Elements Compounds Mixtures
... • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
... • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
FIREWORKS EMC summary notes
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
第一章 绪论
... of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR). Pharmaceutical chemistry is focused on quality aspects of medicines and aims to assure fitness for the purpose of medicinal products. Medicinal chemistry is a highly interdisciplinary scie ...
... of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR). Pharmaceutical chemistry is focused on quality aspects of medicines and aims to assure fitness for the purpose of medicinal products. Medicinal chemistry is a highly interdisciplinary scie ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
... theories to explain his observations and came up with Dalton’s atomic theory. ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... Chapter 9 The Periodic Law I) Basic concepts and Equations 1) Elements: Are the simplest substances from which matter is made up, they can not be decomposed into new elements by chemical means. 2) Compounds: Substances made up of elements which are combined in very well defined proportions, compound ...
... Chapter 9 The Periodic Law I) Basic concepts and Equations 1) Elements: Are the simplest substances from which matter is made up, they can not be decomposed into new elements by chemical means. 2) Compounds: Substances made up of elements which are combined in very well defined proportions, compound ...
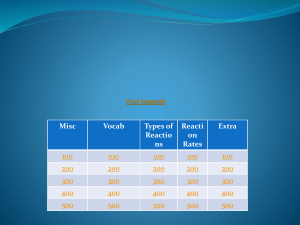
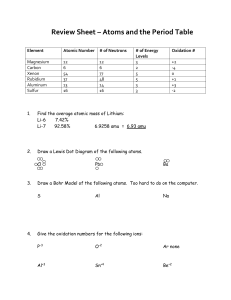
Review Sheet Filled Out
... Can’t tell where an electron is at any moment in time – the uncertainty principle There’s more – the list could be long! ...
... Can’t tell where an electron is at any moment in time – the uncertainty principle There’s more – the list could be long! ...
Foundations of Atomic Theory
... 2. Atoms of a given element are the same in size, mass, and other properties: atoms of Dalton’s Atomic Theory different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to f ...
... 2. Atoms of a given element are the same in size, mass, and other properties: atoms of Dalton’s Atomic Theory different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to f ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds ...
... More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... 20. Said the universe was made of atomos, or small, indivisible particles. Thought these particles were earth, air, fire, and water. __________________ III. Match the laws with their definition. A. Law of Conservation of Mass B. Law of Definite Proportion C. Law of Multiple Proportions _____21. Natu ...
... 20. Said the universe was made of atomos, or small, indivisible particles. Thought these particles were earth, air, fire, and water. __________________ III. Match the laws with their definition. A. Law of Conservation of Mass B. Law of Definite Proportion C. Law of Multiple Proportions _____21. Natu ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 1. some water molecules break apart naturally in water 2. ions formed are called hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH-) ions 3. for life chemistry, proper balance of these ions is necessary 4. the more acidic a solution, the more H+ ions. Acids are substances that donate H+ 5. in your stomach, HCl donate ...
... 1. some water molecules break apart naturally in water 2. ions formed are called hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH-) ions 3. for life chemistry, proper balance of these ions is necessary 4. the more acidic a solution, the more H+ ions. Acids are substances that donate H+ 5. in your stomach, HCl donate ...
Science 9
... in a 100-g beaker, a student added 25 g of lead (II) nitrate to 15 g of sodium iodide. In her notebook, the student recorded the final mass of the products, it was 140 g. Did this reaction conserve mass? Explain your answer. ...
... in a 100-g beaker, a student added 25 g of lead (II) nitrate to 15 g of sodium iodide. In her notebook, the student recorded the final mass of the products, it was 140 g. Did this reaction conserve mass? Explain your answer. ...
Science 9 Unit 2
... Substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants and the products During a chemical reaction the reactants are used up During a chemical reaction the products are created or produced Law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical change the total mass of the new substance is the ...
... Substances that go into a chemical reaction are the reactants and the products During a chemical reaction the reactants are used up During a chemical reaction the products are created or produced Law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical change the total mass of the new substance is the ...
File
... Chemical symbols are used in writing chemical formulas, in which the symbols represent the atoms of the elements present in a compound. ...
... Chemical symbols are used in writing chemical formulas, in which the symbols represent the atoms of the elements present in a compound. ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... properties are used to observe and describe matter. Reactant - a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction Reactivity – the rate at which a chemical substance tends to undergo a chemical reaction Subscript - appear at or below the baseline to show how many of that element e ...
... properties are used to observe and describe matter. Reactant - a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction Reactivity – the rate at which a chemical substance tends to undergo a chemical reaction Subscript - appear at or below the baseline to show how many of that element e ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... properties are used to observe and describe matter. Reactant - a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction Reactivity – the rate at which a chemical substance tends to undergo a chemical reaction Subscript - appear at or below the baseline to show how many of that element e ...
... properties are used to observe and describe matter. Reactant - a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction Reactivity – the rate at which a chemical substance tends to undergo a chemical reaction Subscript - appear at or below the baseline to show how many of that element e ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the
... Elements: simplest forms of matter that cannot be separated by chemical means Compound: substances that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical means Chemical Reaction: when one or more substances change into new substances Reactants: the starting substances (the ones that REACT) Produc ...
... Elements: simplest forms of matter that cannot be separated by chemical means Compound: substances that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical means Chemical Reaction: when one or more substances change into new substances Reactants: the starting substances (the ones that REACT) Produc ...
CHEMISTRY
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
... The nature of most atoms is that they are LONELY and sometimes AGGRESSIVE! Most atoms team up with or overtake other atoms in an attempt to get the “right” number of electrons. This is how molecules are formed. Only the NOBLE GASSES can exist on their own. ATOMS will switch partners when provoked. T ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.