1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... the changes it undergoes. 4. What branch of chemistry is most concerned with the study of carbon compounds? Organic Chemistry 5. What does the word chemical, as used by scientists ,mean? 6. Briefly describe the difference between basic research, applied research, and technological development. Provi ...
... the changes it undergoes. 4. What branch of chemistry is most concerned with the study of carbon compounds? Organic Chemistry 5. What does the word chemical, as used by scientists ,mean? 6. Briefly describe the difference between basic research, applied research, and technological development. Provi ...
- Aboriginal Access to Engineering
... process and reduces fever, swelling and pain. Willow bark tea does exactly the same thing because boiling the bark in water releases salicin. The healing properties of willow bark have been known to the Chinese and Aboriginal peoples for thousands of years; they were only recognized by western scien ...
... process and reduces fever, swelling and pain. Willow bark tea does exactly the same thing because boiling the bark in water releases salicin. The healing properties of willow bark have been known to the Chinese and Aboriginal peoples for thousands of years; they were only recognized by western scien ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... Greeks: Empedocles and Democritus • Suggested the concept of atoms but were not taken seriously or credited with an atomic theory ...
... Greeks: Empedocles and Democritus • Suggested the concept of atoms but were not taken seriously or credited with an atomic theory ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Compound: Composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio. ...
... Compound: Composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio. ...
Ch 02.01-03: Atoms Molecules Ions
... 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element canno ...
... 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element canno ...
CHEMISTRY
... • Coefficients before a formula tell the number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
... • Coefficients before a formula tell the number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
Study Guide Answers
... electron, many are salt forming elements, soft, Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, slightly reactive metals, two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, f ...
... electron, many are salt forming elements, soft, Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, slightly reactive metals, two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, f ...
CHAPTER 1, MATTER AND CHANGE Section 1, Chemistry Is a
... stable substances and is made of one type of atom. (Example: hydrogen) ! A compound is a substance that can be broken down into simple stable substances. Each compound is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. (Example: hydrogen peroxide, H2O2) Properties and changes ...
... stable substances and is made of one type of atom. (Example: hydrogen) ! A compound is a substance that can be broken down into simple stable substances. Each compound is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. (Example: hydrogen peroxide, H2O2) Properties and changes ...
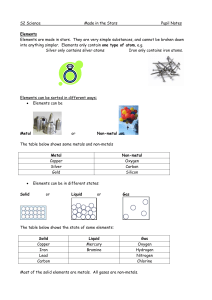
Made in the Stars Notes
... This is a way of organising the elements. Each element has its own chemical symbol, e.g. copper is Cu and Iron is Fe. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called Periods. The vertical columns are called Groups: Group 1 Alkali metals Group 2 Alkali earth metals Group 7 ...
... This is a way of organising the elements. Each element has its own chemical symbol, e.g. copper is Cu and Iron is Fe. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called Periods. The vertical columns are called Groups: Group 1 Alkali metals Group 2 Alkali earth metals Group 7 ...
Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
... Stoichiometry 1 amu = 1.6606 x 10-24 g The amu mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 12 amu 1 mole = count multiplier = 6.022 x 1023 items subscript to the right of an element symbol = atom count multiplier = the number of atoms of the element in a chemical formula number before chemical formula in a chem ...
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... Ex. Sugar is white, sweet and granular. 2. Chemical Property- How a substance reacts to the world round it. Ex. Sugar will turn to a black solid when mixed with Sulfuric Acid. ...
... Ex. Sugar is white, sweet and granular. 2. Chemical Property- How a substance reacts to the world round it. Ex. Sugar will turn to a black solid when mixed with Sulfuric Acid. ...
Chemistry Semester Test Study Guide Chapters
... Be able to use the rules for sig figs for division and subtraction as well. ...
... Be able to use the rules for sig figs for division and subtraction as well. ...
Matter
... with a lot of solute is a concentrated solution. A solution with very little solute is a dilute solution. A solution that has as much solute as it can hold is called a saturated solution. Solutes can be solids, liquids, or gases. A suspension is a kind of mixture that separates if it is left alone f ...
... with a lot of solute is a concentrated solution. A solution with very little solute is a dilute solution. A solution that has as much solute as it can hold is called a saturated solution. Solutes can be solids, liquids, or gases. A suspension is a kind of mixture that separates if it is left alone f ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. • In chemical rea ...
... • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. • In chemical rea ...
Chemistry
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
Topic 3&4 Atoms and the per.table
... Standard Grade Revision Units 3 and 4 Q1. The box below shows the names of some elements. ...
... Standard Grade Revision Units 3 and 4 Q1. The box below shows the names of some elements. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.