Elimination Reactions
... reactions are useful because alkenes are used to manufacture many products such as: Carpets Clothing ...
... reactions are useful because alkenes are used to manufacture many products such as: Carpets Clothing ...
Carbon Compounds - Montgomery County Schools
... 65. Most proteins act as catalysts or __________________ inside of cells. 66. The substance an enzyme is acting upon is called the _____________ and it must ______ into a place called the active site on the enzyme. 69. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be reused & why? ...
... 65. Most proteins act as catalysts or __________________ inside of cells. 66. The substance an enzyme is acting upon is called the _____________ and it must ______ into a place called the active site on the enzyme. 69. After the reaction, what happens to the products? Can the enzyme be reused & why? ...
Qualitative Analysis II Notes
... molecule contains many (more than 2) highly polar groups such as hydroxides or carboxylic acids. Most organic molecules with 4 or fewer carbons are soluble in water. Organic molecules with 5 or 6 carbons are on the edge of being soluble. If they have a very polar group, they may be soluble. If they ...
... molecule contains many (more than 2) highly polar groups such as hydroxides or carboxylic acids. Most organic molecules with 4 or fewer carbons are soluble in water. Organic molecules with 5 or 6 carbons are on the edge of being soluble. If they have a very polar group, they may be soluble. If they ...
Exam only
... Hydrogen bonding is the force that is often responsible for many of the structural aspects of proteins. Hydrogen bonding allows many very large organic molecules to be soluble in water. Sugars are an example. Hydrogen bonding is the force that allows salts like sodium chloride to dissolve in water. ...
... Hydrogen bonding is the force that is often responsible for many of the structural aspects of proteins. Hydrogen bonding allows many very large organic molecules to be soluble in water. Sugars are an example. Hydrogen bonding is the force that allows salts like sodium chloride to dissolve in water. ...
Syntheses, Structures and Photophysical Properties of Metal
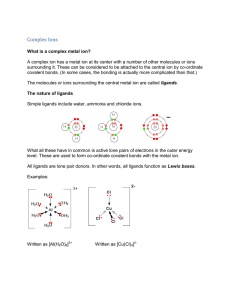
... -The peaks of these bands were in the range of 506-509 nm for the dansyl derivatives while the adridone derivatives had peaks in the 425431 nm range. -The complexed fluorophores were found to have very similar emission wavelengths to the uncomplexed ligands (I and II). -However, an important finding ...
... -The peaks of these bands were in the range of 506-509 nm for the dansyl derivatives while the adridone derivatives had peaks in the 425431 nm range. -The complexed fluorophores were found to have very similar emission wavelengths to the uncomplexed ligands (I and II). -However, an important finding ...
Activation Energy
... Dissociative (D or Id) from experiment 1. Rate of reaction changes only slightly or not at all with changes in the incoming ligand – Aquation (incoming ligand is water) and anation (incoming ligand is an anion) are similar 2. Increasing positive charge on complex decreases the rate of substitution ...
... Dissociative (D or Id) from experiment 1. Rate of reaction changes only slightly or not at all with changes in the incoming ligand – Aquation (incoming ligand is water) and anation (incoming ligand is an anion) are similar 2. Increasing positive charge on complex decreases the rate of substitution ...
File
... Hardening is an addition reaction (hydrogenation) where the unsaturated carbon double bonds are converted to saturated single carbon bonds. Margarines are made by partial hydrogenation of oils using a nickel catalyst. The amount of hydrogenation can produce margarines with different properties. ...
... Hardening is an addition reaction (hydrogenation) where the unsaturated carbon double bonds are converted to saturated single carbon bonds. Margarines are made by partial hydrogenation of oils using a nickel catalyst. The amount of hydrogenation can produce margarines with different properties. ...
What are the functions of biomolecules
... All life processes consist of chemical reaction catalyzed by enzymes What are the primary functions of metabolism? 1. To acquire and use energy 2. To synthesize molecules needed for cellular structure & function 3. For growth & development 4. To remove waste & other toxins ...
... All life processes consist of chemical reaction catalyzed by enzymes What are the primary functions of metabolism? 1. To acquire and use energy 2. To synthesize molecules needed for cellular structure & function 3. For growth & development 4. To remove waste & other toxins ...
More reactions of alkenes Objective
... By removing some double bonds you raise the melting point of the oil so that it becomes solid at room temperature ...
... By removing some double bonds you raise the melting point of the oil so that it becomes solid at room temperature ...
CHM 123 EXAM 2 – PRACTICE PROBLEMS *It is the students
... C) larger hydrogen-bond forces for HBr. D) larger dipole-dipole forces, larger dispersion forces, and larger hydrogen-bond forces for HBr. Question II - Nuclear chemistry (Remember to use integrated law equation to solve for it, no short cut!!!) ...
