Week 8 - Day 3 (End of Chapter 6)
... Bonds between atoms should occur when the orbitals on those atoms interact to make a bond. Audio 0:33:58.699088 The kind of interaction depends on whether the orbitals align along the axis between the nuclei, or outside the axis. ...
... Bonds between atoms should occur when the orbitals on those atoms interact to make a bond. Audio 0:33:58.699088 The kind of interaction depends on whether the orbitals align along the axis between the nuclei, or outside the axis. ...
∙ ∙B x
... atom and gained by a chlorine atom. Using dot-cross diagrams - it means that valence electrons of one atom are represented by dots and those of the second atom as crosses - (and showing a chlorine atom rather than the Cl2 molecule) we can represent this reaction as follows: ...
... atom and gained by a chlorine atom. Using dot-cross diagrams - it means that valence electrons of one atom are represented by dots and those of the second atom as crosses - (and showing a chlorine atom rather than the Cl2 molecule) we can represent this reaction as follows: ...
∙ ∙B x
... atom and gained by a chlorine atom. Using dot-cross diagrams - it means that valence electrons of one atom are represented by dots and those of the second atom as crosses - (and showing a chlorine atom rather than the Cl2 molecule) we can represent this reaction as follows: ...
... atom and gained by a chlorine atom. Using dot-cross diagrams - it means that valence electrons of one atom are represented by dots and those of the second atom as crosses - (and showing a chlorine atom rather than the Cl2 molecule) we can represent this reaction as follows: ...
Medical Physics and Statistics
... Sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms, or between atoms and other covalent bonds. Attraction-to-repulsion stability that forms between atoms when they share electrons. ...
... Sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms, or between atoms and other covalent bonds. Attraction-to-repulsion stability that forms between atoms when they share electrons. ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
... electrons in the valence shell. ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a v ...
Earth Materials
... • Chemical bonding is controlled by outermost shell (valence) electrons • Elements will typically be reactive unless their valence shell is full • Atoms or groups of atoms with unequal numbers of protons and electrons, thus having a non-zero charge, are called ions. Positively charged ions are known ...
... • Chemical bonding is controlled by outermost shell (valence) electrons • Elements will typically be reactive unless their valence shell is full • Atoms or groups of atoms with unequal numbers of protons and electrons, thus having a non-zero charge, are called ions. Positively charged ions are known ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... Polar Covalent Bond: In polar covalent bond, the e tend to be more towards the atom having a higher electro negativity. Ex. H2O Electro negativity difference and bonding: The difference in the electro negativity value of the two atoms will decide as to what kind of bond will be formed. Electro neg ...
... Polar Covalent Bond: In polar covalent bond, the e tend to be more towards the atom having a higher electro negativity. Ex. H2O Electro negativity difference and bonding: The difference in the electro negativity value of the two atoms will decide as to what kind of bond will be formed. Electro neg ...
Atomic combinations: Electronegativity and ionic
... 2.1 The nature of the ionic bond You will remember that when atoms bond, electrons are either shared or they are transferred between the atoms that are bonding. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between the atoms. There is another type of bonding, where electrons are transferred from one ato ...
... 2.1 The nature of the ionic bond You will remember that when atoms bond, electrons are either shared or they are transferred between the atoms that are bonding. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between the atoms. There is another type of bonding, where electrons are transferred from one ato ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... Ionic Bonds In some cases, atoms strip electrons away from their bonding partners Electron transfer between two atoms creates ions Ions • Are atoms with more or fewer electrons than usual (charged atoms) • Such as Na+, Cl-, K+, PO43- ...
... Ionic Bonds In some cases, atoms strip electrons away from their bonding partners Electron transfer between two atoms creates ions Ions • Are atoms with more or fewer electrons than usual (charged atoms) • Such as Na+, Cl-, K+, PO43- ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... matter, viscosity, density, solubility Chemical properties: Flammability, sensitivity to light, oxidation, tarnishing, corrosion of metals ...
... matter, viscosity, density, solubility Chemical properties: Flammability, sensitivity to light, oxidation, tarnishing, corrosion of metals ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Sulfur, another third-period element, is commonly depicted with varying numbers of bonds. In each of the alternative structures sulfur obeys the octet rule, and has one or more positive formal charges. ...
