Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition
... states are mirror images and are equal in energy • However, if the reaction is subject to catalysis, a chiral catalyst can create a lower energy pathway for one enantiomer - called an enantionselective synthesis • Reaction of benzaldehyde with diethylzinc with a chiral titanium-containing catalyst, ...
... states are mirror images and are equal in energy • However, if the reaction is subject to catalysis, a chiral catalyst can create a lower energy pathway for one enantiomer - called an enantionselective synthesis • Reaction of benzaldehyde with diethylzinc with a chiral titanium-containing catalyst, ...
Oxidation notes
... • Should have seen 3 peaks (one for each alkene product), BUT only see 2 peaks… – Poor resolution – “Missing” peak is actually covered up by large peak. ...
... • Should have seen 3 peaks (one for each alkene product), BUT only see 2 peaks… – Poor resolution – “Missing” peak is actually covered up by large peak. ...
Chem 231 Exam #3 Study Guide
... Know the order of substrate reactivities for the different reactions Know how to predict nucleophilicity (two rules) and the relative order of nucleophiles in protic solvent Be able to predict a good versus bad leaving group Know how solvents effect SN1 versus SN2 reactions Know how to name alkenes ...
... Know the order of substrate reactivities for the different reactions Know how to predict nucleophilicity (two rules) and the relative order of nucleophiles in protic solvent Be able to predict a good versus bad leaving group Know how solvents effect SN1 versus SN2 reactions Know how to name alkenes ...
Get cached
... of both C r ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , v :2070, 2012, 1965 cm" ) and N i ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , *> :2050, 1990 cm" ) show more than one C N — band, is taken as evidence that, in this case at least, the V B approach can afford an adequate explanation of the observations. The I R spectra of Cr(O ...
... of both C r ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , v :2070, 2012, 1965 cm" ) and N i ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , *> :2050, 1990 cm" ) show more than one C N — band, is taken as evidence that, in this case at least, the V B approach can afford an adequate explanation of the observations. The I R spectra of Cr(O ...
ch 4 powerpoint - not the powerpoint for fri ch_4_lecture
... is bonded to the carbon skeleton; two oxygens carry negative charges. The phosphate group (—OPO32–, abbreviated P ) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the two ...
... is bonded to the carbon skeleton; two oxygens carry negative charges. The phosphate group (—OPO32–, abbreviated P ) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the two ...
23 • Organic Chemistry
... force” that could not be duplicated in the lab. This changed with Friedrich Wöhler who mixed cyanic acid (HCNO) with ammonium hydroxide making ammonium cyanate (NH4CNO). ...
... force” that could not be duplicated in the lab. This changed with Friedrich Wöhler who mixed cyanic acid (HCNO) with ammonium hydroxide making ammonium cyanate (NH4CNO). ...
Organic Chemistry
... Carbon forms 4 bonds (C has 4 valence e-) Nitrogen forms 3 bonds (N has 5 valence e-) Oxygen forms 2 bonds (O has 6 valence e-) Hydrogen forms 1 bond (H breaks the octet rule) Halogens form 1 bond (all have 7 valence e-) ...
... Carbon forms 4 bonds (C has 4 valence e-) Nitrogen forms 3 bonds (N has 5 valence e-) Oxygen forms 2 bonds (O has 6 valence e-) Hydrogen forms 1 bond (H breaks the octet rule) Halogens form 1 bond (all have 7 valence e-) ...
The collision theory of reactions
... Chlorine atoms are particularly effective at removing ozone. A single atom can remove about 1 million ozone molecules. Add equations 6 and 7 together to produce the equation for the overall reaction caused by chlorine atoms. Comment on the result. What role are Cl atoms playing in the overall reacti ...
... Chlorine atoms are particularly effective at removing ozone. A single atom can remove about 1 million ozone molecules. Add equations 6 and 7 together to produce the equation for the overall reaction caused by chlorine atoms. Comment on the result. What role are Cl atoms playing in the overall reacti ...
Name ……………………………..………...… …….. Index No
... Select one of the detergents that would be suitable for washing in water containing magnessium chloride. Explain. (1mks) ...
... Select one of the detergents that would be suitable for washing in water containing magnessium chloride. Explain. (1mks) ...
