Organic Chemistry
... mechanism as 5 bulky groups would not fit around the C in the transition state - steric hindrance. 1° halogenoalknes are less likely to undergo SN1 as this would involve the formation of a primary carbocation as an intermediate. Alkyl groups push electron density to the C atom they are attached to ( ...
... mechanism as 5 bulky groups would not fit around the C in the transition state - steric hindrance. 1° halogenoalknes are less likely to undergo SN1 as this would involve the formation of a primary carbocation as an intermediate. Alkyl groups push electron density to the C atom they are attached to ( ...
No Slide Title
... • Unsaturated cyclic compounds like benzene, which are unusually stable, are said to exhibit aromaticity. • Stability of the double bonds of benzene is due to the fact that the double bonds are not static. That is, the electrons of the double bond can freely move around the ring. This phenomena is k ...
... • Unsaturated cyclic compounds like benzene, which are unusually stable, are said to exhibit aromaticity. • Stability of the double bonds of benzene is due to the fact that the double bonds are not static. That is, the electrons of the double bond can freely move around the ring. This phenomena is k ...
Module - EPS School Projects - Heriot
... Substitution Reactions – Formation of alkyl halides, including Ph3P/CX4; formation of sulfonates; Use of alkyl halides and sulfonates to prepare amines, nitriles, ethers, etc; the Mitsunobu reaction. Addition Reactions – Revision of Markownikoff addition to alkenes, with further examples; mercuric-c ...
... Substitution Reactions – Formation of alkyl halides, including Ph3P/CX4; formation of sulfonates; Use of alkyl halides and sulfonates to prepare amines, nitriles, ethers, etc; the Mitsunobu reaction. Addition Reactions – Revision of Markownikoff addition to alkenes, with further examples; mercuric-c ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Slide 1 - University of Evansville Faculty
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell et ...
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell et ...
Carbon Compounds - Southgate Schools
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain carbon Carbon has 4 valence electrons ...
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry – study of all compounds that contain carbon Carbon has 4 valence electrons ...
Exam 2 Review Sheet for Friday, March 2 Exam Chem 1120, Spring
... • Define and use the following terms: catenation, hybridization, homologous, saturated, unsaturated, condensed structural formula, general structural formula, radicals, isomers. • Explain why there are so many carbon compounds. • List and explain the different types of hybridization that carbon unde ...
... • Define and use the following terms: catenation, hybridization, homologous, saturated, unsaturated, condensed structural formula, general structural formula, radicals, isomers. • Explain why there are so many carbon compounds. • List and explain the different types of hybridization that carbon unde ...
WEEK 7
... formulas show that there is a difference between the two compounds. The line formulas also show a difference. The line formula for Normal butane is CH3CH2CH2CH3 and the line formula for isobutane is CH3CHCH3CH3. ...
... formulas show that there is a difference between the two compounds. The line formulas also show a difference. The line formula for Normal butane is CH3CH2CH2CH3 and the line formula for isobutane is CH3CHCH3CH3. ...
R-c-H+H-oH:n-J-u oo o il o o o I o
... 14. \tVhichof the following compounds contains a diether linkage? (a) a hemiacetal (b) chloral hydrate (c) aketal (d) camphor 15. \tVhichof the following substancesis used as a preservative of biological specimens? (a) paraldehyde (b) formalin (c) methyl ethyl ketone (d) cinnamaldehyde 16. \Mhich of ...
... 14. \tVhichof the following compounds contains a diether linkage? (a) a hemiacetal (b) chloral hydrate (c) aketal (d) camphor 15. \tVhichof the following substancesis used as a preservative of biological specimens? (a) paraldehyde (b) formalin (c) methyl ethyl ketone (d) cinnamaldehyde 16. \Mhich of ...
Organic Chemistry
... Write out the following reactions using structural formulas. Show only the MAJOR product formed. a. Methyl propene reacts with HBr ...
... Write out the following reactions using structural formulas. Show only the MAJOR product formed. a. Methyl propene reacts with HBr ...
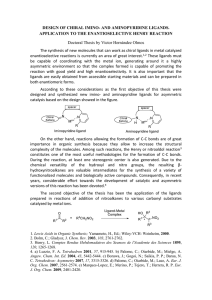
DESIGN OF CHIRAL IMINO- AND AMINOPYRIDINE LIGANDS
... The synthesis of new molecules that can work as chiral ligands in metal catalyzed enantioselective reactions is currently an area of great interest.1,2 These ligands must be capable of coordinating with the metal ion, generating around it a highly asymmetric environment so that the complex formed is ...
... The synthesis of new molecules that can work as chiral ligands in metal catalyzed enantioselective reactions is currently an area of great interest.1,2 These ligands must be capable of coordinating with the metal ion, generating around it a highly asymmetric environment so that the complex formed is ...
lect7
... Alkenes and other unsaturated organic molecules attach side-on to the metal atoms. They also are held in place by "synergic" & bonds. low oxidation-state compounds of these types usually obey the 18-electron rule. CO, PR3 are 2 e- donors, NO is a 3 edonor and unsaturated organic molecules co ...
... Alkenes and other unsaturated organic molecules attach side-on to the metal atoms. They also are held in place by "synergic" & bonds. low oxidation-state compounds of these types usually obey the 18-electron rule. CO, PR3 are 2 e- donors, NO is a 3 edonor and unsaturated organic molecules co ...
