CH CH CH CH2 CH3 CH CH3 Br CH CH CH CH2 CH3 CH CH3 F
... Due to a conjugation, i.e. an interaction of lone electron pairs of a halogen atom with the -electrons of either alkenes or arenes, the carbon – halogen bond gets shorter/longer → higher/lower bond energy needed to break the bond → halogenoalkenes and halogenoarenes are more/less reactive than halo ...
... Due to a conjugation, i.e. an interaction of lone electron pairs of a halogen atom with the -electrons of either alkenes or arenes, the carbon – halogen bond gets shorter/longer → higher/lower bond energy needed to break the bond → halogenoalkenes and halogenoarenes are more/less reactive than halo ...
Organic Compounds
... The alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain one triple bond between two of its carbons. The formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2. The names are derived by taking the prefix for the number of carbons it contains and adding the suffix – yne. Ex: 4 carbon alkyne = But-yne or butyne. ...
... The alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain one triple bond between two of its carbons. The formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2. The names are derived by taking the prefix for the number of carbons it contains and adding the suffix – yne. Ex: 4 carbon alkyne = But-yne or butyne. ...
File
... Quaternary Carbon, 4°, = carbon attached to 4 other carbons, Very unreactive Hydrogens are classified based on carbon they are attached to – The hydrogens on a 1° carbon are called 1° hydrogens ...
... Quaternary Carbon, 4°, = carbon attached to 4 other carbons, Very unreactive Hydrogens are classified based on carbon they are attached to – The hydrogens on a 1° carbon are called 1° hydrogens ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Amino Acid + Amino Acid Protein + H2O that one way molecules can join, a reaction where H2O is formed, is called a “condensation reaction.” that a polymer (“poly” means many, “mer” means parts) consists of many repeating parts. a second way molecules can join, in which a double bond opens to form ...
... Amino Acid + Amino Acid Protein + H2O that one way molecules can join, a reaction where H2O is formed, is called a “condensation reaction.” that a polymer (“poly” means many, “mer” means parts) consists of many repeating parts. a second way molecules can join, in which a double bond opens to form ...
Regiochemistry of Eliminations
... third makes a secondary carbocation, so it’s intermediate. 3) If you took the product mixture from this reaction and ran it through a gas chromatograph, what would you expect to see in terms of relative peak areas and retention times? Answer: The boiling points of the products are 103°C for 3-methyl ...
... third makes a secondary carbocation, so it’s intermediate. 3) If you took the product mixture from this reaction and ran it through a gas chromatograph, what would you expect to see in terms of relative peak areas and retention times? Answer: The boiling points of the products are 103°C for 3-methyl ...
Honors Chemistry Organic Chemistry
... b. carcinogen in burned meat and cigarettes c. organic bases d. hydrogenation e. hydroxyl f. carboxyl g. carbonyl h. containing benzene or benzene-like structures i. from wood distillation / metabolized into formaldehyde j. benzene as a substituent k. reaction in the formation of esters l. phenol ...
... b. carcinogen in burned meat and cigarettes c. organic bases d. hydrogenation e. hydroxyl f. carboxyl g. carbonyl h. containing benzene or benzene-like structures i. from wood distillation / metabolized into formaldehyde j. benzene as a substituent k. reaction in the formation of esters l. phenol ...
5 Alkenes and Alkynes GOB Structures
... • is an important plant hormone involved in promoting the ripening of fruits such as bananas. • accelerates the breakdown of cellulose in plants, which causes flowers to wilt and leaves to fall from trees. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... • is an important plant hormone involved in promoting the ripening of fruits such as bananas. • accelerates the breakdown of cellulose in plants, which causes flowers to wilt and leaves to fall from trees. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Electrophilic addition Typical for alkenes and alkynes Markovnikov´s rule: the more positive part of the agent is attached to the carbon atom (of the double bond) with the greatest number of hydrogens: ...
... Electrophilic addition Typical for alkenes and alkynes Markovnikov´s rule: the more positive part of the agent is attached to the carbon atom (of the double bond) with the greatest number of hydrogens: ...
Organic Chemistry
... between carbon atoms • Called “unsaturated hydrocarbon” because it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • All alkynes end in - yne • Prefixes are the same as alkanes and alkenes ...
... between carbon atoms • Called “unsaturated hydrocarbon” because it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • All alkynes end in - yne • Prefixes are the same as alkanes and alkenes ...
CH 21 Organic Compounds I. Simple Organic Compounds A. All
... 3. Halogenated Hydrocarbons- a member of halogen family replaces hydrogen Ex) CH3Br- methyl bromide- a pesticide C. Petroleum Products- separated by distillation 1. distillation- separated liquids by boiling point- collection and recondensation of vapors 2. Less carbon in molecules = lower molecular ...
