Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
Semester Exam Review - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
H H H H H N HO O NC[ ]- - Teacher`s Tools® Chemistry
... The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act like a Lewis Base in that they donate a pair of electrons. A ligand must therefore have at least one unshared pair of electrons. The type of bond between the metal and the ligand is a coordinate covale ...
... The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act like a Lewis Base in that they donate a pair of electrons. A ligand must therefore have at least one unshared pair of electrons. The type of bond between the metal and the ligand is a coordinate covale ...
Grade 11 Chemistry E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... tell what type of reaction it is. a) lead (II) nitrate and sodium iodide react to make lead iodide and sodium nitrate. b) calcium carbonate when you heat it produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. c) propane reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water d) copper metal and silver nitrate ...
... tell what type of reaction it is. a) lead (II) nitrate and sodium iodide react to make lead iodide and sodium nitrate. b) calcium carbonate when you heat it produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. c) propane reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water d) copper metal and silver nitrate ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... results in unequal sharing of bonding electrons and a permanent dipole. A permanent dipole is therefore a small charge difference across a bond that results from the difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. The greater the difference in electronegativity, the greater the permanent ...
... results in unequal sharing of bonding electrons and a permanent dipole. A permanent dipole is therefore a small charge difference across a bond that results from the difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. The greater the difference in electronegativity, the greater the permanent ...
HOMEWORK 6-1 - losbanosusd.k12.ca.us
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
... 1. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable than those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... none of the above is generally correct ...
... none of the above is generally correct ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... Means that one or more electrons are ____________ from the metal to the nonmetal (no longer neutral) these are now ions ...
... Means that one or more electrons are ____________ from the metal to the nonmetal (no longer neutral) these are now ions ...
Chemistry Review
... The metals are: • Good conductors of heat (used in pots and pans) • Good conductors of electricity (used in wires) • Lustrous (used in jewelry and other ornamental objects) • Almost all are solids (except for mercury) • Malleable (can be hammered into sheets) • Ductile (can be drawn into wires) Exam ...
... The metals are: • Good conductors of heat (used in pots and pans) • Good conductors of electricity (used in wires) • Lustrous (used in jewelry and other ornamental objects) • Almost all are solids (except for mercury) • Malleable (can be hammered into sheets) • Ductile (can be drawn into wires) Exam ...
File
... because of its valence of 3 (Co3+) for charge balance. Jørgensen proposed that for the above compounds • N could form chains because of its valence of 5 • Chloride (Cl-) could be bound to N or to Co3+ ...
... because of its valence of 3 (Co3+) for charge balance. Jørgensen proposed that for the above compounds • N could form chains because of its valence of 5 • Chloride (Cl-) could be bound to N or to Co3+ ...
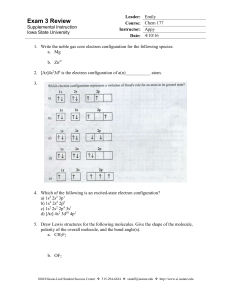
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List three properties that distinguish nonmetals from metals. 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 ...
... d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List three properties that distinguish nonmetals from metals. 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 ...
Nomenclature Notes
... 6. Molecular compound – molecules that contain covalent bonds and whose simplest units are molecules. 7. Chemical Formula – a formula that indicates the relative #’s of atoms of each kind in a chemical compound. Uses atomic symbols and numerical subscripts. Ex. NaCl, Mg(OH)2 8. Polyatomic Ion – A ch ...
... 6. Molecular compound – molecules that contain covalent bonds and whose simplest units are molecules. 7. Chemical Formula – a formula that indicates the relative #’s of atoms of each kind in a chemical compound. Uses atomic symbols and numerical subscripts. Ex. NaCl, Mg(OH)2 8. Polyatomic Ion – A ch ...
File
... • The elements in Group IA and IIA tend to lose electrons for form positive ions • The elements in Group VIA and VIIA tend to gain electrons to form negative ions. ...
... • The elements in Group IA and IIA tend to lose electrons for form positive ions • The elements in Group VIA and VIIA tend to gain electrons to form negative ions. ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
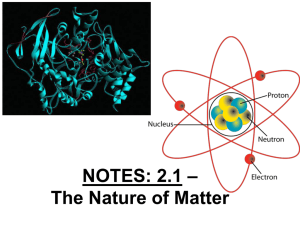
... 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy ...
... 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy ...
Basic Chemistry - Biology with Radjewski
... • Atoms with unfilled outer shells tend to undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms ...
... • Atoms with unfilled outer shells tend to undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms ...
ORGANIC REACTION TYPES:
... an atom’s attraction for electrons that it shares in a chemical bond with other atoms. In the 1930’s, Linus Pauling assigned electronegativity values to all elements relative to F (the most electronegative element), which he gave a value of 4.0 . ...
... an atom’s attraction for electrons that it shares in a chemical bond with other atoms. In the 1930’s, Linus Pauling assigned electronegativity values to all elements relative to F (the most electronegative element), which he gave a value of 4.0 . ...
6.7 – Ionic Compounds
... Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. Ionic attractions result in high melting points. Most ionic compounds can dissolve in water to become an aqueous solution with ions that are free to move around. Therefore, ionic compounds do not conduct ...
... Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. Ionic attractions result in high melting points. Most ionic compounds can dissolve in water to become an aqueous solution with ions that are free to move around. Therefore, ionic compounds do not conduct ...
... c) Identify all of the hydrogen bond donors or acceptors on this molecule; provide a sketch O H showing a water molecule forming a hydrogen bond to the compound (2 pts). H The N-H group will only donate a hydrogen bond. The molecular orbitals on the N are the same as in the amide group, sp2 hybridiz ...
Notes
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
... Key Questions: • Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. • Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. • Explain how compounds are different from their component elements. • Describe the two main types of chemical bonds ...
Chemical Bonding
... oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
... oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 3. What is a molecule? Be able to identify one from a list. Smallest particles of a substance with the same properties of the substance (ex. H2O, O2, N2, CO2) 4. Use the periodic table to explain how elements form bonds. Ex. Group 16 ionically bonds with group 2, Group 17 ionically bonds with Group ...
... 3. What is a molecule? Be able to identify one from a list. Smallest particles of a substance with the same properties of the substance (ex. H2O, O2, N2, CO2) 4. Use the periodic table to explain how elements form bonds. Ex. Group 16 ionically bonds with group 2, Group 17 ionically bonds with Group ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
4. - period2chem
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...


![H H H H H N HO O NC[ ]- - Teacher`s Tools® Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017018154_1-68467b392d8cadb27de319df72045839-300x300.png)