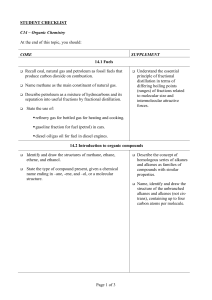
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... from molecular structures. by their reaction with aqueous bromine. ...
... from molecular structures. by their reaction with aqueous bromine. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... State the # of atoms and # of elements in a molecule. Draw isomers of molecules and recognize isomers. Know the bond angle of H-C-H bond. State the bonding capacity of C, H, O, Cl, Br, and I. Given the name of a hydrocarbon, write its formula and vice versa. Know the names and symbols of ...
... State the # of atoms and # of elements in a molecule. Draw isomers of molecules and recognize isomers. Know the bond angle of H-C-H bond. State the bonding capacity of C, H, O, Cl, Br, and I. Given the name of a hydrocarbon, write its formula and vice versa. Know the names and symbols of ...
Islamic University of Gaza Biochemistry School of Nursing Midterm
... the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has three or more carbon atoms attached to it. (incorrect) three 10. The product of the oxi ...
... the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has three or more carbon atoms attached to it. (incorrect) three 10. The product of the oxi ...
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2220, Organic Chem II 1. Rank the
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
Study Guide for Exam 4 Chapter 17
... Know the basic terms, especially those discussed in class and in bold face print in the text From their structural or line-angle formulas, write IUPAC names for aldehydes and ketones. Describe the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones in terms of how their intermolecular forces determin ...
... Know the basic terms, especially those discussed in class and in bold face print in the text From their structural or line-angle formulas, write IUPAC names for aldehydes and ketones. Describe the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones in terms of how their intermolecular forces determin ...
experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... Example 1: Solutions of sodium bromide and potassium nitrate are mixed. The predicted equation for this reaction would be: NaCl(aq) + KNO 3 (aq) KCl (aq) + NaNO 3 (aq) Does a reaction happen? To answer this question we look at the products. Is either one an insoluble compound (we can get this inform ...
... Example 1: Solutions of sodium bromide and potassium nitrate are mixed. The predicted equation for this reaction would be: NaCl(aq) + KNO 3 (aq) KCl (aq) + NaNO 3 (aq) Does a reaction happen? To answer this question we look at the products. Is either one an insoluble compound (we can get this inform ...
15_01_05.html
... end uses: solvent, antifreeze, fuel principal use: preparation of formaldehyde prepared by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide CO + 2H2 CH3OH ...
... end uses: solvent, antifreeze, fuel principal use: preparation of formaldehyde prepared by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide CO + 2H2 CH3OH ...
Chapter 6
... - The chemical reaction H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) describes the formation of water from its elements. - Butane burns in air to produce carbon dioxide and water: 2C4H10(g) + 13O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 10H2O (g) ...
... - The chemical reaction H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) describes the formation of water from its elements. - Butane burns in air to produce carbon dioxide and water: 2C4H10(g) + 13O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 10H2O (g) ...
CHEMISTRY A
... (d) Percentage yield has been used for many years to measure the ‘success’ of a reaction. Recently, chemists have turned their thoughts also to the atom economy of a reaction. (i) ...
... (d) Percentage yield has been used for many years to measure the ‘success’ of a reaction. Recently, chemists have turned their thoughts also to the atom economy of a reaction. (i) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Explain the zone refining and cyanide processes of refining of metals. 12. What is lanthanide contraction? How are individual lanthanides separated by ion-exchange chromatography techniques. ...
... 11. Explain the zone refining and cyanide processes of refining of metals. 12. What is lanthanide contraction? How are individual lanthanides separated by ion-exchange chromatography techniques. ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... When a halogen is attached to an aliphatic chain, it is called an alkyl halide; when attached to an arene ring, it is an aryl halide. Common names of halocarbons begin with the name of the alkyl or aryl group and end with the name of the halogen with an -ide ending. ...
... When a halogen is attached to an aliphatic chain, it is called an alkyl halide; when attached to an arene ring, it is an aryl halide. Common names of halocarbons begin with the name of the alkyl or aryl group and end with the name of the halogen with an -ide ending. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.