IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... The mechanism of Schiff base formation is another variation on the theme of nucleophile addition to the carbonyl group. In this case, the nucleophile is the amine. In the first part of the mechanism, the amine reacts with the aldehyde or ketone to give an unstable addition compound called carbinolam ...
... The mechanism of Schiff base formation is another variation on the theme of nucleophile addition to the carbonyl group. In this case, the nucleophile is the amine. In the first part of the mechanism, the amine reacts with the aldehyde or ketone to give an unstable addition compound called carbinolam ...
Assignment 5 - Answers
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
... We note that more oxidizing forms of nickel than Ni(II) are not included in this diagram; such forms do exist but are highly reactive (e.g. NiO2 in acid solution has a reduction potential to Ni2+ of 1.5 V); this should have been included on the diagram. While all the metal ions have the 2+ oxidation ...
HIGHLY SELECTIVE RHODIUM–CATALYZED C–H BORYLATIONS IN
... Scheme 1-5. Photolytic oxidative addition of metal to alkyl C–H bond ....................................... 9 Scheme 1-6. Pathways for the cyclometalation process via electrophilic bond activation (EBA) (Pathway A) and concerted metalation–deprotonation (CMD) (Pathway B) .......... 11 Scheme 1-7. G ...
... Scheme 1-5. Photolytic oxidative addition of metal to alkyl C–H bond ....................................... 9 Scheme 1-6. Pathways for the cyclometalation process via electrophilic bond activation (EBA) (Pathway A) and concerted metalation–deprotonation (CMD) (Pathway B) .......... 11 Scheme 1-7. G ...
Notes - Text
... N2O4(g) 2NO2(g) • An increase in pressure (by decreasing the volume) favors the formation of colorless N2O4. • The instant the pressure increases, the concentration of both gases increases and the system is not at equilibrium. • The system changes to reduce the number moles of gas. • A new equilib ...
... N2O4(g) 2NO2(g) • An increase in pressure (by decreasing the volume) favors the formation of colorless N2O4. • The instant the pressure increases, the concentration of both gases increases and the system is not at equilibrium. • The system changes to reduce the number moles of gas. • A new equilib ...
The Effects of Ancilliary Ligands on Metal
... complex that activates a wide variety of C-H bonds that have been reported over the last 25 years. As this chemistry developed, addition insight has been obtained that permitted further extensions of the work that have led to a deeper understanding of the factors that influence metal-carbon bond str ...
... complex that activates a wide variety of C-H bonds that have been reported over the last 25 years. As this chemistry developed, addition insight has been obtained that permitted further extensions of the work that have led to a deeper understanding of the factors that influence metal-carbon bond str ...
topic 6 – hydrocarbons (general level)
... (a) What is meant by the term "homologous series"? 1 mark (KU) (b) Suggest a general formula for the dienes. 1 mark (PS) (c) Write the molecular formula for the product of the complete reaction of penta l,3-diene with bromine. 1 mark (PS) (d) Draw a full structural formula for, an isomer of buta-l,3 ...
... (a) What is meant by the term "homologous series"? 1 mark (KU) (b) Suggest a general formula for the dienes. 1 mark (PS) (c) Write the molecular formula for the product of the complete reaction of penta l,3-diene with bromine. 1 mark (PS) (d) Draw a full structural formula for, an isomer of buta-l,3 ...
Synthesis of Fatty Acids
... The synthesis of fatty acids • proceeds in a separate pathway, with different enzymes; it is not a simple reversal of fatty acid oxidation. • occurs in the cytosol using the reduced coenzyme NADPH instead of occurring in the mitochondria, where oxidation takes place using FAD and NAD+. The reduced c ...
... The synthesis of fatty acids • proceeds in a separate pathway, with different enzymes; it is not a simple reversal of fatty acid oxidation. • occurs in the cytosol using the reduced coenzyme NADPH instead of occurring in the mitochondria, where oxidation takes place using FAD and NAD+. The reduced c ...
Cl + CH3OH * HCl + CH2OH
... Where kb(i) is the liquid-phase rate coefficient for reaction of NO3 with organic species (i) with concentration [HC], Dl its diffusion coefficient through the organic matrix and H its solubility. A rough estimate for a generic uptake coefficient for NO3 uptake to saturated alcohols or carbonyls can ...
... Where kb(i) is the liquid-phase rate coefficient for reaction of NO3 with organic species (i) with concentration [HC], Dl its diffusion coefficient through the organic matrix and H its solubility. A rough estimate for a generic uptake coefficient for NO3 uptake to saturated alcohols or carbonyls can ...
Review for Ch. 20 21
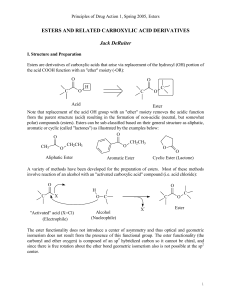
... Like we saw in Ch. 19, you can reduce carbonyl compounds with hydrides. You can do the same with acid derivatives, and you usually end up going from the “three bonds to more electronegative atoms” oxidation state to the “one bond to more electronegative atoms” oxidation state. An important thing to ...
... Like we saw in Ch. 19, you can reduce carbonyl compounds with hydrides. You can do the same with acid derivatives, and you usually end up going from the “three bonds to more electronegative atoms” oxidation state to the “one bond to more electronegative atoms” oxidation state. An important thing to ...
co-ordination compounds
... • A pair of substances with same molecular formula but differ in the rotation of plane polarised light are called as enantiomers. • Enantiomers are non –super imposable. Racemic mixture: • A 1 : 1 equilibrium mixture of d – and l – forms which gives a net zero rotation of plane polarised light is ca ...
