* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxidation and Reduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
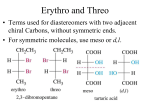
Oxidation and Reduction • • • • Recall oxidation-reduction reactions from Chem 30A. In Chem 30A this was presented with the basic Leo says Ger. In organic chemistry, oxidation of carbon is said to occur when a carbon bonded to a less electronegative atom reacts to form a bond to an atom that is more electronegative than carbon. Thus, carbon goes from having more electron density to having less electron density (oxidation). The reverse would be reduction. When the oxygen content of an organic compound increases and the hydrogen decreases the compound has been oxidized. The reverse is reduction. In the presence of an oxidizing agent primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids, respectively. In the presence of an oxidizing agent aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids. 1 Carbohydrates Monosaccharides: • Simple sugars (simplest carbohydrates); considered as monomers of polymers known as polysaccharides. • Contain 3-7 carbon atoms • Have one aldehyde or ketone functional group making them aldose or ketose, respectively • Fischer Projection is drawn with the aldehyde or ketone at the top (most oxidized C at the top) • If the alcohol on the lowest chiral carbon is to the right it is called D, to the left it is called L – This DOES NOT tell you which direction the compound rotates plane-polarized light. This just gives us a way to distinguish between carbohydrates that exist as enantiomers. Thus, it is best if you do not think of D as standing for dextrorotatory and L as standing for levorotatory. CHO H HO CHO CHO CH2OH OH HO H H H HO H HO H HO H H OH OH H OH H OH H OH HO H OH H OH H CH2OH D-(+)-Glucose CH2OH D-(+)-Mannose OH CH2OH D-(+)-Galactose O H CH2OH D-(-)-Fructose 2 Mutarotation Aldehydes and ketones react with alcohols to form hemiacetals and hemiketals, respectively. Five and six membered rings form. In solution, you would find the open chain and the two closed ring forms of a monosaccharide. 3 A Look Ahead at Ribose and Deoxyribose HO CHO OH O H OH H OH H H H OH H OH HO CH2OH Ribose: found in RNA HO CHO OH O H H H OH H H OH CH2OH H H HO H H H Deoxyribose: found in DNA 4