Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
CHEMISTRY ACTIVITY—MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Go to this
... There is one lone pair of electrons in NH3; in between what H2O and CH4 have. 16. How does the bond angle in NH3 compare with that of H2O & CH4? Is this molecule 2- or 3-dimensional? The bond angles are in between H2O and CH4, having one lone pair does change the bond angles as much as having 2 lone ...
... There is one lone pair of electrons in NH3; in between what H2O and CH4 have. 16. How does the bond angle in NH3 compare with that of H2O & CH4? Is this molecule 2- or 3-dimensional? The bond angles are in between H2O and CH4, having one lone pair does change the bond angles as much as having 2 lone ...
Questions 1- 4 refer to this molecule. 1. What is the hybridization
... Questions 14‐15 refer to these structures: The atoms are C, H, and F. The F is noted. H is small. ...
... Questions 14‐15 refer to these structures: The atoms are C, H, and F. The F is noted. H is small. ...
Homework Set 7
... CO from that perspective and compare it to the Lewis structure. a. Construct an M.O. diagram of CO and use it to ascertain the bond order. When combining the p orbitals, the πb molecular orbital has a lower energy than the σb molecular orbital. b. Draw the Lewis dot structure of CO and assign formal ...
... CO from that perspective and compare it to the Lewis structure. a. Construct an M.O. diagram of CO and use it to ascertain the bond order. When combining the p orbitals, the πb molecular orbital has a lower energy than the σb molecular orbital. b. Draw the Lewis dot structure of CO and assign formal ...
Final exam 2007
... 14. (10) Draw Lewis structures that satisfy the octet rule for CO, CO2, and CO3-2 and predict the order of the C...O bond lengths (which molecule will have the shortest, the longest, and the intermediate bond lengths). ...
... 14. (10) Draw Lewis structures that satisfy the octet rule for CO, CO2, and CO3-2 and predict the order of the C...O bond lengths (which molecule will have the shortest, the longest, and the intermediate bond lengths). ...
document
... share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds swi ...
... share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds swi ...
File
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to become stable ...
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to become stable ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry and
... 1. The number of MO's equal the number of AO's used to make the MO's 2. The more stable the bonding MO, the less stable the antibonding ...
... 1. The number of MO's equal the number of AO's used to make the MO's 2. The more stable the bonding MO, the less stable the antibonding ...
unit 7: bonding - St. Dominic High School
... dipole moment--separation of the charge in a molecule; product of the size of the charge and the distance of separation • align themselves with an electric field (figure b at right) • align with each other as well in the absence of an electric field • water—2 lone pairs establish a strong negative p ...
... dipole moment--separation of the charge in a molecule; product of the size of the charge and the distance of separation • align themselves with an electric field (figure b at right) • align with each other as well in the absence of an electric field • water—2 lone pairs establish a strong negative p ...
Physical bases of dental material science
... The energy released when an electron attaches to an atom in the gas phase (eV/atom; kJ/mol) Exothermic electron attachment: Eea>0 -- incoming electron interacts strongly with the nucleus on its orbital Endothermic electron attachment: Eea<0 -- A- has higher energy than A and e- ...
... The energy released when an electron attaches to an atom in the gas phase (eV/atom; kJ/mol) Exothermic electron attachment: Eea>0 -- incoming electron interacts strongly with the nucleus on its orbital Endothermic electron attachment: Eea<0 -- A- has higher energy than A and e- ...
formation of chemical bonds. -
... Ca+2 + O-2 CaO This is an example for ionic bond. In this bond, two electrons transfers from calcium atom to oxygen atom. 6. A, B, and C are three elements with atomic number 6, 11 and 17 respectively. i. Which of these cannot form ionic bond? Why? ii. Which of these cannot form covalent bond? Why ...
... Ca+2 + O-2 CaO This is an example for ionic bond. In this bond, two electrons transfers from calcium atom to oxygen atom. 6. A, B, and C are three elements with atomic number 6, 11 and 17 respectively. i. Which of these cannot form ionic bond? Why? ii. Which of these cannot form covalent bond? Why ...
The Representative Elements
... sublevel. Because these inner orbitals cannot participate as easily in bonding as the s and p orbitals the chemistry is not greatly affected by the gradual change in the increased number of electrons in the d orbital. ...
... sublevel. Because these inner orbitals cannot participate as easily in bonding as the s and p orbitals the chemistry is not greatly affected by the gradual change in the increased number of electrons in the d orbital. ...
The Representative Elements
... sublevel. Because these inner orbitals cannot participate as easily in bonding as the s and p orbitals the chemistry is not greatly affected by the gradual change in the increased number of electrons in the d orbital. ...
... sublevel. Because these inner orbitals cannot participate as easily in bonding as the s and p orbitals the chemistry is not greatly affected by the gradual change in the increased number of electrons in the d orbital. ...
Chapter 24: Transition Metals Coordination Compounds Part 1
... If the complex is an ion, like the above, it is written in brackets as shown above. Complex ions may also form an ionic salt by combining with an oppositely charged ion. So you could easily form the salt [Ag(NH3)2]Cl. Note how the Cl- anion is outside the brackets. The coordination number of a coord ...
