CHAPTER 8 - REACTION EXAMPLES (Based on the 6th edition of
... OXIDATIVE CLEAVAGE: Ozonolysis In this reaction each of the sp2 carbons involved in the pi bond gets oxidized either to aldehyde or ketone, depending on whether it ends up at the end of a carbon chain or in the middle after the pi bond cleaves. If the oxidized carbon ends up at the end of a carbon ...
... OXIDATIVE CLEAVAGE: Ozonolysis In this reaction each of the sp2 carbons involved in the pi bond gets oxidized either to aldehyde or ketone, depending on whether it ends up at the end of a carbon chain or in the middle after the pi bond cleaves. If the oxidized carbon ends up at the end of a carbon ...
Document
... Addition of hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of platinum (Pt), catalyst, to unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes Alkynes ...
... Addition of hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of platinum (Pt), catalyst, to unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes Alkynes ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
CCCH110D Inorganic vs Organic NOTES
... Addition polymer – polymer in which the monomers simply link together without the elimination of any atoms (e.g. polyethylene), Condensation polymer – polymer that eliminate an atom or a small group of atoms during polymerization. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Addition polymer – polymer in which the monomers simply link together without the elimination of any atoms (e.g. polyethylene), Condensation polymer – polymer that eliminate an atom or a small group of atoms during polymerization. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
doc
... Problem 10.12, p. 334 Rank each of the following series of compounds in order of increasing oxidation level: (Strategy: Compounds that have the same number of carbon atoms can be compared by adding the number of C-O, C-N, and C-X bonds in each and then subtracting the number of C-H bonds. The large ...
... Problem 10.12, p. 334 Rank each of the following series of compounds in order of increasing oxidation level: (Strategy: Compounds that have the same number of carbon atoms can be compared by adding the number of C-O, C-N, and C-X bonds in each and then subtracting the number of C-H bonds. The large ...
2010-09-16 Alcohols
... by a carbon chain. The alcohol present in beverages is ethanol, which is the mildest depressant and narcotic poison of all alcohols. Other alcohols magnify this effect and are often added to ethanol in the lab to make it unpalatable. The addition of the OH group will drastically change the propertie ...
... by a carbon chain. The alcohol present in beverages is ethanol, which is the mildest depressant and narcotic poison of all alcohols. Other alcohols magnify this effect and are often added to ethanol in the lab to make it unpalatable. The addition of the OH group will drastically change the propertie ...
Lecture 4 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... • The C-C double bond is more reactive than a single C-C bond – The electron density is more exposed above and below the plane of the molecule ...
... • The C-C double bond is more reactive than a single C-C bond – The electron density is more exposed above and below the plane of the molecule ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 4 REVIEW SHEET
... Structural Isomer - different covalent arrangement, bond location Geometric Isomer - different spatial arrangement around a double bond but same covalent, have carbon double bond → doesn’t allow moving o cis - isomer : X (atom or group of atoms) on same side o trans - isomer : X (atom or group of at ...
... Structural Isomer - different covalent arrangement, bond location Geometric Isomer - different spatial arrangement around a double bond but same covalent, have carbon double bond → doesn’t allow moving o cis - isomer : X (atom or group of atoms) on same side o trans - isomer : X (atom or group of at ...
Organic Chemistry
... PROBLEM: Draw structures that have different atom arrangements for hydrocarbons with (a) Six C atoms, no multiple bonds, and no rings (b) Four C atoms, one double bond, and no rings (c) Four C atoms, no multiple bonds, and one ring PLAN: In each case, we draw the longest carbon chain first and then ...
... PROBLEM: Draw structures that have different atom arrangements for hydrocarbons with (a) Six C atoms, no multiple bonds, and no rings (b) Four C atoms, one double bond, and no rings (c) Four C atoms, no multiple bonds, and one ring PLAN: In each case, we draw the longest carbon chain first and then ...
amino group - salemmbrothers
... A carboxyl group (-COOH) consists of a carbon atom with a double bond with an oxygen atom and a single bond to a hydroxyl group. Compounds with carboxyl groups are carboxylic acids. A carboxyl group acts as an acid because the combined electro-negativities of the two adjacent oxygen atoms increas ...
