiral building blocks, which can be utilized in various coupling reactions and can undergo functional gro ...
... building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, halo substituted analogues like chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters are even more interesting chiral building blocks, which can be utilized in various coupling reactions and can undergo functional gro ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 24
... III. Nomenclature of carboxylic acid derivatives The names of the carboxylic acid derivatives are based on the name of the parent carboxylic acid. The common names of formic acid and acetic acid are always used in for one and two carbon chains. All carboxylic acid derivatives are principle groups. T ...
... III. Nomenclature of carboxylic acid derivatives The names of the carboxylic acid derivatives are based on the name of the parent carboxylic acid. The common names of formic acid and acetic acid are always used in for one and two carbon chains. All carboxylic acid derivatives are principle groups. T ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... The general order of reactivity of acid derivatives can be explained by taking into account the basicity of the leaving groups. When acyl chlorides react, the leaving group is a chloride ion, and when amides react, the leaving group is an amine (or ammonia). The chloride ions are the weakest bases a ...
... The general order of reactivity of acid derivatives can be explained by taking into account the basicity of the leaving groups. When acyl chlorides react, the leaving group is a chloride ion, and when amides react, the leaving group is an amine (or ammonia). The chloride ions are the weakest bases a ...
13-Elimination Reactions
... ✔ Know the regiochemistry of the product of an elimination reaction ✔ Know how to predict whether a substitution or elimination reaction will occur with a particular substrate and set of reaction conditions ✔ Apply the E and Z descriptors to naming alkenes ✔ Predict the products of elimination react ...
... ✔ Know the regiochemistry of the product of an elimination reaction ✔ Know how to predict whether a substitution or elimination reaction will occur with a particular substrate and set of reaction conditions ✔ Apply the E and Z descriptors to naming alkenes ✔ Predict the products of elimination react ...
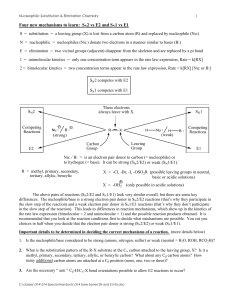
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
M_ScOrganic_Chemistr..
... Free Radical reactions: Methods of generation: Gomberg, photochemical and redox methods. Types of free radical, mechanism at aromatic substrate, reactivity in attacking radicals, free radical substitution reactions, halogenation, oxidation, coupling of alkynes and arylation of aromatics with diazoni ...
... Free Radical reactions: Methods of generation: Gomberg, photochemical and redox methods. Types of free radical, mechanism at aromatic substrate, reactivity in attacking radicals, free radical substitution reactions, halogenation, oxidation, coupling of alkynes and arylation of aromatics with diazoni ...
Thermodynamics Practice Problems Presentation
... Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction in which hydrogen gas, H2 (g), is combined with fluorine gas, F2(g), to produce 2 moles of hydrogen fluoride gas, HF(g). This reaction is represented by the ...
... Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction in which hydrogen gas, H2 (g), is combined with fluorine gas, F2(g), to produce 2 moles of hydrogen fluoride gas, HF(g). This reaction is represented by the ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.