ppt Lewis Dot Diagram Rules
... When compounds are formed they tend to follow the Octet Rule. Octet Rule: An atom will gain or loose e-(s) until it is surrounded by eight valence electrons. (Seek a full octet) ...
... When compounds are formed they tend to follow the Octet Rule. Octet Rule: An atom will gain or loose e-(s) until it is surrounded by eight valence electrons. (Seek a full octet) ...
Chapter 8 & 9 PowerPoint
... Three types of bonding • Metallic bonding – results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons • Ionic bonding – results from the electrical attraction between positive and negative ions. • Covalent bonding – results from the sharing of electron pairs between two a ...
... Three types of bonding • Metallic bonding – results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons • Ionic bonding – results from the electrical attraction between positive and negative ions. • Covalent bonding – results from the sharing of electron pairs between two a ...
oxidation number
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
Chemical Change
... Atoms of Hydrogen and Oxygen are different in the number of subatomic particles they have This means that their reactivity is going to ...
... Atoms of Hydrogen and Oxygen are different in the number of subatomic particles they have This means that their reactivity is going to ...
SCH3U Course Review
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
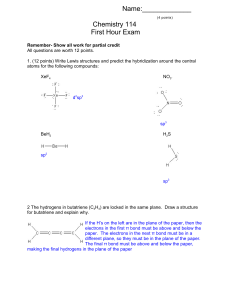
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
Chemistry Part 1
... Rule of eights – Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has 8 electrons – The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold 2 electrons ...
... Rule of eights – Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has 8 electrons – The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold 2 electrons ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
Science notes on Atoms, Periodic table
... Aristotle believed that it was infinitely divisible (you could keep on cutting it forever). He also believed that everything was composed of 5 elements: water, earth, fire, air & aether John Dalton then concluded that there must be particles of different elements. All the atoms of a single eleme ...
... Aristotle believed that it was infinitely divisible (you could keep on cutting it forever). He also believed that everything was composed of 5 elements: water, earth, fire, air & aether John Dalton then concluded that there must be particles of different elements. All the atoms of a single eleme ...
CHEM 11 Practice Exam 2
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... (c) approximately equal to the attractive forces among formula units in ionic bonding. (d) equal to zero. 5. _____ In metals, the valence electrons are considered to be (a) attached to particular positive ions. (c) immobile. (b) shared by all surrounding atoms. (d) involved in covalent bonds. ...
... (c) approximately equal to the attractive forces among formula units in ionic bonding. (d) equal to zero. 5. _____ In metals, the valence electrons are considered to be (a) attached to particular positive ions. (c) immobile. (b) shared by all surrounding atoms. (d) involved in covalent bonds. ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
Practice Exam 2 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Halides of Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Sulfates of Ag+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Exceptions Compounds containing alkali metals ions and the ammonium ion Compounds containing alkali metals ions and the ammonium ion ...
... Halides of Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Sulfates of Ag+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Exceptions Compounds containing alkali metals ions and the ammonium ion Compounds containing alkali metals ions and the ammonium ion ...
document
... E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reacti ...
... E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reacti ...
Document
... It is important that atoms bond. Why? Because they need to bond in order to make _____________, _______________, and other more complex forms of matter. For example, if atoms didn’t bond, you would be quite thirsty all the time! Yes, ______________ is the result of the process of CHEMICAL bonding. T ...
... It is important that atoms bond. Why? Because they need to bond in order to make _____________, _______________, and other more complex forms of matter. For example, if atoms didn’t bond, you would be quite thirsty all the time! Yes, ______________ is the result of the process of CHEMICAL bonding. T ...
10-11 - TAMU Chemistry
... hybrid orbitals have better overlap when bonding (as compared to the unhybridized orbitals on the carbon atom) and this improved overlap provides more energy than that spent in promoting the electron and hybridizing the orbitals in the first place. Thus it is more favorable for the carbon to hybridi ...
... hybrid orbitals have better overlap when bonding (as compared to the unhybridized orbitals on the carbon atom) and this improved overlap provides more energy than that spent in promoting the electron and hybridizing the orbitals in the first place. Thus it is more favorable for the carbon to hybridi ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (2+, reactive) Group 17 = the halogens (1-, very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (0, unreactive) Periods are horizontal rows on the periodic table. ...
... Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (2+, reactive) Group 17 = the halogens (1-, very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (0, unreactive) Periods are horizontal rows on the periodic table. ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... Chapter 4 REVIEW 1. Draw Lewis symbols for atoms of the following elements and predict their bonding capacity: (a) calcium (d) silicon (b) chlorine (e) sulfur (c) phosphorus ...
... Chapter 4 REVIEW 1. Draw Lewis symbols for atoms of the following elements and predict their bonding capacity: (a) calcium (d) silicon (b) chlorine (e) sulfur (c) phosphorus ...
Lone pairs
... Electrons will occupy all valence orbitals before forming electron pairs. Empty bus seat rule Normally a maximum of 8 electrons may occupy a valence energy level. This is ...
... Electrons will occupy all valence orbitals before forming electron pairs. Empty bus seat rule Normally a maximum of 8 electrons may occupy a valence energy level. This is ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... 1. Using the periodic table, where are the metals and nonmetals? What is hydrogen? Metals are in the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? ...
... 1. Using the periodic table, where are the metals and nonmetals? What is hydrogen? Metals are in the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? ...
Chapter 5
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Review for second exam:
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...