Writing Lewis Structures for Exceptions to the
... idea here is that the bonding and nonbonding (lone) pairs around an atom will be positioned as far apart as possible. The rules for using the VSEPR model to predict molecular structure are: 1. Determine the Lewis structure for the molecule. 2. For molecules with resonance structures, use any of the ...
... idea here is that the bonding and nonbonding (lone) pairs around an atom will be positioned as far apart as possible. The rules for using the VSEPR model to predict molecular structure are: 1. Determine the Lewis structure for the molecule. 2. For molecules with resonance structures, use any of the ...
Review-Semester Final (Part I)
... 18. Which holds its electrons more tightly- metals or nonmetals? How does this affect the properties of each? ...
... 18. Which holds its electrons more tightly- metals or nonmetals? How does this affect the properties of each? ...
MatterPP4
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... Reduce electrons by putting in a triple bond |C N| ? Count electrons. Correct number? ...
... Reduce electrons by putting in a triple bond |C N| ? Count electrons. Correct number? ...
ATOMS
... • The ATOMIC NUMBER is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. For example: Carbon’s atomic number is 6. So, there are 6 protons in the nucleus. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8. • How many protons are there? ...
... • The ATOMIC NUMBER is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. For example: Carbon’s atomic number is 6. So, there are 6 protons in the nucleus. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8. • How many protons are there? ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... 11. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. If a plant contained 2.0 g of 14C when it died, how much is left after 34,380 years? mf = 0.03125 mg ...
... 11. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. If a plant contained 2.0 g of 14C when it died, how much is left after 34,380 years? mf = 0.03125 mg ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
... Helium (2 valence electrons) is in the same column as neon (8 valence electrons) because both have full outer energy levels. This gives them similar properties. ...
... Helium (2 valence electrons) is in the same column as neon (8 valence electrons) because both have full outer energy levels. This gives them similar properties. ...
3rd Quarter Test
... 9) Which of the following liquids has the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction between its molecules? a) Xe (l) b) Kr (l) c) Ne (l) d) He (l) 10) Which type of bond exists in a molecule of hydrogen iodide? a) a polar covalent bond with an electronegativity difference of zero b) a polar covale ...
... 9) Which of the following liquids has the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction between its molecules? a) Xe (l) b) Kr (l) c) Ne (l) d) He (l) 10) Which type of bond exists in a molecule of hydrogen iodide? a) a polar covalent bond with an electronegativity difference of zero b) a polar covale ...
Chem Bonding Notes
... Base your answers to questions 38 through 40 on the information below. Naphthalene, a nonpolar substance that sublimes at room temperature, can be used to protect wool clothing from being eaten by moths. 38. Explain, in terms of intermolecularforces, why naphthalene sublimes. [1] 39. Explain why nap ...
... Base your answers to questions 38 through 40 on the information below. Naphthalene, a nonpolar substance that sublimes at room temperature, can be used to protect wool clothing from being eaten by moths. 38. Explain, in terms of intermolecularforces, why naphthalene sublimes. [1] 39. Explain why nap ...
Bond - My CCSD
... Using a car as an analogy for a molecule: You have a Porsche 911 Turbo. How many tires (T), doors (D), and engines (E) does the car have? 4 tires, 2 doors, and 1 engine ...
... Using a car as an analogy for a molecule: You have a Porsche 911 Turbo. How many tires (T), doors (D), and engines (E) does the car have? 4 tires, 2 doors, and 1 engine ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... Phase notations (solid, liquids, gases, aqueous) - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually ...
... Phase notations (solid, liquids, gases, aqueous) - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually ...
Ch 8 Bonding and Molecular Structure 06-Nov
... a. For a neutral atom, the # of e- is the sum of the valence eb. For an anion, add the number of electrons equal to the negative charge c. For a cation, subtract the number of electrons equal to the positive charge The number of valence electron pairs = total # of electrons / 2 Carbon has 4 (from SP ...
... a. For a neutral atom, the # of e- is the sum of the valence eb. For an anion, add the number of electrons equal to the negative charge c. For a cation, subtract the number of electrons equal to the positive charge The number of valence electron pairs = total # of electrons / 2 Carbon has 4 (from SP ...
