Answers to Final Exam Review
... 53. When Cu+2 is mixed with Cl-1, which type of reaction will occur? Synthesis Unit 9: Stoichiometry Practice Problems: 54. Given the balanced chemical equation the reaction, P4 + 5O2 P4O10 What mass of oxygen is needed to completely react with 7.75 g P4? a. 2.00 grams c. 10.00 grams b. 5.00 grams ...
... 53. When Cu+2 is mixed with Cl-1, which type of reaction will occur? Synthesis Unit 9: Stoichiometry Practice Problems: 54. Given the balanced chemical equation the reaction, P4 + 5O2 P4O10 What mass of oxygen is needed to completely react with 7.75 g P4? a. 2.00 grams c. 10.00 grams b. 5.00 grams ...
This is an author version of the contribution published on: Questa è
... the highest catalytic activity. All the products are easily separated from the reaction mixture and isolated in good yields (>75%) and purity. The IL can be recycled after removal of water, with only moderate loss in activity. Reaction rates were further improved under MW irradiation. In conclusion, ...
... the highest catalytic activity. All the products are easily separated from the reaction mixture and isolated in good yields (>75%) and purity. The IL can be recycled after removal of water, with only moderate loss in activity. Reaction rates were further improved under MW irradiation. In conclusion, ...
CHAPTER 9 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl sulfonates creates a good leaving group for subsequent displacement by an anionic nucleophile ...
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl sulfonates creates a good leaving group for subsequent displacement by an anionic nucleophile ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 20. Examine the Lewis structure for propanal, C3H6O. Which of the following descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. T ...
... 20. Examine the Lewis structure for propanal, C3H6O. Which of the following descriptions about its structure is correct? a) This is a correct Lewis structure b) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should be removed. c) There are too many electrons in this diagram. T ...
Document
... • H2/Transition Metal Catalyst (z.b. CuO•CuCr2O4) • NaBH4 and LiAlH4 are Hydride Transfer Agents • Hydride (H¯) Acts as a Nucleophile • Carbonyls Have Varying Degrees of Ease of Reduction: O ...
... • H2/Transition Metal Catalyst (z.b. CuO•CuCr2O4) • NaBH4 and LiAlH4 are Hydride Transfer Agents • Hydride (H¯) Acts as a Nucleophile • Carbonyls Have Varying Degrees of Ease of Reduction: O ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... The oxidation reagent is prepared by dissolving 70 g. (0.70 mole) of chromium trioxide in 100 ml. of water in a 500-ml. beaker. The beaker is immersed in an ice bath, and 112 g. (61 ml., 1.10 moles) of concentrated (18M) sulfuric acid followed by 200 ml. of water is added cautiously with manual stir ...
... The oxidation reagent is prepared by dissolving 70 g. (0.70 mole) of chromium trioxide in 100 ml. of water in a 500-ml. beaker. The beaker is immersed in an ice bath, and 112 g. (61 ml., 1.10 moles) of concentrated (18M) sulfuric acid followed by 200 ml. of water is added cautiously with manual stir ...
Sem4ch3 Assignment
... The coordination number of a metal in coordination compounds is (a) Same as primary valency (b) Sum of primary and secondary valencies (c) Same as secondary valency (d) None of these Ligand in a complex salt are (a) Anions linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion (b) Cations linked ...
... The coordination number of a metal in coordination compounds is (a) Same as primary valency (b) Sum of primary and secondary valencies (c) Same as secondary valency (d) None of these Ligand in a complex salt are (a) Anions linked by coordinate bonds to a central metal atom or ion (b) Cations linked ...
Project Overview
... Alcohols give rise to broad O-H stretching absorptions from 3200 to 3600 cm-1 in IR spectra The alcohol hydroxyl hydrogen typically produces a broad 1H NMR signal of variable chemical shift which can be eliminated by exchange with deuterium from D2O Hydrogen atoms on the carbon of a 1o or 2o alc ...
... Alcohols give rise to broad O-H stretching absorptions from 3200 to 3600 cm-1 in IR spectra The alcohol hydroxyl hydrogen typically produces a broad 1H NMR signal of variable chemical shift which can be eliminated by exchange with deuterium from D2O Hydrogen atoms on the carbon of a 1o or 2o alc ...
Section 16.1 A Model for Reaction Rates
... heavy cart up a hill. If the hill is high, a substantial amount of energy is required to move the cart, and it might take a long time to get it to the top. If the hill is low, less energy is required and the task might be accomplished faster ...
... heavy cart up a hill. If the hill is high, a substantial amount of energy is required to move the cart, and it might take a long time to get it to the top. If the hill is low, less energy is required and the task might be accomplished faster ...
