CH_10_5_Functional_Groups
... Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Eleventh Edition ...
... Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Eleventh Edition ...
01. Introduction of bioorganic chemistry. Classification, structure
... 4. If the same alkyl groups occur more than once, indicate this by prefix (di-, tri-, tetra etc) (dimethyl indicates two methyl groups). The numbers indicating the positions of these alkyl groups are separated by comma, followed by a hyphen, and placed in front of the name (2,3-dimethyl). 5. When se ...
... 4. If the same alkyl groups occur more than once, indicate this by prefix (di-, tri-, tetra etc) (dimethyl indicates two methyl groups). The numbers indicating the positions of these alkyl groups are separated by comma, followed by a hyphen, and placed in front of the name (2,3-dimethyl). 5. When se ...
112 Exam III Lec Outline 2016
... Isomers have the same chemical formula (chemical composition) but exhibit different properties due to different arrangements of atoms. cis [Pt(NH3)2]Cl2 ...
... Isomers have the same chemical formula (chemical composition) but exhibit different properties due to different arrangements of atoms. cis [Pt(NH3)2]Cl2 ...
Lecture - Ch 19
... intermediate, which expels hydride ion as a leaving group and is thereby oxidized – A second aldehyde molecule accepts the hydride ion in another nucleophilic addition step and is thereby reduced ...
... intermediate, which expels hydride ion as a leaving group and is thereby oxidized – A second aldehyde molecule accepts the hydride ion in another nucleophilic addition step and is thereby reduced ...
Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
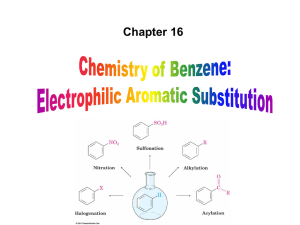
... Three rules for the additive effects of two different groups: 1. If the directing effects of the two groups are the same, the result is additive 2. If the directing effects of two groups oppose each other, the more powerful activating group determines the principal outcome 3. The position between th ...
... Three rules for the additive effects of two different groups: 1. If the directing effects of the two groups are the same, the result is additive 2. If the directing effects of two groups oppose each other, the more powerful activating group determines the principal outcome 3. The position between th ...
Sodium is an abundant metallic element with atomic number as 11
... forms addition compounds with naphthalene and other aromatic polycyclic compounds and with aryl alkenes. -The reaction of sodium with alcohols is similar to the reaction of sodium with water, but slower. There are two general reactions with organic halides. One of them requires the condensation of t ...
... forms addition compounds with naphthalene and other aromatic polycyclic compounds and with aryl alkenes. -The reaction of sodium with alcohols is similar to the reaction of sodium with water, but slower. There are two general reactions with organic halides. One of them requires the condensation of t ...
Non-native transition metal monoxide nanostructures
... Cobaltous oxide typically crystallizes in two crystal phases; c-CoO (space group Fm3m) with octahedral Co2+ ions and h-CoO (space group P63mc) with tetrahedral Co2+ ions. On the basis of its high chemical stability and intriguing catalytic properties, c-CoO has been widely studied for such potential ...
... Cobaltous oxide typically crystallizes in two crystal phases; c-CoO (space group Fm3m) with octahedral Co2+ ions and h-CoO (space group P63mc) with tetrahedral Co2+ ions. On the basis of its high chemical stability and intriguing catalytic properties, c-CoO has been widely studied for such potential ...
Keynote Address
... We have designed molybdenum complexes that will reduce dinitrogen selectively and catalytically to ammonia at 1 atm and room temperature using protons and electrons (~66% yield, ~4 turnovers).1 The most successful catalysts contain the [HIPTN3N]3ligand, where HIPT = 3,5-(2,4,6-i-Pr3C6H2)2C6H3 (HexaI ...
