Name: Date: Period: Who is the Father of Atomic Theory? What
... 7. Radon-226 has a half life of 1600 years. If we start with 2000 g of radon, how much is left after 4800 years? 8. What type of radioactive reaction occurs when a large nucleus breaks into fragments and gives off radiation? 9. What type of radioactive reaction occurs when two light nuclei collide ...
... 7. Radon-226 has a half life of 1600 years. If we start with 2000 g of radon, how much is left after 4800 years? 8. What type of radioactive reaction occurs when a large nucleus breaks into fragments and gives off radiation? 9. What type of radioactive reaction occurs when two light nuclei collide ...
Page 1 of 4 FOSS California Mixtures and Solutions
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
... Carbohydrate: A group of carbon-based nutrients, such as sugars and starches. Carbon-14 dating: A process used to find the age of carbon-based matter. Carbon dioxide gas: A compound made from carbon and oxygen (CO2) Chemical equation: A model of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products. Ch ...
Chapter 2 Introduction to Chemistry
... A substance is a particular kind of matter that has a uniform and definite composition. Pure substances contain only one kind of matter ...
... A substance is a particular kind of matter that has a uniform and definite composition. Pure substances contain only one kind of matter ...
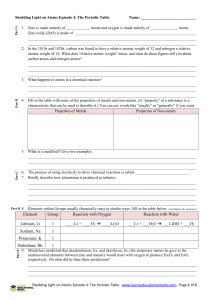
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
Midterm Review.ppt - Chemistry R: 4(AE)
... • Compared to the charge and mass of a proton, an electron has: 1. the same charge and a smaller mass 2. the same charge and the same mass 3. an opposite charge and a smaller mass 4. an opposite charge and the same mass ...
... • Compared to the charge and mass of a proton, an electron has: 1. the same charge and a smaller mass 2. the same charge and the same mass 3. an opposite charge and a smaller mass 4. an opposite charge and the same mass ...
Packet
... 102. What is the minimum amount of uranium called? 103. What is the spontaneous emission of nuclear radiation? 104. Where are protons located? 105. What is the charge of a beta particle? 106. What is a positively charged electron? 107. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its r ...
... 102. What is the minimum amount of uranium called? 103. What is the spontaneous emission of nuclear radiation? 104. Where are protons located? 105. What is the charge of a beta particle? 106. What is a positively charged electron? 107. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its r ...
Matter, Mass and Weight
... Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Like all pure substances, it has its own set of physical and chemical properties. At room temperature, 75 elements are solids, 11 are gases, 2 (mercury and bromine) are liquids. Each element is r ...
... Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Like all pure substances, it has its own set of physical and chemical properties. At room temperature, 75 elements are solids, 11 are gases, 2 (mercury and bromine) are liquids. Each element is r ...
are physical changes - Chemistry Information Site
... - also called "chemical reactions" Examples: ...
... - also called "chemical reactions" Examples: ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
- Lexington JHS
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
Review Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
Classification – 3 main groups
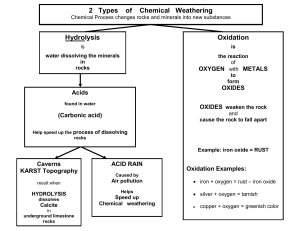
... Chemical Change- The substance has changed in color, or it fizzed, bubbled, created an odor, got warmer or colder ( temp. change caused by the chemical reaction ). The original substance is no longer there; frying an egg, any type of cooking, alka seltzer and water Physical Change- A noticeable chan ...
... Chemical Change- The substance has changed in color, or it fizzed, bubbled, created an odor, got warmer or colder ( temp. change caused by the chemical reaction ). The original substance is no longer there; frying an egg, any type of cooking, alka seltzer and water Physical Change- A noticeable chan ...
Solid - burgess
... remain distinct. Examples are colloids and suspensions such as muddy water ii. homogeneous-has a uniform composition throughout. Example is a solution which is made up of a solvent and a solute such as koolaid or salt water E. Ions 1. Ions are atoms which have gained or lost electrons. 2. examples i ...
... remain distinct. Examples are colloids and suspensions such as muddy water ii. homogeneous-has a uniform composition throughout. Example is a solution which is made up of a solvent and a solute such as koolaid or salt water E. Ions 1. Ions are atoms which have gained or lost electrons. 2. examples i ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... mercury oxide + heat " mercury + O2 Discovery of oxygen critical to: 1.clear distinction between various pure gases and air 2.understanding most fundamental process: FIRE !! ...
... mercury oxide + heat " mercury + O2 Discovery of oxygen critical to: 1.clear distinction between various pure gases and air 2.understanding most fundamental process: FIRE !! ...
Notes on Atomic Structure atoms
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Answers to odd numbered problems in textbook are found in the book’s index. ...
... Answers to odd numbered problems in textbook are found in the book’s index. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.