Organic Chemistry = ______________________ ________________________
... Notice: There is no alkyne corresponding to the methane of the alkane series. That is b/c there must be at least 2 carbon atoms to form a triple bond. ...
... Notice: There is no alkyne corresponding to the methane of the alkane series. That is b/c there must be at least 2 carbon atoms to form a triple bond. ...
File
... SUBSTITUTED HYDROCARBONS Carbon can form stable bonds with several other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and members of the halogen family. If just one atom of another element is substituted for a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon, a different compound is created. Halogens Freon was ba ...
... SUBSTITUTED HYDROCARBONS Carbon can form stable bonds with several other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and members of the halogen family. If just one atom of another element is substituted for a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon, a different compound is created. Halogens Freon was ba ...
CHEM 263 (AS 40) Organic Chemistry II Winter 2017 Instructor: Dr
... functional groups in organic chemistry are discussed. Functional groups covered include alkenes, alkynes, aromatic compounds, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives. The presence of these functional groups in natural products is emphas ...
... functional groups in organic chemistry are discussed. Functional groups covered include alkenes, alkynes, aromatic compounds, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives. The presence of these functional groups in natural products is emphas ...
Chapter 4 mastery check
... they have different chemical properties they have the same molecular formula their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences they are a result of restricted movement around a carbon double bond their possible numbers increase as carbon skeletons increase in size. ...
... they have different chemical properties they have the same molecular formula their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences they are a result of restricted movement around a carbon double bond their possible numbers increase as carbon skeletons increase in size. ...
7. AS mechanisms
... The rate of these substitution reactions depends on the strength of the C-X bond The weaker the bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction. The iodoalkanes are the fastest to substitute and the fluoroalkanes are the slowest. The strength of the C-F bond is such that fluoroalkanes ar ...
... The rate of these substitution reactions depends on the strength of the C-X bond The weaker the bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction. The iodoalkanes are the fastest to substitute and the fluoroalkanes are the slowest. The strength of the C-F bond is such that fluoroalkanes ar ...
Organic Chemistry
... 4. Name the hydrocarbon groups attached to the longest chain by adding –yl to the stem name. Akyl Indicate the point of attachment by the number of Groups the carbon atoms to which the group is attached ...
... 4. Name the hydrocarbon groups attached to the longest chain by adding –yl to the stem name. Akyl Indicate the point of attachment by the number of Groups the carbon atoms to which the group is attached ...
Slide 1
... they are called peptide bonds in biology. Many amino acids combine in this way to form proteins. amino group from one acid ...
... they are called peptide bonds in biology. Many amino acids combine in this way to form proteins. amino group from one acid ...
Chem 3.5 Answers #7
... Aldehydes are produced by the oxidation of primary alcohols using acidified potassium dichromate solution. The aldehyde must be distilled off as it is made or it will oxidise further, up to the carboxylic acid. Ketones are made by the same oxidation reaction with secondary alcohols, but they do not ...
... Aldehydes are produced by the oxidation of primary alcohols using acidified potassium dichromate solution. The aldehyde must be distilled off as it is made or it will oxidise further, up to the carboxylic acid. Ketones are made by the same oxidation reaction with secondary alcohols, but they do not ...
Organic Chemistry - Salisbury Composite High | Home
... Ex) ethene b.p = -103.8oC vs ethane b.p = -88.6oC ...
... Ex) ethene b.p = -103.8oC vs ethane b.p = -88.6oC ...
1 - contentextra
... Foam A dispersed mixture of two components which normally do not mix in which the dispersed component is gaseous. Food Any substance, whether processed, semi-processed or raw that is intended for human consumption, and includes beverages, chewing gum and any substance that has been used in the manu ...
... Foam A dispersed mixture of two components which normally do not mix in which the dispersed component is gaseous. Food Any substance, whether processed, semi-processed or raw that is intended for human consumption, and includes beverages, chewing gum and any substance that has been used in the manu ...
Organic Chem Functional Groups
... lowest position number Alcohols containing 2, 3, and 4 of the -OH substituents are named diols, triols, and tetrols respectively ...
... lowest position number Alcohols containing 2, 3, and 4 of the -OH substituents are named diols, triols, and tetrols respectively ...
chm 103 general chemistry
... f. Asphalt. g. Crude oil (a mixture with wide range of b. p.’s). Separated into useful components by fractional distillation. ...
... f. Asphalt. g. Crude oil (a mixture with wide range of b. p.’s). Separated into useful components by fractional distillation. ...
ch-22 HW answers - HCC Learning Web
... C) organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. D) organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. E) None of the above. ...
... C) organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. D) organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. E) None of the above. ...
(Q.3) Carbon completes its octet by
... (Q.6) The hydrocarbons having the general formula of CnH2n-2 , CnH2n+2 and CnH2n+1 are known as (Q.7) The next higher homologue of pentane and propylene is (Q.8) The IUPAC name of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is ________and ________ (Q.9) What is meant by homologous series? State any four character ...
... (Q.6) The hydrocarbons having the general formula of CnH2n-2 , CnH2n+2 and CnH2n+1 are known as (Q.7) The next higher homologue of pentane and propylene is (Q.8) The IUPAC name of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is ________and ________ (Q.9) What is meant by homologous series? State any four character ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
91165 Organic Chemistry Cornell Notes.
... Solubility falls off as the hydrocarbon chains get longer noticeably so after 5 carbons. They form alkaline solutions that affect indicators (as above), The small amines smell very similar to ammonia but as the amines get bigger, they tend to smell more "fishy", or of decay. Or perhaps we should put ...
... Solubility falls off as the hydrocarbon chains get longer noticeably so after 5 carbons. They form alkaline solutions that affect indicators (as above), The small amines smell very similar to ammonia but as the amines get bigger, they tend to smell more "fishy", or of decay. Or perhaps we should put ...
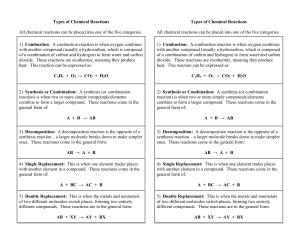
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
90309 Describe the structural formulae and reactions of compounds
... Larger organic molecules may be used in questions involving the linking of structure and reactivity. ...
... Larger organic molecules may be used in questions involving the linking of structure and reactivity. ...
chemistry_23 - Bonar Law Memorial
... What reactions of alkenes may be used to introduce functional groups into organic molecules? Addition reactions of alkenes are an important method of introducing new functional groups into organic molecules. In an addition reaction, a substance is added at the double or triple bond of an alkene or a ...
... What reactions of alkenes may be used to introduce functional groups into organic molecules? Addition reactions of alkenes are an important method of introducing new functional groups into organic molecules. In an addition reaction, a substance is added at the double or triple bond of an alkene or a ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.