... C) larger hydrogen-bond forces for HBr. D) larger dipole-dipole forces, larger dispersion forces, and larger hydrogen-bond forces for HBr. Question II - Nuclear chemistry (Remember to use integrated law equation to solve for it, no short cut!!!) ...
Transition Metal Catalyzed Coupling Reactions
... Pd catalysts tends to be less sensitive to oxygen and are believed to be less toxic than their Ni counterparts. Furthermore they tend to react without the intervention of radical intermediates that can lead to side products (e.g. homocoupling, racemization, isomerization). ...
... Pd catalysts tends to be less sensitive to oxygen and are believed to be less toxic than their Ni counterparts. Furthermore they tend to react without the intervention of radical intermediates that can lead to side products (e.g. homocoupling, racemization, isomerization). ...
Test 2
... 13. A sample of limestone (containing calcium carbonate, CaCO3) weighing 413mg is treated with oxalic acid (H2C2O4) to give 472mg calcium oxalate (CaC2O4). CaCO3(s) + H2C2O4(aq) CaC2O4(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l). What is the percentage of calcium carbonate in the limestone? ...
... 13. A sample of limestone (containing calcium carbonate, CaCO3) weighing 413mg is treated with oxalic acid (H2C2O4) to give 472mg calcium oxalate (CaC2O4). CaCO3(s) + H2C2O4(aq) CaC2O4(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l). What is the percentage of calcium carbonate in the limestone? ...
Mr. Kent`s Organic Chemistry Unit Notes B. ______ will not only
... carboxylic acids. The alkyl (R') group is named first (the carbon chain from the alcohol). The R-CO-O part is then named as a separate word based on the carboxylic acid name, with the ending changed from oic acid to “-oate”. ...
... carboxylic acids. The alkyl (R') group is named first (the carbon chain from the alcohol). The R-CO-O part is then named as a separate word based on the carboxylic acid name, with the ending changed from oic acid to “-oate”. ...
Nature’s Chemistry
... In order to oxidise a primary or secondary alcohol an appropriate oxidising agent should be used. Commonly used oxidising agents are listed below. Acidified potassium dichromate solution Acidified potassium permanganate solution Heated solid copper (II) oxide ...
... In order to oxidise a primary or secondary alcohol an appropriate oxidising agent should be used. Commonly used oxidising agents are listed below. Acidified potassium dichromate solution Acidified potassium permanganate solution Heated solid copper (II) oxide ...
Chemistry: Selected Topics
... some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechanism. The second part of the course deals with the properties of some important types of ...
... some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechanism. The second part of the course deals with the properties of some important types of ...
EXPERIMENT 6 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... In the first step of this mechanism the acid catalyst, H3O+, protonates the oxygen of the carbonyl group giving it a +1 charge. In the second step, the weakly nucleophilic oxygen of methanol donates a pair of electrons toward the carbon of the carbonyl group to form a new bond. In the third step the ...
... In the first step of this mechanism the acid catalyst, H3O+, protonates the oxygen of the carbonyl group giving it a +1 charge. In the second step, the weakly nucleophilic oxygen of methanol donates a pair of electrons toward the carbon of the carbonyl group to form a new bond. In the third step the ...
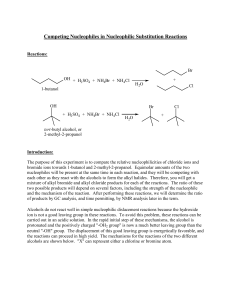
Competing Nucleophiles in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Alcohols do not react well in simple nucleophilic dislacement reactions because the hydroxide ion is not a good leaving group in these reactions. To avoid this problem, these reactions can be carried out in an acidic solution. In the rapid initial step of these mechanisms, the alcohol is protonated ...
... Alcohols do not react well in simple nucleophilic dislacement reactions because the hydroxide ion is not a good leaving group in these reactions. To avoid this problem, these reactions can be carried out in an acidic solution. In the rapid initial step of these mechanisms, the alcohol is protonated ...
CHEM1102 Worksheet 7: Reactions of Carbonyls and Acid
... Grignard reagents (RMgBr) are excellent nucleophiles, and are a very good way to form new carbon-carbon bonds. ...
... Grignard reagents (RMgBr) are excellent nucleophiles, and are a very good way to form new carbon-carbon bonds. ...
Naming organic compounds
... Indicate the position of the branches with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. If there is more than one branch, the branches are identified in alphabetical order ignoring any di, tri etc. Be aware! Each branch needs to be numbered individually, even if they are attached t ...
... Indicate the position of the branches with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. If there is more than one branch, the branches are identified in alphabetical order ignoring any di, tri etc. Be aware! Each branch needs to be numbered individually, even if they are attached t ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.