... If the complex is an ion, like the above, it is written in brackets as shown above. Complex ions may also form an ionic salt by combining with an oppositely charged ion. So you could easily form the salt [Ag(NH3)2]Cl. Note how the Cl- anion is outside the brackets. The coordination number of a coord ...
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... If we could see electron pairs, what would this look like? What 3–D shape would result? ...
... If we could see electron pairs, what would this look like? What 3–D shape would result? ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... What is a cation? ____________________________________ What is an anion? ____________________________________ The charge becomes positive when what has happened? ___________________________________________________________________ The charge becomes negative when what has happened? __________________ ...
... What is a cation? ____________________________________ What is an anion? ____________________________________ The charge becomes positive when what has happened? ___________________________________________________________________ The charge becomes negative when what has happened? __________________ ...
File
... your knowledge of chemical bonding and on the Lewis electron-dot diagrams of H2S, CO 2, and F 2 below. ...
... your knowledge of chemical bonding and on the Lewis electron-dot diagrams of H2S, CO 2, and F 2 below. ...
notes and handout
... from the valence electrons (#1 above). Arrange these around the atoms until all of them satisfy the octet rule: Remember, ALL elements EXCEPT hydrogen want eight electrons around them, total. Hydrogen only wants two electrons. Let's do an example: CO2 Note: Each of the numbers below correspond to ...
... from the valence electrons (#1 above). Arrange these around the atoms until all of them satisfy the octet rule: Remember, ALL elements EXCEPT hydrogen want eight electrons around them, total. Hydrogen only wants two electrons. Let's do an example: CO2 Note: Each of the numbers below correspond to ...
Honors Unit 5 Practice Test
... A negative ion is known as a(n) a. ionic radius. c. cation. b. valence electron. d. anion. In a row in the periodic table, as the atomic number increases, the atomic radius generally a. decreases. c. increases. b. remains constant. d. becomes immeasurable. In the alkaline-earth group, atoms with the ...
... A negative ion is known as a(n) a. ionic radius. c. cation. b. valence electron. d. anion. In a row in the periodic table, as the atomic number increases, the atomic radius generally a. decreases. c. increases. b. remains constant. d. becomes immeasurable. In the alkaline-earth group, atoms with the ...
VSEPR theory From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Valence shell
... 1. Pairs of electrons in the valence shell of a central atom repel each other. 2. These pairs of electrons tend to occupy positions in space that minimize repulsions and maximize the distance of separation between them. 3. The valence shell is taken as a sphere with electron pairs localizing on the ...
... 1. Pairs of electrons in the valence shell of a central atom repel each other. 2. These pairs of electrons tend to occupy positions in space that minimize repulsions and maximize the distance of separation between them. 3. The valence shell is taken as a sphere with electron pairs localizing on the ...
The Shortest Metal−Metal Bond Yet: Molecular and Electronic
... Because of the redox ambiguity of diimine and other imine containing ligands,5 the Cr atoms in 2 could formally be assigned as Cr(II) coordinated by dianionic enediamide ligands, Cr(I) with monoanionic ligand-centered radical ligands, or Cr(0) with neutral diimine ligands. The long C-N distances (1. ...
... Because of the redox ambiguity of diimine and other imine containing ligands,5 the Cr atoms in 2 could formally be assigned as Cr(II) coordinated by dianionic enediamide ligands, Cr(I) with monoanionic ligand-centered radical ligands, or Cr(0) with neutral diimine ligands. The long C-N distances (1. ...
Chemical Bonding Ionic bonds result from an electrostatic attraction
... Bonding orbitals are a composite of the orbitals that the electrons came from A sigma bond (σ) is formed by the end-to end overlap of orbitals All single bonds are sigma bonds A pi (π) bond results • from side-to-side overlap of orbitals • A double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. • A tri ...
... Bonding orbitals are a composite of the orbitals that the electrons came from A sigma bond (σ) is formed by the end-to end overlap of orbitals All single bonds are sigma bonds A pi (π) bond results • from side-to-side overlap of orbitals • A double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. • A tri ...
Low oxidation state diphosphorus and diarsenic compounds
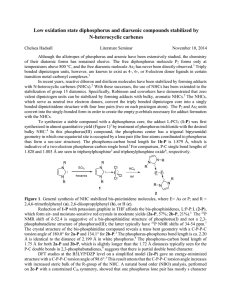
... To synthesize a stable compound with a diphosphorus core, the adduct L:PCl3 (1-P) was first synthesized in almost quantitative yield (Figure 1)3 by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with the desired bulky NHC.4 In this phosphorus(III) compound, the phosphorus center has a trigonal bipyramidal geom ...
... To synthesize a stable compound with a diphosphorus core, the adduct L:PCl3 (1-P) was first synthesized in almost quantitative yield (Figure 1)3 by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with the desired bulky NHC.4 In this phosphorus(III) compound, the phosphorus center has a trigonal bipyramidal geom ...