* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COORDINATION COMPOUNDS COMPLEX
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Spin crossover wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
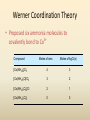
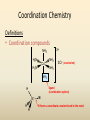
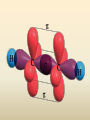
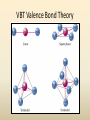
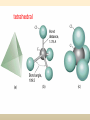
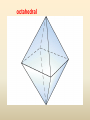
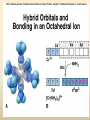
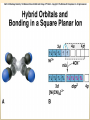
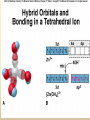
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS COMPLEX By s. r. ratnam Alfred Werner (1866-1919) • 1893, age 26: coordination theory • Nobel prize for Chemistry, 1913 • Addition of 6 mol NH3 to CoCl3(aq) Alfred Werner Switzerland University of Zurich Switzerland b. 1866 d. 1919 Conductivity studies Precipitation with AgNO3 Werner’s explanation of coordination complexes Metal ions exhibit two kinds of valence: primary and secondary valences The primary valence is the oxidation number (positive charge) of the metal (usually 2+ or 3+) The secondary valence is the number of atoms that are directly bonded (coordinated) to the metal The secondary valence is also termed the “coordination number” of the metal in a coordination complex Werner Coordination Theory NH3 Cl Co NH3 NH3 Cl– attached to NH3 may be dissociated NH3 NH3 Cl NH3 Cl Compound Moles of ions Moles of AgCl(s) “CoCl3.6NH3” 4 3 “CoCl3.5NH3” 3 2 “CoCl3.4NH3” 2 1 “CoCl3.3NH3” 0 0 Werner Coordination Theory • Proposed six ammonia molecules to covalently bond to Co3+ Compound Moles of ions Moles of AgCl(s) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 4 3 [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 3 2 [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl 2 1 [Co(NH3)3Cl3] 0 0 Coordination Chemistry Definitions • Coordination compounds – compounds composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules) that are formally donating electrons to the metal center Miessler, Tarr, p. 278 Coordination Chemistry Definitions • Coordination compounds 3+ NH3 H3N Co H3N NH3 3Cl– (counterion) NH3 NH3 ligand (coordination sphere) H N H H M N forms a coordinate covalent bond to the metal Coordination Chemistry Definitions • Ligands – simple, ‘complex’ • Denticity – different number of donor atoms • Chelates – compounds formed when ligands are chelating (Gk. crab’s claw) O H3C M C bidentate O Valence Bond Theory Developed by Linus Pauling Bonding in Coordination Compounds Valence Bond Theory Overlap of an empty orbital with a fullyfilled orbital leads to the formation of a co-ordinate covalent bond or dative bond VBT explains • • • • Geometry of complex Magnetic properties of complex Electronic configuration of Metal ion Nature of Bonding Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 15 VBT Valence Bond Theory Geometries in Complex Ions Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 20 tetrahedral octahedral Polydentate Ligands Ethylenediaminetetraacetate, mercifully abbreviated EDTA, has six donor atoms. Valence Bond Theory • Metal or metal ion: Lewis acid • Ligand: Lewis base • Hybridization of s, p, d orbitals C.N. Geometry Hybrids 4 4 5 6 tetrahedral square planar trigonal bipyramidal octahedral sp3 dsp2 dsp3 or sp3d d2sp3 or sp3d2 : Valence Bond Theory Example 1: [Co(NH3)6]3+ Co [Ar] 3d7 4s2 Co3+ [Ar] 3d6 3d 4s d2sp3 octahedral if complex is diamagnetic 4p 4d Valence Bond Theory Example 2: [CoF6]3– Co [Ar] 3d7 4s2 Co3+ [Ar] 3d6 3d 4s 4p 4sp3d2 octahedral if complex is paramagnetic 4d Valence Bond Theory Example 3: [PtCl4]2–, diamagnetic Pt2+ [Xe] 4f14 5d8 5d 6s dsp2 square planar 6p Valence Bond Theory Example 4: [NiCl4]2–, tetrahedral Ni2+ [Ar] 3d8 3d 4s 4p 4sp3 paramagnetic Valence Bond Theory • Ligands (Lewis base) form coordinate covalent bonds with metal center (Lewis acid) • Relationship between hybridization, geometry, and magnetism • Inadequate explanation for colors of complex ions e.g., [Cr(H2O)6]3+, [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+






















![Coordination Compounds [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000678035_1-c20c75fd4abb97d3ba4a0b0fce26e10b-150x150.png)



![Consider the diamagnetic complex, [Os(NH3)5(CO)]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006728268_1-5aa3fd1c498fab420574702fa8076d3a-150x150.png)





