Classifying Chemical Reactions 9-3
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that it undergoes. We have learned about how chemical compounds are formed We have also learned the language of chemistry, chemical formulas Certain chemicals interact with the human body in a negative way and are known as toxins Now we will equations ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that it undergoes. We have learned about how chemical compounds are formed We have also learned the language of chemistry, chemical formulas Certain chemicals interact with the human body in a negative way and are known as toxins Now we will equations ...
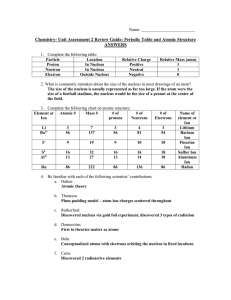
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... 17.) How are chemical reactions different than nuclear reactions? How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to each type of reaction? Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true ...
... 17.) How are chemical reactions different than nuclear reactions? How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to each type of reaction? Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... PART I: You should know the basics (terms & basic facts) about… Hypothesis theory law scientific method mass weight volume physical change chemical change mixture element compound molecule heterogeneous homogeneous states of matter ...
... PART I: You should know the basics (terms & basic facts) about… Hypothesis theory law scientific method mass weight volume physical change chemical change mixture element compound molecule heterogeneous homogeneous states of matter ...
CHAPTER 2: MATTER
... – lowest energy , atoms/molecules vibrate, but have a fixed position – definite volume and definite shape Liquid – moderate energy – atoms/molecules roll and tumble about each other, flow definite volume and variable shape Gas – high energy, atoms/molecules are moving rapidly and colliding with ...
... – lowest energy , atoms/molecules vibrate, but have a fixed position – definite volume and definite shape Liquid – moderate energy – atoms/molecules roll and tumble about each other, flow definite volume and variable shape Gas – high energy, atoms/molecules are moving rapidly and colliding with ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
... elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - Polyatomic ions have a charge and consist of two or more atoms bonded together. See Table 2.6. - They are primarily anions, but there are two polyatomic cations: Ammonium is NH4+1 and mercury (I) is Hg22+ - Oxoanions contain oxygen along with another element. Oxygen (almost) always has –2 charge. ...
... - Polyatomic ions have a charge and consist of two or more atoms bonded together. See Table 2.6. - They are primarily anions, but there are two polyatomic cations: Ammonium is NH4+1 and mercury (I) is Hg22+ - Oxoanions contain oxygen along with another element. Oxygen (almost) always has –2 charge. ...
AP Chemistry Jeopardy
... The Law of Dulong and Petit says that the molar specific heat of solid elements is approximately 25 J/mol•K. This suggests that. . . ...
... The Law of Dulong and Petit says that the molar specific heat of solid elements is approximately 25 J/mol•K. This suggests that. . . ...
Test #1 Study Guide
... Scientific Theory – A model for nature that explains not only what it does, but why. Formed by one or more well established hypotheses. Experiments – Highly controlled procedures designed to generate observations. ...
... Scientific Theory – A model for nature that explains not only what it does, but why. Formed by one or more well established hypotheses. Experiments – Highly controlled procedures designed to generate observations. ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... 1. Read over notes in this package. 2. Redo these worksheets as well as extra practice sheets that have been provided. 3. Go through your grade 9 and 10 notes (should you still have them). 4. Topics to be covered include: Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diag ...
... 1. Read over notes in this package. 2. Redo these worksheets as well as extra practice sheets that have been provided. 3. Go through your grade 9 and 10 notes (should you still have them). 4. Topics to be covered include: Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diag ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-metal State that elements are listed in the periodic table in order of ...
... Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-metal State that elements are listed in the periodic table in order of ...
Atomic
... • Mass #- The total number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus of an atom – the mass # that appears on the periodic table is an average of all masses of all isotopes of a given element ...
... • Mass #- The total number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus of an atom – the mass # that appears on the periodic table is an average of all masses of all isotopes of a given element ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... EXAMPLES: O2(g), H2(g) à there are others but know these Name the following examples of MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS (see your notes or textbook to help you): • CO2(g) à carbon dioxide • NH3(g) à nitrogen ...
... EXAMPLES: O2(g), H2(g) à there are others but know these Name the following examples of MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS (see your notes or textbook to help you): • CO2(g) à carbon dioxide • NH3(g) à nitrogen ...
Name ______ Period ______ 7th Grade Science Study Guide 1 7
... 7-1.3 Controlled Scientific Investigation 6. Why is it important to test only 1 variable at a time in an experiment? 7. Circle the correct word in bold: a. Quantitative measurements use numbers/senses b. Qualitative measurements use numbers/senses. 8. Identify the following as QN for Quantitative an ...
... 7-1.3 Controlled Scientific Investigation 6. Why is it important to test only 1 variable at a time in an experiment? 7. Circle the correct word in bold: a. Quantitative measurements use numbers/senses b. Qualitative measurements use numbers/senses. 8. Identify the following as QN for Quantitative an ...
Slide 1
... 1. Compared to the charge and mass of a proton, an electron has: 1. the same charge and a smaller mass 2. the same charge and the same mass 3. an opposite charge and a smaller mass 4. an opposite charge and the same mass ...
... 1. Compared to the charge and mass of a proton, an electron has: 1. the same charge and a smaller mass 2. the same charge and the same mass 3. an opposite charge and a smaller mass 4. an opposite charge and the same mass ...
Chapter 10 Handouts_1
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the elemen ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the elemen ...
Chapter 10 Handouts - Bakersfield College
... distillation reverse osmosis Physical Property hardness color texture ...
... distillation reverse osmosis Physical Property hardness color texture ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.