Document
... The large rate difference between methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, and tert-butyl bromides reflects the steric hindrance each offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituen ...
... The large rate difference between methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, and tert-butyl bromides reflects the steric hindrance each offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituen ...
Aldehydes & Ketones
... • Oxidation of a secondary alcohol yields a ketone. • Tertiary alcohols do not react under these conditions. ...
... • Oxidation of a secondary alcohol yields a ketone. • Tertiary alcohols do not react under these conditions. ...
General properties of urea : It is water
... General properties of urea : It is water-soluble crystalline compound acting only as a weak base giving sparingly soluble salts with HNO3 and ethanedioic acid (COOH)2 . In its chemical properties, urea gives the typical reaction expected from an amide (twice over) Its properties are essentially thos ...
... General properties of urea : It is water-soluble crystalline compound acting only as a weak base giving sparingly soluble salts with HNO3 and ethanedioic acid (COOH)2 . In its chemical properties, urea gives the typical reaction expected from an amide (twice over) Its properties are essentially thos ...
c - Down the Rabbit Hole
... • They are the chemically reactive groups of atoms within an organic molecule • They give organic molecules distinctive chemical properties • There are six functional groups ...
... • They are the chemically reactive groups of atoms within an organic molecule • They give organic molecules distinctive chemical properties • There are six functional groups ...
Final Exam Practice 2016 (MC)
... descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair of electrons on carbon should make a double bond with hydrogen. ...
... descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair of electrons on carbon should make a double bond with hydrogen. ...
67 Preview of Carbonyl Chemistry Kinds of carbonyls 1. Aldehydes
... Organocopper reagents are primarily used for conjugates addition reactions with α,β-unsaturated ketones; however, they also undergo direct addition to non-conjugated ketones (1,2-additions), aldehydes and will react with alkyl halides and tosylates, and epoxides Mechanism of conjugate addition by or ...
... Organocopper reagents are primarily used for conjugates addition reactions with α,β-unsaturated ketones; however, they also undergo direct addition to non-conjugated ketones (1,2-additions), aldehydes and will react with alkyl halides and tosylates, and epoxides Mechanism of conjugate addition by or ...
Ch17-2 Driving Forces of Reactions
... Gas has more entropy than liquid …liquid more entropy than solid S L g Increase in entropy + S …..more crazy random (favored) delta ...
... Gas has more entropy than liquid …liquid more entropy than solid S L g Increase in entropy + S …..more crazy random (favored) delta ...
File - chemistryattweed
... The polymerisation of HDPE uses an ionic catalyst called the Ziegler-Natta catalyst. This consists of mixtures of compounds such as TiCl4 and Al(C2H5)3. In this process ethene molecules are added to the growing polymer molecule on the surface of the catalyst which reduces the amount of branching. HD ...
... The polymerisation of HDPE uses an ionic catalyst called the Ziegler-Natta catalyst. This consists of mixtures of compounds such as TiCl4 and Al(C2H5)3. In this process ethene molecules are added to the growing polymer molecule on the surface of the catalyst which reduces the amount of branching. HD ...
Pd presentation
... Created by Athena Anderson, Brette Chapin, Michelle Hansen and Kanny Wan and posted on VIPEr June 2010. Copyright Brette Chapin 2010. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike License. To view a copy of this license visit http://creativecommons.org/about ...
... Created by Athena Anderson, Brette Chapin, Michelle Hansen and Kanny Wan and posted on VIPEr June 2010. Copyright Brette Chapin 2010. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike License. To view a copy of this license visit http://creativecommons.org/about ...
Mr. Farnworth
... bonded compound that contains CARBON • Carbon atoms form FOUR covalent bonds in organic compounds • Methane CH4 (Draw structure) • Carbon atoms have four valence electrons for bonding. Each of theses electrons forms a different C-H Bond ...
... bonded compound that contains CARBON • Carbon atoms form FOUR covalent bonds in organic compounds • Methane CH4 (Draw structure) • Carbon atoms have four valence electrons for bonding. Each of theses electrons forms a different C-H Bond ...
to get Period 2 8
... A substituted hydrocarbon is when one atom of another element is substituted for a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon Hydrocarbon: They only contain carbon hydrogen Carbon can form stable bond with oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Substituted Hydrocarbons include halogen-containing compounds, alcohol ...
... A substituted hydrocarbon is when one atom of another element is substituted for a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon Hydrocarbon: They only contain carbon hydrogen Carbon can form stable bond with oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Substituted Hydrocarbons include halogen-containing compounds, alcohol ...
Biology Name: TEACHER KEY Life Substances Notes
... a lot of smaller units together into long chains. i. Large carbon compounds are built up from smaller simpler molecules called monomers (mono = one ) ii. Monomers can bind to one another to form complex molecules known as polymers (poly = many) iii. A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, whic ...
... a lot of smaller units together into long chains. i. Large carbon compounds are built up from smaller simpler molecules called monomers (mono = one ) ii. Monomers can bind to one another to form complex molecules known as polymers (poly = many) iii. A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, whic ...
The Natural Standard (09/01/10)
... Description: The process of converting carbohydrates into alcohol and carbon dioxide or organic acids. Glucosidation of Fatty Alcohol and Glucose Reagents: None Catalysts: Toluene Sulfonic Acid Agricultural Inputs: Glucose and Fatty Alcohol Description: The process of attaching glucose to an alcohol ...
