Lewis Structures
... compound phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is formed. In the gaseous and liquid states, this substance consists of PCl5 molecules, but in the solid state it consists of a 1 : 1 mixture of PCl4+ and PCl6- ions. Predict the geometric structures of PCl5, PCl4+, and PCl6-. ...
... compound phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is formed. In the gaseous and liquid states, this substance consists of PCl5 molecules, but in the solid state it consists of a 1 : 1 mixture of PCl4+ and PCl6- ions. Predict the geometric structures of PCl5, PCl4+, and PCl6-. ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... a fixed ratio • examples: NaCl, H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 • cmpds. have unique properties beyond those of the combined elements ...
... a fixed ratio • examples: NaCl, H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 • cmpds. have unique properties beyond those of the combined elements ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
... ions; usually the reaction between a metal and nonmetal. Cause very high melting points and usually a solid state since the attraction is SO strong that the ions are VERY close together in a crystal formation. Covalent bonds—electrons are shared by nuclei [careful, sharing is hardly ever 50-50!] ...
... ions; usually the reaction between a metal and nonmetal. Cause very high melting points and usually a solid state since the attraction is SO strong that the ions are VERY close together in a crystal formation. Covalent bonds—electrons are shared by nuclei [careful, sharing is hardly ever 50-50!] ...
Chapter 8 - ETSU.edu
... of chemical bonds. When describing bonds with non metals covalent bonds are good models and when a metal is involved we say that it is an ionic bond. A covalent bond acquires some ionic character if one atom has a greater electron withdrawing power than the other atom. This electron withdrawing powe ...
... of chemical bonds. When describing bonds with non metals covalent bonds are good models and when a metal is involved we say that it is an ionic bond. A covalent bond acquires some ionic character if one atom has a greater electron withdrawing power than the other atom. This electron withdrawing powe ...
Worksheet 20.2
... 1- Atoms can achieve a noble gas structure by gaining, losing or sharing electrons with other atoms. 2- The rule states that, except for hydrogen , an atom combines with other atoms to form bonds in order to have 8 electrons in its valence energy level ( like noble gases). Lewis dot symbols are repr ...
... 1- Atoms can achieve a noble gas structure by gaining, losing or sharing electrons with other atoms. 2- The rule states that, except for hydrogen , an atom combines with other atoms to form bonds in order to have 8 electrons in its valence energy level ( like noble gases). Lewis dot symbols are repr ...
Chapter 7 Section 1
... energy level. The group number of a representative element tells you the number of valence electrons. Helium is the one exception Valence electrons are the electrons ...
... energy level. The group number of a representative element tells you the number of valence electrons. Helium is the one exception Valence electrons are the electrons ...
chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... H is 2.1 and O is 3.5. 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 so the bond between H and O is a polar covalent bond. By definition a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is a molecule. So, the H2O particle is a molecule H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2 ...
... H is 2.1 and O is 3.5. 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 so the bond between H and O is a polar covalent bond. By definition a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is a molecule. So, the H2O particle is a molecule H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2 ...
ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
... properties of an alloy are often superior to those of its component elements. ...
... properties of an alloy are often superior to those of its component elements. ...
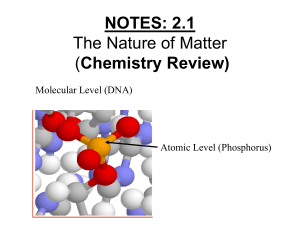
The Nature of Matter
... • Has a negative charge • # of protons= #of electrons • Balances out protons positive charge • In constant motion • Valence electrons are in outermost shell • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...
... • Has a negative charge • # of protons= #of electrons • Balances out protons positive charge • In constant motion • Valence electrons are in outermost shell • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...
Lecture Notes 14 - La Salle University
... (atmosphere and solvents) for preparation and use. In general, the reactivity parallels the ionic character of the carbon-metal bond, which may be estimated from the proton and carbon chemical shifts of methyl derivatives. % Ionic Character of H3C – Metal (CH3)2Hg < (CH3)2Cd < (CH3)2Zn < (CH3)2Mg < ...
