3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
... Alphabetize by sub. (di-, tri-count only if part of sub. name) Order #’s from low to high; use smallest possible numbers Capitalize the first letter only Write as one word with commas and hyphens as needed ...
... Alphabetize by sub. (di-, tri-count only if part of sub. name) Order #’s from low to high; use smallest possible numbers Capitalize the first letter only Write as one word with commas and hyphens as needed ...
Organic Chemistry The Chemistry Of Life / The Chemistry of Carbon
... 2. Will form strong “di-sulfide bonds” (S-S) with other thiols 3. Will greatly influence shape of proteins ...
... 2. Will form strong “di-sulfide bonds” (S-S) with other thiols 3. Will greatly influence shape of proteins ...
CHEMISTRY 263
... Do Not turn in, answers available in "Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry" for Solomons. This is available in the Bookstore or can be borrowed from Cameron Library's Reserve Reading Room Chapter 11: 11.2 to11.4; 11.9; 11.13 to 11.16; 11.25 to 11.27; 11.34 Chapter 22: 22.1; 22. ...
... Do Not turn in, answers available in "Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry" for Solomons. This is available in the Bookstore or can be borrowed from Cameron Library's Reserve Reading Room Chapter 11: 11.2 to11.4; 11.9; 11.13 to 11.16; 11.25 to 11.27; 11.34 Chapter 22: 22.1; 22. ...
Chapter 7
... the atoms of many other elements. 5. Carbon may form compounds that contain different structural arrangements and combinations with the same molecular formula. isomers: carbon compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. ...
... the atoms of many other elements. 5. Carbon may form compounds that contain different structural arrangements and combinations with the same molecular formula. isomers: carbon compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. ...
File
... Treatment of the ionic rhodium complex [Rh(COD)2][BF4] (COD = cyclo-octa-1,4-diene) with bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (‘dppe’) in n-butanol leads to the formation of a highlyeffective system for the hydrogenation of alkenes (a) Draw a catalytic cycle for the conversion of ethene and hydrogen to eth ...
... Treatment of the ionic rhodium complex [Rh(COD)2][BF4] (COD = cyclo-octa-1,4-diene) with bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (‘dppe’) in n-butanol leads to the formation of a highlyeffective system for the hydrogenation of alkenes (a) Draw a catalytic cycle for the conversion of ethene and hydrogen to eth ...
Practice Problem
... dialkylcopper (Gilman reagents) 3. Lithium dialkylcopper reagents react with alkyl halides to give alkanes ...
... dialkylcopper (Gilman reagents) 3. Lithium dialkylcopper reagents react with alkyl halides to give alkanes ...
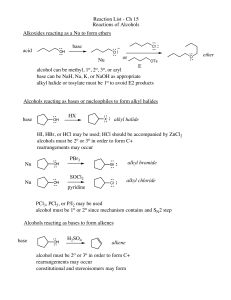
Reaction List - Ch 15 Reactions of Alcohols Alkoxides reacting as a
... base can be NaH, Na, K, or NaOH as appropriate alkyl halide or tosylate must be 1o to avoid E2 products Alcohols reacting as bases or nucleophiles to form alkyl halides base ...
... base can be NaH, Na, K, or NaOH as appropriate alkyl halide or tosylate must be 1o to avoid E2 products Alcohols reacting as bases or nucleophiles to form alkyl halides base ...
lecture 12 catalysis_transformation of alkenes_alkynes
... SAMPLE PROBLEM: Assume 2-pentene and 2-hexene undergo metathesis. AT equilibrium what are all the possible alkenes that would be present, neglecting stereochemistry about the double bond? Remember to consider self metathesis reactions. ...
... SAMPLE PROBLEM: Assume 2-pentene and 2-hexene undergo metathesis. AT equilibrium what are all the possible alkenes that would be present, neglecting stereochemistry about the double bond? Remember to consider self metathesis reactions. ...
Chapter 4 - Nomenclature and Conformations of Alkanes and
... - Branching that produces highly symmetric molecules have abnormally high melting points - Cycloalkanes have a much higher melting point than non-cyclic alkane counterparts - The alkanes and cycloalkanes are the least dense of all groups of organic compounds - Alkanes and cycloalkanes are almost tot ...