... We have designed molybdenum complexes that will reduce dinitrogen selectively and catalytically to ammonia at 1 atm and room temperature using protons and electrons (~66% yield, ~4 turnovers).1 The most successful catalysts contain the [HIPTN3N]3ligand, where HIPT = 3,5-(2,4,6-i-Pr3C6H2)2C6H3 (HexaI ...
Training Presentation - SALEM
... 2. m.p. from Fe to Zn due to the of unpaired d-electrons (from 4 to 0) ...
... 2. m.p. from Fe to Zn due to the of unpaired d-electrons (from 4 to 0) ...
II. Main types of organometallic compounds
... Some carbonaceous organic group such as alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aromatic, acyl in the formation of the M – C bonding, there is only one carbon atom directly bonding with metal atom, which is σ ligands, they typically provide a pair of σ electron as anion (formal charge - 1), and its coordination wa ...
... Some carbonaceous organic group such as alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aromatic, acyl in the formation of the M – C bonding, there is only one carbon atom directly bonding with metal atom, which is σ ligands, they typically provide a pair of σ electron as anion (formal charge - 1), and its coordination wa ...
LABORATORY 5 DETECTION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN
... carboxylic acids depend on organic part that is connected to carboxylic group or the presence of additional functional group. ...
... carboxylic acids depend on organic part that is connected to carboxylic group or the presence of additional functional group. ...
Lecture 7a
... quality of separation The separation of compounds in a mixture is based on the different affinities for the stationary phase and the mobile phase. Thus, each compound has a different partition coefficient between these two phases. The higher the affinity of the compound towards the stationary ph ...
... quality of separation The separation of compounds in a mixture is based on the different affinities for the stationary phase and the mobile phase. Thus, each compound has a different partition coefficient between these two phases. The higher the affinity of the compound towards the stationary ph ...
CH4 Student Revision Guides pdf | GCE AS/A
... In an alkene such as ethene, C2H4, the double bond prevents this rotation. There is no rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond and the molecule is confined to a planar shape. This means that in compounds such as 1,2-dichloroethene, represented by the ball and stick diagrams below, two forms ar ...
... In an alkene such as ethene, C2H4, the double bond prevents this rotation. There is no rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond and the molecule is confined to a planar shape. This means that in compounds such as 1,2-dichloroethene, represented by the ball and stick diagrams below, two forms ar ...
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
... • Hydrolysis of esters produces carboxylic acids & alcohols • Ester hydrolysis can be speeded up by using acid as a catalyst. • H+ works by first protonating the carbonyl oxygen to make it more reactive • Like the reverse rxn (esterification) hydrolysis is an equilibrium process with a tetrahedral i ...
... • Hydrolysis of esters produces carboxylic acids & alcohols • Ester hydrolysis can be speeded up by using acid as a catalyst. • H+ works by first protonating the carbonyl oxygen to make it more reactive • Like the reverse rxn (esterification) hydrolysis is an equilibrium process with a tetrahedral i ...
Siloxane-containing polymers
... is known in the prior art. Thus, British Pat. No. ually added under anhydrous conditions to a reaction 1,062,418, published March, 1967 discloses that linear mixture containing the aforementioned metal salt and a polysiloxanes of formula ...
... is known in the prior art. Thus, British Pat. No. ually added under anhydrous conditions to a reaction 1,062,418, published March, 1967 discloses that linear mixture containing the aforementioned metal salt and a polysiloxanes of formula ...
Worksheets for this unit
... break down these large molecules to useable size is called ___________________. There are two types called ______________ and _________________________. 7. The opposite to cracking is called ____________________________ ...
... break down these large molecules to useable size is called ___________________. There are two types called ______________ and _________________________. 7. The opposite to cracking is called ____________________________ ...
Ch. 16: Solutions - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... Carboxylic Acid Properties Carboxylic acids are extremely polar They have higher boiling pts than alcohols, ketones, and aldehydes of similar mass ...
... Carboxylic Acid Properties Carboxylic acids are extremely polar They have higher boiling pts than alcohols, ketones, and aldehydes of similar mass ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.