1 H NT Ch 12—Stoichiometry I. Review: Chemical Equations a
... ii. Predict and balance the reaction of solid aluminum with hydrochloric acid. What mass of hydrogen can be produced if you start with 6.000 mol of aluminum? ...
... ii. Predict and balance the reaction of solid aluminum with hydrochloric acid. What mass of hydrogen can be produced if you start with 6.000 mol of aluminum? ...
Questions for the chemistry test
... 9. Explain the test for a halide ion. 10. Explain the test for ammonia, what colour will the litmus paper turn? 11. Give 2 uses of Ion identification used in industries? 12. What type of water makes a lather? 13. Name the ions in hard water? 14. Which types of water cannot be softened? 15. What typ ...
... 9. Explain the test for a halide ion. 10. Explain the test for ammonia, what colour will the litmus paper turn? 11. Give 2 uses of Ion identification used in industries? 12. What type of water makes a lather? 13. Name the ions in hard water? 14. Which types of water cannot be softened? 15. What typ ...
Protecting Groups Introduction to Carbonyl
... Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is called “protection.” [2] Carry ou ...
... Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is called “protection.” [2] Carry ou ...
Yeast Reduction #812
... Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are effective reducing agents. Treatment of a ketone with either agent will reduce the carbonyl group to yield an alcohol. However, these reducing agents do not react to form a chiral alcohol because the hydride can attack both sides of the planar carb ...
... Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are effective reducing agents. Treatment of a ketone with either agent will reduce the carbonyl group to yield an alcohol. However, these reducing agents do not react to form a chiral alcohol because the hydride can attack both sides of the planar carb ...
Carbonyls
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Iron complexes of bidentate nitrogen donor ligands as
... A different approach, leading to the same result, is the so called reverse ATRP.2 This technique follows the same ATRP reactions of Scheme 1 but differs for the initiation reaction. In this case a typical radical initiator (e.g. 2,2’-azo-bisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), 1,1,2,2-tetraphenyl-1,2-ethanedio ...
... A different approach, leading to the same result, is the so called reverse ATRP.2 This technique follows the same ATRP reactions of Scheme 1 but differs for the initiation reaction. In this case a typical radical initiator (e.g. 2,2’-azo-bisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), 1,1,2,2-tetraphenyl-1,2-ethanedio ...
top 5 organic - No Brain Too Small
... Be able to distinguish between them – use UI or litmus o o ...
... Be able to distinguish between them – use UI or litmus o o ...
Oxidation of Alcohols
... Acid-catalyzed dehydration to alkenes (Chapter 5) Conversion to p-toluenesulfonate esters (Chapter 8 Conversion to ethers (Chapter 15.7) Conversion to esters (Chapter 15.8) ...
... Acid-catalyzed dehydration to alkenes (Chapter 5) Conversion to p-toluenesulfonate esters (Chapter 8 Conversion to ethers (Chapter 15.7) Conversion to esters (Chapter 15.8) ...
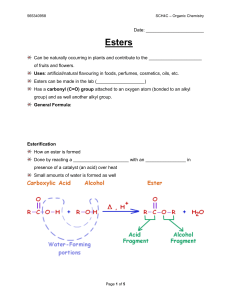
Esters - Mr. Lee`s Science
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
... - Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones for both steric and electronic reasons. - First, the H creates less steric hindrance so that the carbonyl C is more accessible. - Second, an organic group provides e- donating induction which stabilizes the + carbonyl C and makes it less reactive. - Formal ...
Industrial Chemistry - Deans Community High School
... ΔHof / kJmol-1 : CO2(g), -394; H2O(g), -286; C2H5OH(l), -278 calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion of ethanol i.e. the enthalpy change for the reaction C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ...
... ΔHof / kJmol-1 : CO2(g), -394; H2O(g), -286; C2H5OH(l), -278 calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion of ethanol i.e. the enthalpy change for the reaction C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ...