... - Branching that produces highly symmetric molecules have abnormally high melting points - Cycloalkanes have a much higher melting point than non-cyclic alkane counterparts - The alkanes and cycloalkanes are the least dense of all groups of organic compounds - Alkanes and cycloalkanes are almost tot ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 05. Why group transfer reactions are neither cycloaddition nor sigmatropic rearrangement reactions? 06. Does hydroboration of alkene follow Markonikov’s addition? Justify your answer with suitable example. 07. How is catalytic hydrogenation different from dissolving metal reduction? Give reasons. 08 ...
... 05. Why group transfer reactions are neither cycloaddition nor sigmatropic rearrangement reactions? 06. Does hydroboration of alkene follow Markonikov’s addition? Justify your answer with suitable example. 07. How is catalytic hydrogenation different from dissolving metal reduction? Give reasons. 08 ...
- EdShare - University of Southampton
... Alkenes are unsaturated compounds that can be used in organic synthesis. They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to comp ...
... Alkenes are unsaturated compounds that can be used in organic synthesis. They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to comp ...
Organic Chemistry chapter 2
... • A polysaccharide like cellulose (on the right) is many monosaccharides linked together. ...
... • A polysaccharide like cellulose (on the right) is many monosaccharides linked together. ...
PowerPoint
... storage. Carbohydrates are the starting materials for many organic compounds like fats and amino acids. Example: Glucose C6H12O6 ...
... storage. Carbohydrates are the starting materials for many organic compounds like fats and amino acids. Example: Glucose C6H12O6 ...
IGCSE Chemistry Definitions – LEARN THESE! Melting
... Exothermic Reaction - A reaction which gives out heat (ΔH is negative) Endothermic Reaction - A reaction which takes in heat (ΔH is positive). pH - A scale of 0 – 14 which identifies solution as acidic, neutral or alkaline. Base - A substance with a pH higher than 7, they react with acids to form a ...
... Exothermic Reaction - A reaction which gives out heat (ΔH is negative) Endothermic Reaction - A reaction which takes in heat (ΔH is positive). pH - A scale of 0 – 14 which identifies solution as acidic, neutral or alkaline. Base - A substance with a pH higher than 7, they react with acids to form a ...
Organic Chemistry1
... • Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures – Structural Isomers: compounds that have the same molecular formula, but the atoms are joined together in a different order Differ in physical properties like boiling and melting points Also have different chemical ...
... • Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures – Structural Isomers: compounds that have the same molecular formula, but the atoms are joined together in a different order Differ in physical properties like boiling and melting points Also have different chemical ...
Lecture 2 - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... The 2-methylcyclohexanol provided is a mixture of cis and trans isomers (~47:53 by GC). For both isomers the conformer on the left is the major conformer because it is energetically lower (DG‡(axialequatorial): CH3: 7.28 kJ/mol, OH: 3.90 kJ/mol). The leaving group has to be in axial position for the ...
... The 2-methylcyclohexanol provided is a mixture of cis and trans isomers (~47:53 by GC). For both isomers the conformer on the left is the major conformer because it is energetically lower (DG‡(axialequatorial): CH3: 7.28 kJ/mol, OH: 3.90 kJ/mol). The leaving group has to be in axial position for the ...
Carbon and Organic Compounds
... • When the carbon in organic compounds forms only single bonds we say that the compound is saturated (can’t add anything more). • If there are double or triple bonds, these can be broken to add more atoms. In this case we say that the compound is unsaturated. ...
... • When the carbon in organic compounds forms only single bonds we say that the compound is saturated (can’t add anything more). • If there are double or triple bonds, these can be broken to add more atoms. In this case we say that the compound is unsaturated. ...
Chemistry - Choithram School
... ii) Haloarenes are much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. iii)Reaction of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH , alkenes are the major products. iv)Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured b ...
... ii) Haloarenes are much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. iii)Reaction of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH , alkenes are the major products. iv)Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured b ...
1 Big-Picture Exam Topics
... All bonds except C-H bonds are shown as lines. C-H bonds are NOT SHOWN on the line structure. Single bonds are shown as single lines; double bonds are shown as 2 lines; triple bonds are shown as 3 lines. Carbon atoms are not labeled. ALL atoms EXCEPT carbon and hydrogen are labeled with ...
... All bonds except C-H bonds are shown as lines. C-H bonds are NOT SHOWN on the line structure. Single bonds are shown as single lines; double bonds are shown as 2 lines; triple bonds are shown as 3 lines. Carbon atoms are not labeled. ALL atoms EXCEPT carbon and hydrogen are labeled with ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.