... Description: The process of converting carbohydrates into alcohol and carbon dioxide or organic acids. Glucosidation of Fatty Alcohol and Glucose Reagents: None Catalysts: Toluene Sulfonic Acid Agricultural Inputs: Glucose and Fatty Alcohol Description: The process of attaching glucose to an alcohol ...
Applications of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Organic Reactions
... Comparison between NHC ligand and trialkyl Phosphane Ø A number of studies have suggested that as ligands, nucleophilic carbenes have advntages over electron rich trialkylphosphanes (strong s donors). Ø Phosphane ligands suffer from significant P–C bond degradation at elevated temperatures, while N ...
... Comparison between NHC ligand and trialkyl Phosphane Ø A number of studies have suggested that as ligands, nucleophilic carbenes have advntages over electron rich trialkylphosphanes (strong s donors). Ø Phosphane ligands suffer from significant P–C bond degradation at elevated temperatures, while N ...
Chapter 18 – Carbonyl Compounds II (Last Chapter we mostly talk
... to protect a functional group from reacting is quite common in organic chemistry.) (Because they protect functional groups from reacting the groups that are added are called protecting groups. So in the case above, the ketal would be ...
... to protect a functional group from reacting is quite common in organic chemistry.) (Because they protect functional groups from reacting the groups that are added are called protecting groups. So in the case above, the ketal would be ...
Practice Questions - Elevate Education
... 4.Draw the structural formulae for formaldehyde and for formic acid. 5. Give the correct IUPAC name for formaldehyde. 6.Consider the reaction of methanol with ethanoic acid. 7. Write the balanced chemical equation to represent this reaction. 8. Draw the structural formula of the ester produced in th ...
... 4.Draw the structural formulae for formaldehyde and for formic acid. 5. Give the correct IUPAC name for formaldehyde. 6.Consider the reaction of methanol with ethanoic acid. 7. Write the balanced chemical equation to represent this reaction. 8. Draw the structural formula of the ester produced in th ...
Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
2 Other Organic Compounds
... Other Organic Compounds • Table R – for most of these you will use Table R for examples ...
... Other Organic Compounds • Table R – for most of these you will use Table R for examples ...
Design and synthesis optimization of bis(β
... polylactide less useful.[11] Alkoxides of different metals such as tin, germanium, calcium and iron have been prepared and evaluated in ROP of lactide.[12-‐17] These findings were crucial in terms ...
... polylactide less useful.[11] Alkoxides of different metals such as tin, germanium, calcium and iron have been prepared and evaluated in ROP of lactide.[12-‐17] These findings were crucial in terms ...
10.3 Alcohols
... 10.3 Alcohols • These compounds have an -OH attached to the carbon chain. • This functional group is called a hydroxyl group. • Note: The oxygen is bonded to the carbon in a covalent bond. • The hydrogen is then bonded in a covalent bond to the oxygen, it is not a hydroxide ion that is attached to t ...
... 10.3 Alcohols • These compounds have an -OH attached to the carbon chain. • This functional group is called a hydroxyl group. • Note: The oxygen is bonded to the carbon in a covalent bond. • The hydrogen is then bonded in a covalent bond to the oxygen, it is not a hydroxide ion that is attached to t ...
Amine-functionalized boehmite nanoparticle-supported
... BNPs. This was confirmed by TEM image of BNPs (Fig. 4(a)). In this image, needle‐shaped BNPs were seen with a length of over 50 nm and a width of up to 10 nm. According to the BET analysis, the efficient surface area for BNPs was 326 m2 g−1. BNPs themselves have promising catalytic ...
... BNPs. This was confirmed by TEM image of BNPs (Fig. 4(a)). In this image, needle‐shaped BNPs were seen with a length of over 50 nm and a width of up to 10 nm. According to the BET analysis, the efficient surface area for BNPs was 326 m2 g−1. BNPs themselves have promising catalytic ...
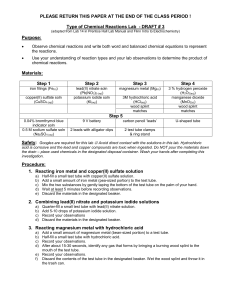
Type of Chemical Reactions Lab
... for the conduction of electricity and the indicator just shows us that a reaction is taking place that changes pH. The reaction would take place without either of these present… we just wouldn’t know it. b) Then write the state symbols for each chemical (s, l, g, aq). c) Then balance the equation us ...
... for the conduction of electricity and the indicator just shows us that a reaction is taking place that changes pH. The reaction would take place without either of these present… we just wouldn’t know it. b) Then write the state symbols for each chemical (s, l, g, aq). c) Then balance the equation us ...
Document
... OH), a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not ...
... OH), a hydrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not ...
Chapter 7: Alkene reactions
... Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism and terpene biosynthesis – it’s catalyzed in vivo by specific enzymes. In the lab, dehydration is an acid-catalyzed elimination reaction. The mechanism involves formation of a carbocation intermediate (more on eli ...
... Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism and terpene biosynthesis – it’s catalyzed in vivo by specific enzymes. In the lab, dehydration is an acid-catalyzed elimination reaction. The mechanism involves formation of a carbocation intermediate (more on eli ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.