Organic Functional Groups to know ASAP!
... Organic Functional Groups *The following organic functional groups will be studied throughout the course of the year: naming, physical/chemical properties, reactions, mechanisms, & synthesis. *Your first assignment is to become familiar (memorize) the following information so that you can easily wor ...
... Organic Functional Groups *The following organic functional groups will be studied throughout the course of the year: naming, physical/chemical properties, reactions, mechanisms, & synthesis. *Your first assignment is to become familiar (memorize) the following information so that you can easily wor ...
ORGANIC REACTIONS IN A CLAY MICROENVIRONMENT
... reacted after 15 h at 220~ with Al-bentonite, with di-(but-1-yl) amine as almost the sole product of the elimination reaction. In contrast to the behaviour of secondary alcohols, the amine cyclohexylamine gave a good yield of di-cyclohexylamine (57%) by inter-molecular elimination of ammonia, but fa ...
... reacted after 15 h at 220~ with Al-bentonite, with di-(but-1-yl) amine as almost the sole product of the elimination reaction. In contrast to the behaviour of secondary alcohols, the amine cyclohexylamine gave a good yield of di-cyclohexylamine (57%) by inter-molecular elimination of ammonia, but fa ...
Chem 30CL-Lecture 15..
... • Pauson–Khand reaction • The Pauson–Khand reaction is a [2+2+1] cycloaddition reaction between an alkene, alkyne and carbon monoxide to form an α,β-cyclopentenone ...
... • Pauson–Khand reaction • The Pauson–Khand reaction is a [2+2+1] cycloaddition reaction between an alkene, alkyne and carbon monoxide to form an α,β-cyclopentenone ...
Chemistry 112A Second Midterm Review Sheet Summary of
... rearrangements occur Unimolecular. More substituted carbon centers react faster because carbocation intermediate is more stable, which stabilizes T.S. Reactive carbon center must be able to attain sp2 hybridization in transition state Weak bases are better leaving groups. Conjugate acids of good lea ...
... rearrangements occur Unimolecular. More substituted carbon centers react faster because carbocation intermediate is more stable, which stabilizes T.S. Reactive carbon center must be able to attain sp2 hybridization in transition state Weak bases are better leaving groups. Conjugate acids of good lea ...
Alkene-Addn-PartB-2012-ques
... Regiochemistry withstanding, in order to understand the stereochemistry of the product, you must consider two things: (1) Stereochemistry of the starting alkene (cis or trans; Z or E) (2) Stereochemistry of the addition (syn or anti) ...
... Regiochemistry withstanding, in order to understand the stereochemistry of the product, you must consider two things: (1) Stereochemistry of the starting alkene (cis or trans; Z or E) (2) Stereochemistry of the addition (syn or anti) ...
Carbohydrates
... atom reacts to form a bond to an atom that is more electronegative than carbon. Thus, carbon goes from having more electron density to having less electron density (oxidation). The reverse would be reduction. When the oxygen content of an organic compound increases and the hydrogen decreases the com ...
... atom reacts to form a bond to an atom that is more electronegative than carbon. Thus, carbon goes from having more electron density to having less electron density (oxidation). The reverse would be reduction. When the oxygen content of an organic compound increases and the hydrogen decreases the com ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... atom reacts to form a bond to an atom that is more electronegative than carbon. Thus, carbon goes from having more electron density to having less electron density (oxidation). The reverse would be reduction. When the oxygen content of an organic compound increases and the hydrogen decreases the com ...
... atom reacts to form a bond to an atom that is more electronegative than carbon. Thus, carbon goes from having more electron density to having less electron density (oxidation). The reverse would be reduction. When the oxygen content of an organic compound increases and the hydrogen decreases the com ...
Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring `00 What product is formed when
... e) addtion of a hydride ion and a proton more or less at the same time 18. Which of the following describes “reductive amination?” a) an aldehyde or a ketone + a tertiary amine + H2/zeolite b) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + ...
... e) addtion of a hydride ion and a proton more or less at the same time 18. Which of the following describes “reductive amination?” a) an aldehyde or a ketone + a tertiary amine + H2/zeolite b) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + ...
here
... Alkanes (paraffins or saturated HC): relatively stable to chemical reactions. Low molecular weight alkanes are gases or liquids, high MW are solids. Alkenes (olefins ): unsaturated HC because they don’t have the maximum number of atoms each carbon is able to accommodate; physical properties are clos ...
... Alkanes (paraffins or saturated HC): relatively stable to chemical reactions. Low molecular weight alkanes are gases or liquids, high MW are solids. Alkenes (olefins ): unsaturated HC because they don’t have the maximum number of atoms each carbon is able to accommodate; physical properties are clos ...
Organic Chemistry Notes
... -number the longest chain giving the position of the hydroxyl group the lowest possible number. -alcohols containing two, three and four hydroxyl branches are called diols, triols, and tetrols. (Don’t drop the ‘e’ on the parent name. Parent-addresses-prefix‘ol’) Eg. ...
... -number the longest chain giving the position of the hydroxyl group the lowest possible number. -alcohols containing two, three and four hydroxyl branches are called diols, triols, and tetrols. (Don’t drop the ‘e’ on the parent name. Parent-addresses-prefix‘ol’) Eg. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.