... A carboxyl group (-COOH) consists of a carbon atom with a double bond with an oxygen atom and a single bond to a hydroxyl group. Compounds with carboxyl groups are carboxylic acids. A carboxyl group acts as an acid because the combined electro-negativities of the two adjacent oxygen atoms increas ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... • What is the name of the following alkane? ...
... • What is the name of the following alkane? ...
ch15
... PROBLEM: Draw structures that have different atom arrangements for hydrocarbons with (a) Six C atoms, no multiple bonds, and no rings (b) Four C atoms, one double bond, and no rings (c) Four C atoms, no multiple bonds, and one ring PLAN: In each case, we draw the longest carbon chain first and then ...
... PROBLEM: Draw structures that have different atom arrangements for hydrocarbons with (a) Six C atoms, no multiple bonds, and no rings (b) Four C atoms, one double bond, and no rings (c) Four C atoms, no multiple bonds, and one ring PLAN: In each case, we draw the longest carbon chain first and then ...
Reacciones redox
... • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes (RCHO) under mild reaction conditions using PCC in CH2Cl2. • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) under harsher reaction conditions: Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7, or CrO3 in the presence of H2O and H2SO4. ...
... • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes (RCHO) under mild reaction conditions using PCC in CH2Cl2. • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) under harsher reaction conditions: Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7, or CrO3 in the presence of H2O and H2SO4. ...
Organic Chemistry IB Organic Chemistry 2016
... Alkene Addition Rxns • Moves from unsaturated to saturated • Hydrogenation – addition of hydrogen on the double bond – Margarine is solid at room temperature because it has been hydrogenated and is saturated (higher melting points) ...
... Alkene Addition Rxns • Moves from unsaturated to saturated • Hydrogenation – addition of hydrogen on the double bond – Margarine is solid at room temperature because it has been hydrogenated and is saturated (higher melting points) ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Are compounds that contain only the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Properties of Hydrocarbons: 1. Hydrocarbons mix poorly with water 2. Hydrocarbons are flammable. Chemical Formulas of Hydrocarbons: ...
... • Are compounds that contain only the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Properties of Hydrocarbons: 1. Hydrocarbons mix poorly with water 2. Hydrocarbons are flammable. Chemical Formulas of Hydrocarbons: ...
Chapter 9 – Compounds of Carbon
... • It is possible to replace a hydrogen atom in an alkane with a chlorine, to form a chloroalkanes. • The systematic name for a chloroalkane starts with chloro followed by the name of the alkane. • In chains higher than two carbons it is possible to put chlorines on different carbons. • In this case, ...
... • It is possible to replace a hydrogen atom in an alkane with a chlorine, to form a chloroalkanes. • The systematic name for a chloroalkane starts with chloro followed by the name of the alkane. • In chains higher than two carbons it is possible to put chlorines on different carbons. • In this case, ...
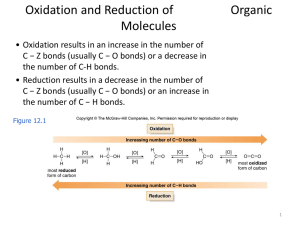
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
Carbon
... • Living matter-mainly of carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) with smaller amounts of sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P). SINGLE BOND shares pair of electrons ...
... • Living matter-mainly of carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) with smaller amounts of sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P). SINGLE BOND shares pair of electrons ...
1.2 The Chemicals of Life - Father Michael McGivney
... Hydrocarbons • Nonpolar and form straight or branched chains and ring shaped structures. • Names reflect the number of carbons, the number and location of any double or triple bonds and any functional groups. • Names based on the number of carbons in the longest carbon chain: 1 carbon......meth 2 c ...
... Hydrocarbons • Nonpolar and form straight or branched chains and ring shaped structures. • Names reflect the number of carbons, the number and location of any double or triple bonds and any functional groups. • Names based on the number of carbons in the longest carbon chain: 1 carbon......meth 2 c ...
L3 - Alcohol and Phenol Reactions
... oxidized by removing two hydrogen atoms from the same molecule, one from a hydroxyl group and the second from the carbon of the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of a double bond between the carbon and remaining oxygen ...
... oxidized by removing two hydrogen atoms from the same molecule, one from a hydroxyl group and the second from the carbon of the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of a double bond between the carbon and remaining oxygen ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.