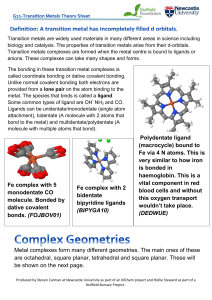
Polydentate ligand (macrocycle) bound to Fe via 4 N atoms. This is
... Octahedral: One of the most common geometries is octahedral which comes from it having 8 faces. There are 6 atoms around the atom in total, 4 atoms in one plane with the other 2 above and below this plane. All bond angles should be 90o. (FUBYIK) Octahedral molecules can form isomers such as cis/tra ...
... Octahedral: One of the most common geometries is octahedral which comes from it having 8 faces. There are 6 atoms around the atom in total, 4 atoms in one plane with the other 2 above and below this plane. All bond angles should be 90o. (FUBYIK) Octahedral molecules can form isomers such as cis/tra ...
AP Notes Chapter 11
... Metals capable of taking on multiple oxidation numbers. Exist in 3 series 1st the 3d 2nd the 4d and the 3rd 5d The 2nd and 3rd series are almost identical in radii size due to the 4f and 5f orbitals, the addition of these 14 protons and little shielding effect cause the similarity in size this is ca ...
... Metals capable of taking on multiple oxidation numbers. Exist in 3 series 1st the 3d 2nd the 4d and the 3rd 5d The 2nd and 3rd series are almost identical in radii size due to the 4f and 5f orbitals, the addition of these 14 protons and little shielding effect cause the similarity in size this is ca ...
2.1 Atoms and Bonds
... A chemical change occurs when compounds are formed Reactants are particles that are present before the reaction Products are particles that are present after the reaction Of the form: Reactant Products ◦ Ex: 2H2 + O2 2H2O ...
... A chemical change occurs when compounds are formed Reactants are particles that are present before the reaction Products are particles that are present after the reaction Of the form: Reactant Products ◦ Ex: 2H2 + O2 2H2O ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
Organometallic Chemistry Bonding in Coordination Compounds
... C. A. Tolman, Chem. Soc. Rev., 1972, 1, 337 ...
... C. A. Tolman, Chem. Soc. Rev., 1972, 1, 337 ...
To do List - kurtniedenzu
... [Other types of intermolecular bonding will be discussed later.] The above types of bonding are intramolecular. 1) ionic - transfer of electrons and subsequent union of an anion with a cation - formation of ionic bond. Ions are held together by electrostatic forces - some of the strongest bonds that ...
... [Other types of intermolecular bonding will be discussed later.] The above types of bonding are intramolecular. 1) ionic - transfer of electrons and subsequent union of an anion with a cation - formation of ionic bond. Ions are held together by electrostatic forces - some of the strongest bonds that ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
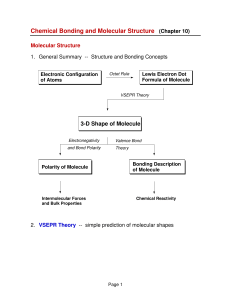
3-D Shape of Molecule
... if only s and p orbitals are used, the angles ought to be 90° since the p orbitals are mutually perpendicular! modify the theory of atomic orbitals and use: ...
... if only s and p orbitals are used, the angles ought to be 90° since the p orbitals are mutually perpendicular! modify the theory of atomic orbitals and use: ...
Practice Exam 3
... Part (2) - Show all your work. ( 8 points each) 21. For CO3 2 - , sulfate ion, draw the Lewis structure (by counting valence electrons of each atom), determine the electron-domain geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, and show the angle between the bonds in a drawing. S is the central atom, ...
... Part (2) - Show all your work. ( 8 points each) 21. For CO3 2 - , sulfate ion, draw the Lewis structure (by counting valence electrons of each atom), determine the electron-domain geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, and show the angle between the bonds in a drawing. S is the central atom, ...
Review Test 2 CHM 1032C *memorize the names and symbols of
... a) Polyatomic ions *memorize the names, formulas and charges for the polyatomic ions* b) Naming Ionic compounds •Covalent bonds a) naming binary covalent compounds b) sharing electrons c) Lewis Structures • Polyatomic ions (Be able to draw Lewis structures for all 10) d) Formal Charges e) Single dou ...
... a) Polyatomic ions *memorize the names, formulas and charges for the polyatomic ions* b) Naming Ionic compounds •Covalent bonds a) naming binary covalent compounds b) sharing electrons c) Lewis Structures • Polyatomic ions (Be able to draw Lewis structures for all 10) d) Formal Charges e) Single dou ...