* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
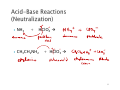
1 2 ` ` Precipitation – a solid forms when mixing solutions. Acid-Base – An acid or base are neutralized. ◦ Acid – Donates H+ ◦ Base – Accepts H+ ◦ Transfer of hydronium ion (H+ ) from the acid to the base 3 ` ` ` ` ` ` HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 Æ H+ Ca+2 NO3OHCH3COOH + Al(OH)3 Æ CH3COOAl+3 H+ OH- 4 ` NH3 + HClO4 Æ ` CH3CH2NH2 + HClO3 Æ 5 ` What makes a substance behave as an acid? ` When it reacts with water it donates the H+ to water: ` ` ` ` HNO3 + H2O Æ acid base Strong acids are 100% ionized. CH3COOH + H2O Æ Weak acids are only slightly ionized because the products combine to form reactants. Equilibrium 6 Hydrochloric Acid HCl Hydrobromic Acid HBr Hydroiodic Acid HI Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Nitric Acid HNO3 Perchloric Acid HClO4 Chloric Acid HClO3 7 ` pH is used to indicate the strength of an acid or base. pH is related to the amount of H+ or H3O+ available. pH scale: ` 0 ` ` ` acid 7 basic 14 8 ` ` One of the largest group of reactions known. Recognized by the transfer of electrons from an electron donor – oxidation to an electron acceptor – reduction. 9 ` ` Oxidation involves the loss of electrons. Substance that gives electrons away Reduction involves the gain of electrons. Substance that accepts electrons. 10 Oxidation Reduction Reactions ` Write the reaction for the formation of sodium chloride from its elements: ` What is the charge of sodium in the reactant side? ` What is the charge of chlorine in the reactant side? ` Who is getting reduced? - 1e- per Na 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) + 1e- per Cl •Oxidizing agent gets reduced and helps the other substance get oxidized. •Reducing agent gets oxidized and helps the other substance get reduced. 12 ` ` ` Formation of ionic compounds from their elements. Decomposition of ionic compounds into their elements. Charge of elements in their standard state is zero. ` ` Metal Displacement – A metal displaces a metal cation from its place by giving its electrons. Hydrogen Displacement – A metal displaces hydrogen from an acid solution by giving its electrons. Cu (s) + AgNO3 Æ Metal Displacement Reaction 15 Anytime that a substance is burned in the presence of oxygen (reacts with O2). CH4(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) Who gets oxidized? Who gets reduced? 16 ` An atom is oxidized if it ◦ gains oxygen (is attached to more oxygen atoms in the product than in the reactant) OR ◦ loses hydrogen (is attached to fewer hydrogen atoms in the product than in the reactant) ` An atom is reduced if it ◦ loses oxygen (is attached to fewer oxygen atoms) OR ◦ gains hydrogen (is attached to more hydrogen atoms) Important for organic compounds. 17 ` ` Acid-Base Redox ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Combustion Acid Displacement Metal Displacement Formation, Decomposition 18 ` ` ` Addition of hydrogen gas (H2) in the presence of platinum (Pt), catalyst, to unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes Alkynes 19 Is oxidation or reduction occurring? Important in Biological Reactions 20 Draw and name the product formed when the alkenes react with H2 and Pt. a. 3-chloro-1-butene b. 1,3-dimethylcyclopentene How many molecules of H2 are needed for 1-butyne? 22 Water is a reactant or product in a number of reactions important to organic and biochemistry. In this section we will take a look at three of them – 1. hydration 2. dehydration 3. hydrolysis 23 Hydration Water is added to a double bond but needs acid (H+) as catalyst. What functional group forms? Alkene Æ alcohol 24 ` ` Dehydration is the reverse of hydration. Water is removed to form a double bond. Hydrogen in the adjacent carbon has to be available. Alcohol Æ Alkene 25 ` ` ` Water (hydro) is used to split (lyse) a molecule. Esters are one class of molecules that undergo hydrolysis – when treated with water in the presence of hydroxide ion (OH-) they split to form a carboxylate ion and an alcohol. Reaction used to make soap. 26 27 ` Hydrolysis is one of the factors that determine the length of time that some drugs remain active. ` ` Ester Æ carboxylate + alcohol 28 Alkenes can be hydrated. ` Alcohols ` Esters can be dehydrated. can be hydrolyzed. 29 1 C C C 2 3 4 C C C OH C 5 C 6 C 7 H+ heat H2O H+ H2O OH- 30 Draw the missing reactant for each reaction. 31