... (atmosphere and solvents) for preparation and use. In general, the reactivity parallels the ionic character of the carbon-metal bond, which may be estimated from the proton and carbon chemical shifts of methyl derivatives. % Ionic Character of H3C – Metal (CH3)2Hg < (CH3)2Cd < (CH3)2Zn < (CH3)2Mg < ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
... ______ 3. A molecule with polar bonds must itself be polar. ______ 4. If two or more atoms are covalently bonded together, a molecule of a compound results. ______ 5. To attain a noble gas electron structure, a nitrogen atom must lose its five valence electrons. ______ 6. The compound OF2 contains t ...
... ______ 3. A molecule with polar bonds must itself be polar. ______ 4. If two or more atoms are covalently bonded together, a molecule of a compound results. ______ 5. To attain a noble gas electron structure, a nitrogen atom must lose its five valence electrons. ______ 6. The compound OF2 contains t ...
Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... broken and the actual new bonds formed. • Use whichever way works best for you! ...
... broken and the actual new bonds formed. • Use whichever way works best for you! ...
Ch. 8 Sections 8.1-8.3 Powerpoint
... •In ionic bonding the participating atoms are so different that one or more electrons are transferred to form oppositely charged ions, when then attract each other. •In covalent bonding (also called nonpolar covalent bonding) two identical atoms share electrons equally. •There are intermediate case ...
... •In ionic bonding the participating atoms are so different that one or more electrons are transferred to form oppositely charged ions, when then attract each other. •In covalent bonding (also called nonpolar covalent bonding) two identical atoms share electrons equally. •There are intermediate case ...
Bonding practice lessons 1-3
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
... The results of these tests suggest that A) both solids contain only ionic bonds B) both solids contain only covalent bonds C) solid A contains only covalent bonds and solid B contains only ionic bonds D) solid A contains only ionic bonds and solid B contains only covalent bonds 22. The bonds between ...
Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. ...
... • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I
... above with the double bond and single bond. The double bond should be shorter than the single bond however, from experimentation it has been found that the bonds in ozone are ...
... above with the double bond and single bond. The double bond should be shorter than the single bond however, from experimentation it has been found that the bonds in ozone are ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Answers to odd numbered problems in textbook are found in the book’s index. ...
... Answers to odd numbered problems in textbook are found in the book’s index. ...
Introduction to the Chemistry of Organosilicon Compounds
... RnSi(OH)4-n which are condensating, e.g.: ...
... RnSi(OH)4-n which are condensating, e.g.: ...
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS COMPLEX
... The primary valence is the oxidation number (positive charge) of the metal (usually 2+ or 3+) The secondary valence is the number of atoms that are directly bonded (coordinated) to the metal The secondary valence is also termed the “coordination number” of the metal in a coordination complex ...
... The primary valence is the oxidation number (positive charge) of the metal (usually 2+ or 3+) The secondary valence is the number of atoms that are directly bonded (coordinated) to the metal The secondary valence is also termed the “coordination number” of the metal in a coordination complex ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quantum shell How does the atom fill this cell?- by forming a chemical bond Types of Bonding (1) strong, primary or chemical bonds: Covalent Bon ...
... - When 2 atoms or more atoms are more stable as an aggregate, a chemical bond is formed. What is the criteria for an unstable atom?- an incompletely filled quantum shell How does the atom fill this cell?- by forming a chemical bond Types of Bonding (1) strong, primary or chemical bonds: Covalent Bon ...
Bonding Challenge
... 5) Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry explain each of the following observations. Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of your explanations. For each observation your answer must include references to both substances. (a) The bonds in ...
... 5) Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry explain each of the following observations. Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of your explanations. For each observation your answer must include references to both substances. (a) The bonds in ...