Name
... Ⓡ 8.5 (D) Chemical Formulas: Students will be able to recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element. Ⓡ 8.5 (E) Chemical Reactions: Students will be able to investigate how evidences of chemical reactions indicate that new substance ...
... Ⓡ 8.5 (D) Chemical Formulas: Students will be able to recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element. Ⓡ 8.5 (E) Chemical Reactions: Students will be able to investigate how evidences of chemical reactions indicate that new substance ...
Pure Substances and Mixtures
... – Molecules are small groups of atoms that make up matter. Example: Water is a molecule of two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom • Atoms are the smallest particles of elements ...
... – Molecules are small groups of atoms that make up matter. Example: Water is a molecule of two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom • Atoms are the smallest particles of elements ...
Terminology 1
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
... (The chemical identity of an atom can be determined solely by it’s atomic number) When the atom is neutral, i.e. not electrically charged, the atomic number equals the number of electrons in its shells ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... * Gases do not have a definite volume or definite shape, but they take the volume & shape of their container * Chemical Changes in matter are essential to all life processes * Biologists study chemistry because all living things are made of the same kinds of matter that make up nonliving things ...
... * Gases do not have a definite volume or definite shape, but they take the volume & shape of their container * Chemical Changes in matter are essential to all life processes * Biologists study chemistry because all living things are made of the same kinds of matter that make up nonliving things ...
Elements, Compounds and Chemical Reactions
... then silicon, and our bodies are oxygen and then carbon. ...
... then silicon, and our bodies are oxygen and then carbon. ...
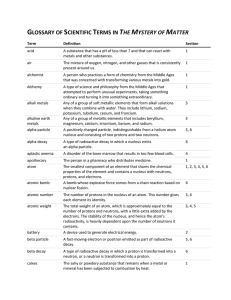
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... A type of science and philosophy from the Middle Ages that attempted to perform unusual experiments, taking something ordinary and turning it into something extraordinary. Any of a group of soft metallic elements that form alkali solutions when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, ...
... A type of science and philosophy from the Middle Ages that attempted to perform unusual experiments, taking something ordinary and turning it into something extraordinary. Any of a group of soft metallic elements that form alkali solutions when they combine with water. They include lithium, sodium, ...
Test 1 - UTC.edu
... 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's mass is equal to that of a proton plus an electron. D) An ...
... 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's mass is equal to that of a proton plus an electron. D) An ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... CHEMISTRY CP1 – 1st SEMESTER MIDYEAR EXAM REVIEW STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, q ...
... CHEMISTRY CP1 – 1st SEMESTER MIDYEAR EXAM REVIEW STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, q ...
Document
... 21. The __________ _____________ tells you how many electrons an atom must gain, lose, or share to become stable. 22. Numbers that precede symbols and formulas in a chemical equation are ______________. 23. A chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form another substance is call ...
... 21. The __________ _____________ tells you how many electrons an atom must gain, lose, or share to become stable. 22. Numbers that precede symbols and formulas in a chemical equation are ______________. 23. A chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form another substance is call ...
What is matter made of?
... substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
... substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
10th Grade Chemistry X (TJ) GRADE(S)/LEVELS SUBJECT Power
... charge. Molecular compounds are composed of two or more elements bonded together in a fixed proportion by sharing electrons between atoms, forming covalent bonds. LT 1 Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed. LT2 ...
... charge. Molecular compounds are composed of two or more elements bonded together in a fixed proportion by sharing electrons between atoms, forming covalent bonds. LT 1 Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed. LT2 ...
Final Exam review semester 1
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ...
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ...
4.5b.notes
... Eg. Plants convert carbon dioxide gas and water into glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen ...
... Eg. Plants convert carbon dioxide gas and water into glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... Unit 2C Standards Quiz on Monday, November 24. It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structur ...
... Unit 2C Standards Quiz on Monday, November 24. It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structur ...
can be determined without changing the identity of matter
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
Chemistry 101 Chapter 4 Elements, Atoms, and Ions = =
... elements in columns 1A to 8A. 2- transition elements: the element in columns 1B to 8B (or 3 to 12). 3- inner transition elements: we put them outside the main body to make a more compact presentation. However, they actually should be between columns 3B and 4B. There are three classes of elements: 1- ...
... elements in columns 1A to 8A. 2- transition elements: the element in columns 1B to 8B (or 3 to 12). 3- inner transition elements: we put them outside the main body to make a more compact presentation. However, they actually should be between columns 3B and 4B. There are three classes of elements: 1- ...
Lecture notes chapter 4
... elements in columns 1A to 8A. 2- transition elements: the element in columns 1B to 8B (or 3 to 12). 3- inner transition elements: we put them outside the main body to make a more compact presentation. However, they actually should be between columns 3B and 4B. There are three classes of elements: 1- ...
... elements in columns 1A to 8A. 2- transition elements: the element in columns 1B to 8B (or 3 to 12). 3- inner transition elements: we put them outside the main body to make a more compact presentation. However, they actually should be between columns 3B and 4B. There are three classes of elements: 1- ...
Are You suprised ?
... 1. Discuss Rutherford’s experiment. What was he testing for? What was his hypothesis? What did he discover? How did this change the theory of the atom? 2. Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the following elements: a. C-12 ...
... 1. Discuss Rutherford’s experiment. What was he testing for? What was his hypothesis? What did he discover? How did this change the theory of the atom? 2. Give the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the following elements: a. C-12 ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Periodic Chemical Properties • Understood in terms of ...
... Periodic Chemical Properties • Understood in terms of ...
Atomic Theories- Part I - Tenafly Public Schools
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.