Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
... matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
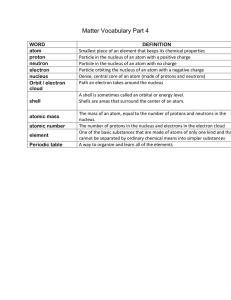
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Basic Chemistry notes
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... – Carbon-12, with 6 protons and 6 neutrons, is the most common form of carbon – Carbon-13, with 6 protons and 7 neutrons, is stable (non-radioactive) and rare – Carbon-14, with 6 protons and 8 neutrons, is unstable (radioactive) and rare ...
... – Carbon-12, with 6 protons and 6 neutrons, is the most common form of carbon – Carbon-13, with 6 protons and 7 neutrons, is stable (non-radioactive) and rare – Carbon-14, with 6 protons and 8 neutrons, is unstable (radioactive) and rare ...
Classification of Matter
... Also the original solid (HgO) and the product (Hg) are not the same colour. HgO is red and Hg is shiny and silvery. We have gas escaping (as suggested by the loss in solid mass: 432 vs. 400g) and a solid that is different from the original (difference in colour); the combination of these two observ ...
... Also the original solid (HgO) and the product (Hg) are not the same colour. HgO is red and Hg is shiny and silvery. We have gas escaping (as suggested by the loss in solid mass: 432 vs. 400g) and a solid that is different from the original (difference in colour); the combination of these two observ ...
Review Sheet: Unit 6 Name__________________ CHEMISTRY: A
... information about the chemical composition of a compound. Consequently, chemists rely on a chemical ____________ when representing a chemical compound. ____________ compounds are composed of a metal and a nonmetal while ____________ compounds are formed between nonmetals. In formulas for binary ioni ...
... information about the chemical composition of a compound. Consequently, chemists rely on a chemical ____________ when representing a chemical compound. ____________ compounds are composed of a metal and a nonmetal while ____________ compounds are formed between nonmetals. In formulas for binary ioni ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 2. Predict the products and write a balanced chemical equation for the following chemical reactions: a) Copper wire is added to an aqueous solution of silver nitrate. (3 marks) ...
... 2. Predict the products and write a balanced chemical equation for the following chemical reactions: a) Copper wire is added to an aqueous solution of silver nitrate. (3 marks) ...
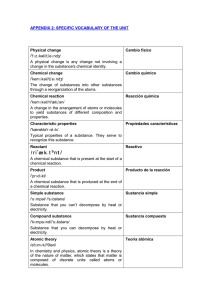
specific vocabulary of the unit
... Estequiometric coefficients They inform you of the number of molecules or estequiométricos atoms that take part in a chemical reaction. reaction Acid rain /'æsɪd//reɪn/ ...
... Estequiometric coefficients They inform you of the number of molecules or estequiométricos atoms that take part in a chemical reaction. reaction Acid rain /'æsɪd//reɪn/ ...
8th Grade: First Semester Final Review
... chemical formula in an equation 41. a substance produced in a chemical reaction 43. a process in which atoms of one or more substances rearrange to form one or more new substances Short Answer 1. Identify one way that homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures are different. ...
... chemical formula in an equation 41. a substance produced in a chemical reaction 43. a process in which atoms of one or more substances rearrange to form one or more new substances Short Answer 1. Identify one way that homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures are different. ...
Regents_Chem_Core_for_review
... 4. have collisions that may result in the transfer of energy between gas particles, but the total energy of the system remains constant. 30 Chemistry V.16 Collision theory states that a reaction is most likely to occur if reactant particles collide with the proper energy and orientation. (3.4d) V.17 ...
... 4. have collisions that may result in the transfer of energy between gas particles, but the total energy of the system remains constant. 30 Chemistry V.16 Collision theory states that a reaction is most likely to occur if reactant particles collide with the proper energy and orientation. (3.4d) V.17 ...
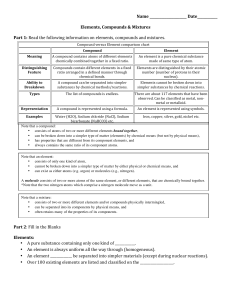
Compound vs Element chart
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
Isotopes - Cloudfront.net
... Any physical attribute of a substance such as color, density, texture, hardness, & phase Each substance has unique physical properties Examples ...
... Any physical attribute of a substance such as color, density, texture, hardness, & phase Each substance has unique physical properties Examples ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Hg (mercury) can exist by itself...but, oxygen will need to bond with another oxygen to make O2 (diatomic) To balance the atoms we need to: Put the coefficient of 2 in front of reactant HgO. Put the coefficient of 2 in front the product Hg. ...
... Hg (mercury) can exist by itself...but, oxygen will need to bond with another oxygen to make O2 (diatomic) To balance the atoms we need to: Put the coefficient of 2 in front of reactant HgO. Put the coefficient of 2 in front the product Hg. ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
Dalton Model of the Atom - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... • Each compound has a specific ratio of elements • It is a ratio by mass • Water is always 8 grams of oxygen for every one gram of hydrogen ...
... • Each compound has a specific ratio of elements • It is a ratio by mass • Water is always 8 grams of oxygen for every one gram of hydrogen ...
Elements
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
Family
... which appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest. When Mendeleev proposed his periodic table, he noted gaps in the table, and predicted that as-of-yet unknown elements existed with properties appropriate to fill those gap. ...
... which appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest. When Mendeleev proposed his periodic table, he noted gaps in the table, and predicted that as-of-yet unknown elements existed with properties appropriate to fill those gap. ...
Periodic Table
... • Many are gases at room temperature; those that are solids lack the luster of metals. ...
... • Many are gases at room temperature; those that are solids lack the luster of metals. ...
Matter
... particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT a solution. ...
... particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT a solution. ...
1 - M*W
... c) A hypothesis may develop into a theory d) The kinetic energy of an object relates to its motion 51) A control in an experiment a) Are the variables that are kept the same through each trial b) Means that the scientist has everything under control c) Is required only if the hypothesis leads to the ...
... c) A hypothesis may develop into a theory d) The kinetic energy of an object relates to its motion 51) A control in an experiment a) Are the variables that are kept the same through each trial b) Means that the scientist has everything under control c) Is required only if the hypothesis leads to the ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.