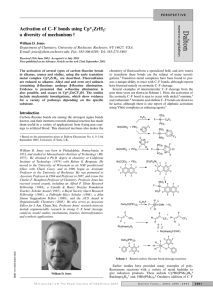
Activation of C–F bonds using Cp*2ZrH2: a
... result in smaller conversions to the same products. This reaction can be explained by two reasonable mechanisms: (1) olefin insertion/β-fluoride elimination, or (2) hydride attack/fluoride metathesis as shown in Scheme 6. Olefin insertion is well known for this zirconium hydride, and regioselective inse ...
... result in smaller conversions to the same products. This reaction can be explained by two reasonable mechanisms: (1) olefin insertion/β-fluoride elimination, or (2) hydride attack/fluoride metathesis as shown in Scheme 6. Olefin insertion is well known for this zirconium hydride, and regioselective inse ...
Chapter 7
... • The original substances are reactants • The substances produced by the reaction are called products for example: carbon can collide with oxygen and make carbon dioxide Chemical Equation: ...
... • The original substances are reactants • The substances produced by the reaction are called products for example: carbon can collide with oxygen and make carbon dioxide Chemical Equation: ...
Periodicity (AHL) - slider-dpchemistry-11
... As we have seen previously, the configurations of the first row d-block mostly fill the 3d subshell in order. The exceptions come from Cr and Cu where we see more stable configurations from the half-filled and filled 3d subshell. This is possible because the 4s and 3d subshells are so similar in ene ...
... As we have seen previously, the configurations of the first row d-block mostly fill the 3d subshell in order. The exceptions come from Cr and Cu where we see more stable configurations from the half-filled and filled 3d subshell. This is possible because the 4s and 3d subshells are so similar in ene ...
KHSO4-SiO2-MeOH – An efficient selective solid
... zeolite3c, acid resin4, etc that are generally in use suffer from certain limitations such as requirement in large volume, pore size dependency, substrate specificity, etc. Recently selective cleavage of only prenyl esters using silica-supported sodium hydrogen sulphate in a nonprotic solvent was re ...
... zeolite3c, acid resin4, etc that are generally in use suffer from certain limitations such as requirement in large volume, pore size dependency, substrate specificity, etc. Recently selective cleavage of only prenyl esters using silica-supported sodium hydrogen sulphate in a nonprotic solvent was re ...
Chem 174-Lecture 15a..
... All of these aquo complexes have higher Ka-values than CpH itself (Ka=1.0*10-16), which means that they are stronger acids ...
... All of these aquo complexes have higher Ka-values than CpH itself (Ka=1.0*10-16), which means that they are stronger acids ...
organic chemistry - Madison County Schools
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
... A group of atoms that give characteristics and properties to organic compounds. These functional groups may be aldehydes, alcohols, ethers, ketones, amino acids, amides, and others. We will study the alcohols because of their wide use in combustion reactions. ...
Topic 7 Assessed Homework - A
... C8H18 is obtained by the catalytic cracking of suitable heavy fractions. State what is meant by the term cracking and name the catalyst used in catalytic cracking. Write an equation to show how one molecule of C14H30 is cracked to form one molecule of C8H18 and one molecule of another hydrocarbon. E ...
... C8H18 is obtained by the catalytic cracking of suitable heavy fractions. State what is meant by the term cracking and name the catalyst used in catalytic cracking. Write an equation to show how one molecule of C14H30 is cracked to form one molecule of C8H18 and one molecule of another hydrocarbon. E ...
A Diels-Alder Synthesis
... Look-up the "12 Principles" of Green Chemistry. (wikipedia anyone?) Which of these principles are conformed with by our synthetic method? Which of these principles are explicitly violated? ...
... Look-up the "12 Principles" of Green Chemistry. (wikipedia anyone?) Which of these principles are conformed with by our synthetic method? Which of these principles are explicitly violated? ...
Ch 4 Slides - people.iup.edu
... What makes carbon “special”? • makes more bonds than other elements • makes single, double or triple bonds • bonds with many other elements • imparts shape to molecules These properties are the result of electron ...
... What makes carbon “special”? • makes more bonds than other elements • makes single, double or triple bonds • bonds with many other elements • imparts shape to molecules These properties are the result of electron ...
Ch 4 Slides
... What makes carbon “special”? • makes more bonds than other elements • makes single, double or triple bonds • bonds with many other elements • imparts shape to molecules These properties are the result of electron ...
... What makes carbon “special”? • makes more bonds than other elements • makes single, double or triple bonds • bonds with many other elements • imparts shape to molecules These properties are the result of electron ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... is carefully neutralized with 52.3 g. (1.25 mole) of 90.6% formic acid over a 1-hour period. A magnetic stirring bar is added, the flask is fitted with a short path distillation head, and the reaction mixture is placed in a silicon oil bath which is rapidly heated to 220–250°. The azeotropic mixture ...
... is carefully neutralized with 52.3 g. (1.25 mole) of 90.6% formic acid over a 1-hour period. A magnetic stirring bar is added, the flask is fitted with a short path distillation head, and the reaction mixture is placed in a silicon oil bath which is rapidly heated to 220–250°. The azeotropic mixture ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.