Organic Reactions
... a. Alkenes have pi bonds in which electrons are easily accessible b/c they aren’t trapped between two nuclei as sigma bonding electrons are. b. Other functional groups have highly electronegative atoms like O, N or halogens ...
... a. Alkenes have pi bonds in which electrons are easily accessible b/c they aren’t trapped between two nuclei as sigma bonding electrons are. b. Other functional groups have highly electronegative atoms like O, N or halogens ...
Organic Chemistry
... members fit the general formula CnH2n+2. They have trends in physical properties e.g. density and m.p. and b.p. all increase with Mr. They all undergo similar chemical reactions. Alkanes are SATURATED HYDROCARBONS. i.e. they contain only single C to C bonds and are made up of C and H atoms only. ...
... members fit the general formula CnH2n+2. They have trends in physical properties e.g. density and m.p. and b.p. all increase with Mr. They all undergo similar chemical reactions. Alkanes are SATURATED HYDROCARBONS. i.e. they contain only single C to C bonds and are made up of C and H atoms only. ...
SCH4U Organic Chemistry Portfolio Name: This portfolio is due on
... 1. In household fires, it is often the smoke produced that creates a danger as great as the flames. Many plastic materials in the house contain polyvinylchloride (PVC); the formula for this compound is (C2H3Cl)n. Write an equation for the combustion of PVC in oxygen – no need to balance. Suggest a r ...
... 1. In household fires, it is often the smoke produced that creates a danger as great as the flames. Many plastic materials in the house contain polyvinylchloride (PVC); the formula for this compound is (C2H3Cl)n. Write an equation for the combustion of PVC in oxygen – no need to balance. Suggest a r ...
Organic Naming Guide
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry Chemistry
... this mechanism is that it only takes place in UV light and the addition of tetramethyl lead increases the rate. The formation of an ester may be regarded as an example of a substitution reaction since the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by an alkyl group. ...
... this mechanism is that it only takes place in UV light and the addition of tetramethyl lead increases the rate. The formation of an ester may be regarded as an example of a substitution reaction since the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid has been replaced by an alkyl group. ...
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE
... Elimination results in net loss of HBr to form a new C=C bond. ...
... Elimination results in net loss of HBr to form a new C=C bond. ...
Exam 3 Review
... How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more reactive than ketones? Classify the following compounds as either alcohols, diols, ethers, ...
... How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more reactive than ketones? Classify the following compounds as either alcohols, diols, ethers, ...
N - Dr. May Notes
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
review sheet plus practice problems
... Questions that may appear on the exam: What is the name for this alkyl halide / alcohol / ether? Is an alcohol 1°, 2°, or 3°? What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/uv light)? Give the chain mechanism for free radical halogenation. What is the selectivity for bromin ...
... Questions that may appear on the exam: What is the name for this alkyl halide / alcohol / ether? Is an alcohol 1°, 2°, or 3°? What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/uv light)? Give the chain mechanism for free radical halogenation. What is the selectivity for bromin ...
organometallic reagents
... product is to work the synthesis backwards on paper. This approach is called retrosynthetic analysis. In this approach, strategic C-C bonds in the target molecule are broken at points where bond formation seems possible. The reason that retrosynthetic analysis is useful is that fewer possible reacti ...
... product is to work the synthesis backwards on paper. This approach is called retrosynthetic analysis. In this approach, strategic C-C bonds in the target molecule are broken at points where bond formation seems possible. The reason that retrosynthetic analysis is useful is that fewer possible reacti ...
Organic Nomenclature - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
... double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typical molecule, we have to specify where it is ...
Organic_Nomenclature_packet
... and the bond length between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at vari ...
... and the bond length between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at vari ...
Mechanisms of organic reactions
... Again: initiation (creation of radicals), propagation (radicals attack neutral molecules, producing more and more radicals), termination (radicals react with each other, forming a stable product; the chain reaction is terminated) E.g.: polymerization of ethylene using dibenzoyl peroxide as an initia ...
... Again: initiation (creation of radicals), propagation (radicals attack neutral molecules, producing more and more radicals), termination (radicals react with each other, forming a stable product; the chain reaction is terminated) E.g.: polymerization of ethylene using dibenzoyl peroxide as an initia ...
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS
... resulting alkyl halides • Tertiary Alcohol→ turns cloudy immediately (the alkyl halide is not soluble in water and precipitates out) • Secondary Alcohol → turns cloudy after 5 minutes • Primary Alcohol → takes much longer than 5 minutes to turn cloudy ...
... resulting alkyl halides • Tertiary Alcohol→ turns cloudy immediately (the alkyl halide is not soluble in water and precipitates out) • Secondary Alcohol → turns cloudy after 5 minutes • Primary Alcohol → takes much longer than 5 minutes to turn cloudy ...
8.2-Organic Nomenclature packet
... between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typic ...
... between the carbon atoms is shorter in the double bond. It is also more reactive than a single bond since the bond (the second pair of electrons) is farther from the nuclei. Naming is a little bit more complex for alkenes than alkanes. Since the double bond could appear at various sites in a typic ...
Chem174-Lecture 11a_.. - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Metal carbonyls are used in many industrial processes aiming at carbonyl compounds i.e., Monsanto process (acetic acid), Fischer Tropsch process or Reppe carbonylation (vinyl esters) Vaska’s complex (IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2) absorbs oxygen reversibly and serves as model for the oxygen absorption of myog ...
... Metal carbonyls are used in many industrial processes aiming at carbonyl compounds i.e., Monsanto process (acetic acid), Fischer Tropsch process or Reppe carbonylation (vinyl esters) Vaska’s complex (IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2) absorbs oxygen reversibly and serves as model for the oxygen absorption of myog ...
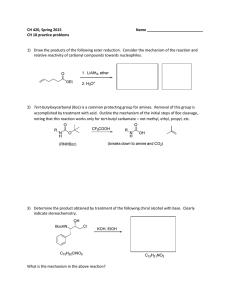
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
Topic 3 – Chemical Structure and Bonding
... The rules for naming organic compounds were devised by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). They are as follows. 1) The functional group gives the ending of the name e.g. –ol for an alcohol 2) The number of carbons gives the first part of the name e.g. prop- or propan- for 3 ca ...
... The rules for naming organic compounds were devised by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). They are as follows. 1) The functional group gives the ending of the name e.g. –ol for an alcohol 2) The number of carbons gives the first part of the name e.g. prop- or propan- for 3 ca ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.