... • Sulfur, another third-period element, is commonly depicted with varying numbers of bonds. In each of the alternative structures sulfur obeys the octet rule, and has one or more positive formal charges. ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... (E) mixture of elements 2. Based on the activity series, which one of the reactions below will occur? (A) Zn (s) + MnI2 (aq) ZnI2 (aq) + Mn (s) (B) SnCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Sn (s) + CuCl2 (aq) (C) 2AgNO3 (aq) + Pb (s) 2Ag (s) + Pb(NO3 )2 (aq) (D) 3Hg (l) + 2Cr(NO3 )3 (aq) 3Hg(NO3 )2 + 2Cr (s) (E) ...
... (E) mixture of elements 2. Based on the activity series, which one of the reactions below will occur? (A) Zn (s) + MnI2 (aq) ZnI2 (aq) + Mn (s) (B) SnCl2 (aq) + Cu (s) Sn (s) + CuCl2 (aq) (C) 2AgNO3 (aq) + Pb (s) 2Ag (s) + Pb(NO3 )2 (aq) (D) 3Hg (l) + 2Cr(NO3 )3 (aq) 3Hg(NO3 )2 + 2Cr (s) (E) ...
Proton sharing in bis(4-carbamoylpyridinium) squarate
... (Fig. 2; Farrugia, 1999) of the electron density associated with this H atom shows this to be smeared out between the N and O atoms, with the maximum lying closer to the N than the O atom, rather than being bound closely to the N atom to give a discrete ion pair. This has consequences for the assign ...
... (Fig. 2; Farrugia, 1999) of the electron density associated with this H atom shows this to be smeared out between the N and O atoms, with the maximum lying closer to the N than the O atom, rather than being bound closely to the N atom to give a discrete ion pair. This has consequences for the assign ...
Organic Chemistry I: Contents
... Polar Covalent bonds •Atoms with equal or nearly equal electronegativities form pure covalent bond or nonpolar covalent bond as C - C and C - H bonds. ...
... Polar Covalent bonds •Atoms with equal or nearly equal electronegativities form pure covalent bond or nonpolar covalent bond as C - C and C - H bonds. ...
Unit 4: Chemical Bonding Notes Chemical Bond—a mutual
... • A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds (usually composed only of ...
... • A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds (usually composed only of ...
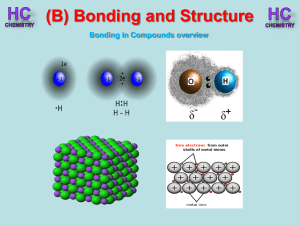
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
01 Intro Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
02Ch02chemistry2005
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
... Two atoms can share more than one pair of electrons double bonds (2 pairs of electrons) triple bonds (3 pairs of electrons) ...
Metal-Metal Bonds
... • Single, double, triple, and quadruple bonds are possible in transition metal complexes. – Figure 15-7; [Re3Cl12]3- and [Re2Cl8]2– The metal-metal bond distance in the dimer is 224 pm. It was the first complex found to have a quadruple bond. Look at other complexes that have metal-metal bonds. ...
... • Single, double, triple, and quadruple bonds are possible in transition metal complexes. – Figure 15-7; [Re3Cl12]3- and [Re2Cl8]2– The metal-metal bond distance in the dimer is 224 pm. It was the first complex found to have a quadruple bond. Look at other complexes that have metal-metal bonds. ...
Stoichiometry Mole Concept Balancing Chemical Equations
... Use the relative masses of the atoms to do calculations Gases conveniently treated in terms of P, V & T ...
... Use the relative masses of the atoms to do calculations Gases conveniently treated in terms of P, V & T ...
Bonding - Berkeley City College
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... f) Brackets are sometimes used to contain groups of atoms (called polyatomic ions). If a number appears to the right and below (subscript) the bracket, the subscript is ONLY multiplied by the atoms appearing inside the brackets. i.e. Al(NO3)3 This compound contains the following atoms: 1 x Al = 1 a ...
... f) Brackets are sometimes used to contain groups of atoms (called polyatomic ions). If a number appears to the right and below (subscript) the bracket, the subscript is ONLY multiplied by the atoms appearing inside the brackets. i.e. Al(NO3)3 This compound contains the following atoms: 1 x Al = 1 a ...