* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework Set #1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
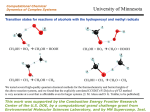
Homework Set #7 Chemistry 1315 Spring 2004 ______Answer key_____ Name Handed Out: Due: 3-26-04 4-1-04 at 9:30am in class Late Policy: One day late (4-2-04 10am): 50% off Two days late (4-3-04 10am): 75% off After 10am 4-3-04: no credit You may work in groups of up to 3 students. However, each student must make contributions to the answers. Total: Questions Points possible 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 20 10 10 10 10 20 10 Your Score 100 1 Question #1 (10 points) Draw beta-L-glucopyranose (cyclic beta-L-glucose) in its most stable chair conformation. Label the substituents as axial or equatorial. OH OH O Ring Flip HOH2C O OH HO CH2OH OH OH HO OH Most stable, all equatorial 2 Question #2 (20 points) At equilibrium in aqueous solution, D-fructose consists of 70% betapyranose, 2% alpha pyranose, 23% beta furanose, and 5% alpha furanose forms. Draw all four. HOH2C CH2OH O HOH2C HO O OH HO OH CH2OH OH OH alpha Furanose beta Furanose CH2OH O HO OH OH OH O CH2OH OH HO HO alpha Pyranose HO beta Pyranose 3 Question #3 (10 points) The two stereoisomers (alpha and beta) of maltose (a disaccharide) undergo mutarotation which means they interconvert into each other. Based on your understanding of carbonyl and alcohol chemistry, provide a mechanism that will account for this exchange. OH O HO OH HO HO O O HO O OH HO HO HO O HO HO O OH O HO OH HO HO OH O HO HO OH O O HO OH HO HO OH H-Transfer OH HO HO HO O HO O HO OH HO H-Transfer O OH HO HO O O HO OH HO 4 Question #4 (10 points) D-2-deoxyribose is found in DNA. Draw the structure. Deoxyribose and ribose form esters with phosphoric acid in DNA and RNA. Can both monosaccharides react to form the same number of ester combinations? Show the reactive sites for esterfication. CH2OH O OH OH 2-deoxy-D-ribose CH2OH O OH OH OH D-Ribose The reactive groups you need are alcohols or carboxylic acid derivatives. You don't have any of the second class but a number of alcohols. Ribose has one more, therefore, it can undergo one more ester. 5 Question #5 (10 points) Give the IUPAC name for the following carboxylic acids: A) H3C CO2H B) H 2C CH3 O HO C) H3C a) b) c) CO2H trans-2-butenoic acid 2-methyl-3-propenoic acid 4-methyl-benzoic acid 6 Question #6 (10 points) Predict the product from the reaction of phenylacetic acid with each of the following reagents: a) KOH, b) SOCl2, c) LiAlH4 then H2O, and d) CH3CH2OH, H+ a) the potassium salt b) makes the acid chloride c) the alcohol d) the ethyl ester 7 Question #7 (20 points) Outline a sequence of reaction(s) that will allow pentanal to be converted into a) pentanoic acid, b) hexanoic acid, and c) 2-hydroxy hexanoic acid. Several possible ways. Here is an example: OH 2-Hydroxy-hexanoic acid Hydrolysis H2O, HCl CO2H OH CN NaCN H+ O Jones Reagent CrO3 O Pentanoic acid OH LiAlH4 OH HX X Grignard, Mg MgX CO2 H3O+ CO2H Hexanoic Acid 8 Question #8 (10 points) Describe two methods for the preparation of 5-methyl hexanoic acid from 4-methyl-1-pentanol. You have to remove the OH and add CO2H. There are a number of ways to do this but the easiest are Grignard chemistry and nitrile hydrolysis. To make life easy, transfer the alcohol into an alkyl halide using some of the reactions we discussed in class or activate the alcohol and make it a good leaving group. Then do Grignard chemistry for one way to introduce CO2 or add CN and then hydrolyze the CN to the acid. 9