Design and Analysis of Chain and Network Structures from Organic
... in this study: a difunctional cluster, [W6O25H(AsR)2]5(R ) C6H4-4-NH2), and a tetrafunctional cluster, [Mo12O46(AsR)4]4- (R ) C6H4-4-NH3+). The former is isostructural with the previously reported phenyl derivative17 and similar to the molybdenum derivatives, [Mo6O24(AsC6H4NH2)2]4-.18 The cluster co ...
... in this study: a difunctional cluster, [W6O25H(AsR)2]5(R ) C6H4-4-NH2), and a tetrafunctional cluster, [Mo12O46(AsR)4]4- (R ) C6H4-4-NH3+). The former is isostructural with the previously reported phenyl derivative17 and similar to the molybdenum derivatives, [Mo6O24(AsC6H4NH2)2]4-.18 The cluster co ...
[CON`TRIBUTlON FROM THE DEPARTME NT 0F CHEMISTRY
... These results indicated that thermodynamics alone would not prevent the synthesis of nitroacetate from carbon dioxide, nitromethane and magnesium meth-oxide, although the yield achievable under these conditions could not be high. To investigate this possibility, a solution of magne-sium methoxide in ...
... These results indicated that thermodynamics alone would not prevent the synthesis of nitroacetate from carbon dioxide, nitromethane and magnesium meth-oxide, although the yield achievable under these conditions could not be high. To investigate this possibility, a solution of magne-sium methoxide in ...
Kekulé structure of benzene
... Each successive model can be seen as a working hypothesis that best explains current observations, but which is only tentative in nature, as new information may require revision or even replacement of the current model. 34 of 36 ...
... Each successive model can be seen as a working hypothesis that best explains current observations, but which is only tentative in nature, as new information may require revision or even replacement of the current model. 34 of 36 ...
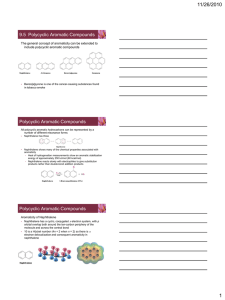
Aromatic Compounds
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
chapter 8
... reaction has taken place. For example, you can see in Figure 1.1 that the decomposition of ammonium dichromate is accompanied by the evolution of energy as heat and light. And you can see evidence that a chemical reaction occurs between natural gas and oxygen if you burn gas for cooking in your hous ...
... reaction has taken place. For example, you can see in Figure 1.1 that the decomposition of ammonium dichromate is accompanied by the evolution of energy as heat and light. And you can see evidence that a chemical reaction occurs between natural gas and oxygen if you burn gas for cooking in your hous ...
CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS
... adapted for chromatography and processes for preparing or regenerating thereof ...
... adapted for chromatography and processes for preparing or regenerating thereof ...
carboxylic acids
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
... • Low molecular weight carboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature and have characteristically sharp or unpleasant odors. • The –COOH group is very polar. Hydrogen bonding between –COOH groups creates dimers (two identical molecules bonded together). ...
5.Hard and Soft Acid and Bases
... 3. The Qual Scheme, a series of chemical reactions used to separate and identify the presence of dozens of metal ions, is based largely on the hard and soft properties of the metal ions. The softer metals are precipitated out as chlorides or sulfides, with the harder ions formed as carbonates. ...
... 3. The Qual Scheme, a series of chemical reactions used to separate and identify the presence of dozens of metal ions, is based largely on the hard and soft properties of the metal ions. The softer metals are precipitated out as chlorides or sulfides, with the harder ions formed as carbonates. ...
Developments in Synthetic Application of Selenium(IV) Oxide and
... Selenium(IV) oxide allylic hydroxylations are highly regiospecific and occur at the α-position to the more substituted carbon of the double bond with a reactivity order CH2 > CH3 > CH. When the double bond is inside a ring, oxidation occurs in the ring when possible, and in the α-position to the mor ...
... Selenium(IV) oxide allylic hydroxylations are highly regiospecific and occur at the α-position to the more substituted carbon of the double bond with a reactivity order CH2 > CH3 > CH. When the double bond is inside a ring, oxidation occurs in the ring when possible, and in the α-position to the mor ...
Synthesis of enantiopure alcohols
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
Aluminum Anode Production
... Aluminum is a truly valuable metal with a dynamic future. It has an excellent combination of light weight, high strength, superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity. It is very easy to recycle - only 5% of the energy required to make primary aluminum is required for recyclin ...
... Aluminum is a truly valuable metal with a dynamic future. It has an excellent combination of light weight, high strength, superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity. It is very easy to recycle - only 5% of the energy required to make primary aluminum is required for recyclin ...