... 3. Halogenated Hydrocarbons- a member of halogen family replaces hydrogen Ex) CH3Br- methyl bromide- a pesticide C. Petroleum Products- separated by distillation 1. distillation- separated liquids by boiling point- collection and recondensation of vapors 2. Less carbon in molecules = lower molecular ...
Alkynes
... Note that we still have an acidic hydrogen and, thus, can react with another alkyl group in this way to make RCCR’ Alkyl halides can be obtained from alcohols ...
... Note that we still have an acidic hydrogen and, thus, can react with another alkyl group in this way to make RCCR’ Alkyl halides can be obtained from alcohols ...
TYPES OF ORGANIC CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... A substitution reaction occurs whenever one atom of an organic molecule is replaced by another. Substitution reactions often require heat and/or a catalyst in order to occur. Example: Substitution of an alkane H H H C H + Cl2 H C Cl + HCl H H HEAT ...
... A substitution reaction occurs whenever one atom of an organic molecule is replaced by another. Substitution reactions often require heat and/or a catalyst in order to occur. Example: Substitution of an alkane H H H C H + Cl2 H C Cl + HCl H H HEAT ...
Seminar_1 1. Classification and nomenclature of organic
... Virtually all organic reactions fall into one of four categories: They are either substitutions, additions (cycloaddition), eliminations, or rearrangements, Ox/Red. (S) Substitutions are the characteristic reactions of saturated compounds such as alkanes and alkyl halides, and of aromatic compounds ...
... Virtually all organic reactions fall into one of four categories: They are either substitutions, additions (cycloaddition), eliminations, or rearrangements, Ox/Red. (S) Substitutions are the characteristic reactions of saturated compounds such as alkanes and alkyl halides, and of aromatic compounds ...
Oxidative Addition
... characteristic shift of the ν(CO) stretching frequency to lower energy in the IR spectrum of the complex as a result of the greater mass of 13C over normal carbon. ...
... characteristic shift of the ν(CO) stretching frequency to lower energy in the IR spectrum of the complex as a result of the greater mass of 13C over normal carbon. ...
Worksheet Key - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... para-dibromobenzene 4. Name the following alkenes: a. 5-bromo-3-ethyl-2-hexene ...
... para-dibromobenzene 4. Name the following alkenes: a. 5-bromo-3-ethyl-2-hexene ...
File
... • The longest continuous chain must contain the double bond. • The base name now ends in –ene. • The carbons are numbered so as to keep the number for the double bond as low as possible. • The base name is given a number which identifies the location of the double bond. This takes priority to functi ...
... • The longest continuous chain must contain the double bond. • The base name now ends in –ene. • The carbons are numbered so as to keep the number for the double bond as low as possible. • The base name is given a number which identifies the location of the double bond. This takes priority to functi ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014
... carbon dioxide are formed. It is acid-base because the propanoic acid donates a proton, forming the propanoate ion. When propanamine reacts with HCl or H2SO4, acid-base reactions occur. Amines are bases and as a result amines accept protons from acids. In these two reactions both sulfuric acid and h ...
... carbon dioxide are formed. It is acid-base because the propanoic acid donates a proton, forming the propanoate ion. When propanamine reacts with HCl or H2SO4, acid-base reactions occur. Amines are bases and as a result amines accept protons from acids. In these two reactions both sulfuric acid and h ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Carbon Chemistry)
... The PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are generally determined by three factors: a) The carbon skeleton is a very stable, chemically unreactive structure. b) The presence of double or triple bonds increases the reactivity of carbon skeletons. c) “Functional groups" which are other atoms or groups of a ...
... The PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are generally determined by three factors: a) The carbon skeleton is a very stable, chemically unreactive structure. b) The presence of double or triple bonds increases the reactivity of carbon skeletons. c) “Functional groups" which are other atoms or groups of a ...
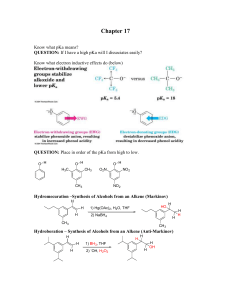
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
Hydrocarbons - New York Science Teacher
... possible isomers increases considerably. • For example, Octane (C8H18), there are 18 possible isomers including a continuous chain of 8 carbons. ...
... possible isomers increases considerably. • For example, Octane (C8H18), there are 18 possible isomers including a continuous chain of 8 carbons. ...
Functional Groups and Preparations
... electronegativity difference between hydrogen and carbon It was traditionally used as a solvent but was found to be carcinogenic so methyl benzene (toluene is now used instead) Would you predict it would be soluble in water or ...
... electronegativity difference between hydrogen and carbon It was traditionally used as a solvent but was found to be carcinogenic so methyl benzene (toluene is now used instead) Would you predict it would be soluble in water or ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.