1 fisier.indd - Chemistry Journal of Moldova
... The study of the elementary reactions that take place in the process of the H 2 O2 decomposition is of a great importance both from the theoretical point of view (in order to understand the mechanisms of the numerous processes in the chemical and biological systems, in the processes of photolysis, r ...
... The study of the elementary reactions that take place in the process of the H 2 O2 decomposition is of a great importance both from the theoretical point of view (in order to understand the mechanisms of the numerous processes in the chemical and biological systems, in the processes of photolysis, r ...
Document
... trienes, and so forth. • Always choose the longest chain that contains both atoms of the double bond. • In naming cycloalkenes, the double bond is located between C1 and C2, and the “1” is usually omitted in the name. The ring is numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent t ...
... trienes, and so forth. • Always choose the longest chain that contains both atoms of the double bond. • In naming cycloalkenes, the double bond is located between C1 and C2, and the “1” is usually omitted in the name. The ring is numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent t ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... What is dendritic catalysis? Cite two reactions catalyzed by a dendritic catalyst. ...
... What is dendritic catalysis? Cite two reactions catalyzed by a dendritic catalyst. ...
A Model for Catalytically Active Zinc(I1) Ion in Liver
... 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane,L2),Zn"[ 14]aneN4, 3 ([ 14]aneN4 = 1,4,8,1I-tetraazacyclotetradecane,LJ,and free Zn" salts, 4. Variations in Zn" acidity and coordination environment in these complexes result in varying degrees of catalytic activity in the reduction of p-nitrobenzaldehyde (9) and an N ...
... 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane,L2),Zn"[ 14]aneN4, 3 ([ 14]aneN4 = 1,4,8,1I-tetraazacyclotetradecane,LJ,and free Zn" salts, 4. Variations in Zn" acidity and coordination environment in these complexes result in varying degrees of catalytic activity in the reduction of p-nitrobenzaldehyde (9) and an N ...
W19 Aldehydes ketones I
... physical properties of aldehydes and ketones reaction scheme of aldehydes and ketones nucleophilic addition AN to C=O group: ...
... physical properties of aldehydes and ketones reaction scheme of aldehydes and ketones nucleophilic addition AN to C=O group: ...
22. Oxidation of Cyclohexanol
... chemistry. Oxidation of alcohols to form aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation. In this experiment c ...
... chemistry. Oxidation of alcohols to form aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation. In this experiment c ...
Main types of Chemical Reactions
... A. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble substance formed by the reaction of two aqueous substances. Two ions bond together so strongly that water can not pull them apart. You must know your solubility rules to write these net ionic equations! Ex. Solutions of silver nitrate and ...
... A. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble substance formed by the reaction of two aqueous substances. Two ions bond together so strongly that water can not pull them apart. You must know your solubility rules to write these net ionic equations! Ex. Solutions of silver nitrate and ...
KEY Final Exam Review - Iowa State University
... NO3¯ ---> NO 2) balance each half-reaction: 8H2S ---> S8 + 16H+ + 16e¯ 3e¯ + 4H+ + NO3¯ ---> NO + 2H2O 3) Make the number of electrons equal: 24H2S ---> 3S8 + 48H+ + 48e¯ <--- multiplied by a factor of 3 48e¯ + 64H+ + 16NO3¯ ---> 16NO + 32H2O <--- multiplied by a factor of 16 Note that 16 and 3 have ...
... NO3¯ ---> NO 2) balance each half-reaction: 8H2S ---> S8 + 16H+ + 16e¯ 3e¯ + 4H+ + NO3¯ ---> NO + 2H2O 3) Make the number of electrons equal: 24H2S ---> 3S8 + 48H+ + 48e¯ <--- multiplied by a factor of 3 48e¯ + 64H+ + 16NO3¯ ---> 16NO + 32H2O <--- multiplied by a factor of 16 Note that 16 and 3 have ...
Document
... The large rate difference between methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, and tert-butyl bromides reflects the steric hindrance each offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituen ...
... The large rate difference between methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, and tert-butyl bromides reflects the steric hindrance each offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituen ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.