... • A pair of substances with same molecular formula but differ in the rotation of plane polarised light are called as enantiomers. • Enantiomers are non –super imposable. Racemic mixture: • A 1 : 1 equilibrium mixture of d – and l – forms which gives a net zero rotation of plane polarised light is ca ...
Ch.17Outline_001
... Polyfunctional acids - contain other functional groups Priority for naming compounds (by functional group) 1.Carboxyl 4. Alkene 2.Carbonyl 5. Alkyne a)Aldehyde 6. Alkoxy b)Ketone 7. Alkyl 3.Alcohol 8. Halogen Common P.A.s: Unsaturated (with double bond) Hydroxyl (with -OH group) Keto (with carbonyl ...
... Polyfunctional acids - contain other functional groups Priority for naming compounds (by functional group) 1.Carboxyl 4. Alkene 2.Carbonyl 5. Alkyne a)Aldehyde 6. Alkoxy b)Ketone 7. Alkyl 3.Alcohol 8. Halogen Common P.A.s: Unsaturated (with double bond) Hydroxyl (with -OH group) Keto (with carbonyl ...
Nanostructured Transition Metal Chalcogenides as - KIT
... lies with the design and elaboration of new electrode materials which might lead to higher cell potentials, capacities and/or energy densities. Promising with this respect are for example compounds with multi-electron redox couples like Cr6+/Cr3+. Another important issue is the influence of the morp ...
... lies with the design and elaboration of new electrode materials which might lead to higher cell potentials, capacities and/or energy densities. Promising with this respect are for example compounds with multi-electron redox couples like Cr6+/Cr3+. Another important issue is the influence of the morp ...
Topic 5 Energetics File
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
TRIPURA UNIVERSITY Syllabus For
... polarizability, formation of σ and π bonds, localized and delocalized chemical bonds , van der Waals interaction, resonance, tautomerism, steric inhibition of resonance, hyperconjugation , inductive and field effects, H-bonding, dipole moment- bond moment and group moment, physical properties(mp, bp ...
... polarizability, formation of σ and π bonds, localized and delocalized chemical bonds , van der Waals interaction, resonance, tautomerism, steric inhibition of resonance, hyperconjugation , inductive and field effects, H-bonding, dipole moment- bond moment and group moment, physical properties(mp, bp ...
Heterobimetallic chemistry: Heterobimetallic complexes derived
... has been obtained from direct reaction of copper (II) chloride with preformed dihydrazone in 3: 1 molar ratio in methanol. When his complex was treated with Mo0 2(acach or uranyl acetate or second metal acetates in methanol, the heterobimetallic complexes [MCu(L)H 20)] (M=U0 2(2),Zn(4» and [MCu(L)(H ...
... has been obtained from direct reaction of copper (II) chloride with preformed dihydrazone in 3: 1 molar ratio in methanol. When his complex was treated with Mo0 2(acach or uranyl acetate or second metal acetates in methanol, the heterobimetallic complexes [MCu(L)H 20)] (M=U0 2(2),Zn(4» and [MCu(L)(H ...
m3 isomerismintro
... There are two structural isomers of C4H10. One is a straight chain molecule where all the carbon atoms are in a single row. The other is a branched molecule where three carbon atoms are in a row and one carbon atom sticks out of the main chain. ...
... There are two structural isomers of C4H10. One is a straight chain molecule where all the carbon atoms are in a single row. The other is a branched molecule where three carbon atoms are in a row and one carbon atom sticks out of the main chain. ...
$doc.title
... species and subsequent quenching with the alkylating agent, three products were afforded i.e. the orange monocarbene complex 22, the purple biscarbene complex 23 as well as the pink orange decomposition product, complex 24. Three analogous compounds were yielded upon reaction with tungsten hexacarb ...
... species and subsequent quenching with the alkylating agent, three products were afforded i.e. the orange monocarbene complex 22, the purple biscarbene complex 23 as well as the pink orange decomposition product, complex 24. Three analogous compounds were yielded upon reaction with tungsten hexacarb ...
Exam 3, Fall 2013 - Mattson Creighton
... that of a halogen (example: I2). Predict the products of the following sequence in a non-reactive solvent. Identify A – D. Identify E for a 2 pt bonus! Re2(CO)10 + 2 Na à A A + CH3I à B + NaI B + PPh3 à C (and no other byproduct) A + PhCH2Cl à D + a white inorganic solid D + heat à E + CO A. Na ...
... that of a halogen (example: I2). Predict the products of the following sequence in a non-reactive solvent. Identify A – D. Identify E for a 2 pt bonus! Re2(CO)10 + 2 Na à A A + CH3I à B + NaI B + PPh3 à C (and no other byproduct) A + PhCH2Cl à D + a white inorganic solid D + heat à E + CO A. Na ...
15alcpp - Knockhardy
... • Recall the definition of a covalent bond • Recall the difference types of physical bonding • Be able to balance simple equations • Be able to write out structures for simple organic molecules • Understand the IUPAC nomenclature rules for simple organic compounds • Recall the chemical properties of ...
... • Recall the definition of a covalent bond • Recall the difference types of physical bonding • Be able to balance simple equations • Be able to write out structures for simple organic molecules • Understand the IUPAC nomenclature rules for simple organic compounds • Recall the chemical properties of ...
Rutgers...Ch17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... This step is also when the electrophile binds to the ring (i.e. governs the location of substitution). The enhanced rate and substitution pattern for toluene can be explained by considering the structures of the intermediate sigma complexes for substitution at each of the different positions. The RD ...
... This step is also when the electrophile binds to the ring (i.e. governs the location of substitution). The enhanced rate and substitution pattern for toluene can be explained by considering the structures of the intermediate sigma complexes for substitution at each of the different positions. The RD ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.