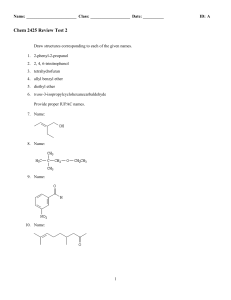
Chem 2425-Test 2 Review
... 29. The substance formed on addition of water to an aldehyde or ketone is called a hydrate or a/an: a. b. c. d. ...
... 29. The substance formed on addition of water to an aldehyde or ketone is called a hydrate or a/an: a. b. c. d. ...
Scheme A Topic Checklist Atomic Structure 1.1
... understand that E-Z isomers exist due to restricted rotation about the C=C bond understand that the double bond in an alkene is a centre of high electron density Addition reactions of alkenes understand the mechanism of electrophilic addition of alkenes with HBr, H2SO4 and Br2 know that bromine ca ...
... understand that E-Z isomers exist due to restricted rotation about the C=C bond understand that the double bond in an alkene is a centre of high electron density Addition reactions of alkenes understand the mechanism of electrophilic addition of alkenes with HBr, H2SO4 and Br2 know that bromine ca ...
Mechanistic study of catalytic copper
... hydrosilylation reaction of carbonyls by experimental methods, kinetic studies and DFT calculations. We first developed two synthetic pathways to unprecedented (NHC)Cu(I) bifluoride complexes and tested their catalytic activity in several known Cu(I) catalyzed reactions, demonstrating high catalytic ...
... hydrosilylation reaction of carbonyls by experimental methods, kinetic studies and DFT calculations. We first developed two synthetic pathways to unprecedented (NHC)Cu(I) bifluoride complexes and tested their catalytic activity in several known Cu(I) catalyzed reactions, demonstrating high catalytic ...
CHEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 3 – answer key December 03
... 21. (5 pts) The two isomeric carboxylic acids (C5H10O2), whose 1H NMR spectra are shown below, were produced using the malonic ester synthesis. a. Propose structures for the acids. b. What alkyl halide(s) was (were) used in each case? ...
... 21. (5 pts) The two isomeric carboxylic acids (C5H10O2), whose 1H NMR spectra are shown below, were produced using the malonic ester synthesis. a. Propose structures for the acids. b. What alkyl halide(s) was (were) used in each case? ...
SAMPLE AP CHEMISTRY EXAM QUESTIONS
... Solid barium oxide is added to distilled water. Chlorine gas is bubbled into a cold, dilute solution of potassium hydroxide. A solution of iron(II) nitrate is exposed to air for an extended period of time. Excess concentrated sulfuric acid is added to solid calcium phosphate. Hydrogen sulfide gas is ...
... Solid barium oxide is added to distilled water. Chlorine gas is bubbled into a cold, dilute solution of potassium hydroxide. A solution of iron(II) nitrate is exposed to air for an extended period of time. Excess concentrated sulfuric acid is added to solid calcium phosphate. Hydrogen sulfide gas is ...
The Fundamentals and Stoichiometry Recitation
... Therefore in this reaction, C60 is the limiting reagent because it is used up first and yields the smallest amount of product. A maximum product yield is 1.5 x 10-3 g for this reaction. The limiting reagent is always used to determine the possible yield. The fullerene reaction is an example of a syn ...
... Therefore in this reaction, C60 is the limiting reagent because it is used up first and yields the smallest amount of product. A maximum product yield is 1.5 x 10-3 g for this reaction. The limiting reagent is always used to determine the possible yield. The fullerene reaction is an example of a syn ...
Reaction Mechanism of d-metal complexes Chapter 20
... k2 arises from associative mechanism, attack of Y on PtL3X, and is dominant when Y is a good nucleophile; but k1 term, which may indicate a concurrent dissociative pathway; in polar solvents k1 becomes dominant, its contribution diminishing in non-polar solvents Thus solvent participates, and rate e ...
... k2 arises from associative mechanism, attack of Y on PtL3X, and is dominant when Y is a good nucleophile; but k1 term, which may indicate a concurrent dissociative pathway; in polar solvents k1 becomes dominant, its contribution diminishing in non-polar solvents Thus solvent participates, and rate e ...
The Carbonyl Group - Angelo State University
... • Carbonyl compounds cannot hydrogen-bond to each other, but they can hydrogen-bond to water through the carbonyl oxygen. • Low-molecular weight aldehydes and ketones are water-soluble; water solubility decreases as the size of the molecule increases. ...
... • Carbonyl compounds cannot hydrogen-bond to each other, but they can hydrogen-bond to water through the carbonyl oxygen. • Low-molecular weight aldehydes and ketones are water-soluble; water solubility decreases as the size of the molecule increases. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.