Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... 30-C1.2k identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life, demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsatur ...
... 30-C1.2k identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life, demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsatur ...
Organic - NUS Chemistry
... reaction mechanisms; the collision theory of reaction rates; the activated complex theory of reaction rates. ...
... reaction mechanisms; the collision theory of reaction rates; the activated complex theory of reaction rates. ...
Chemistry 217 Problem Set 3 Recommended Problems from the Book
... of the carbons are attached to four groups, which should make them sp3-hybridized. However, the bond angles of the three-membered ring must be 60°, an angle more consistent with an sp2 hybridized carbon than an sp3, which has bond angles of 109.5°. 5. IR spectroscopy is commonly used by crime labs t ...
... of the carbons are attached to four groups, which should make them sp3-hybridized. However, the bond angles of the three-membered ring must be 60°, an angle more consistent with an sp2 hybridized carbon than an sp3, which has bond angles of 109.5°. 5. IR spectroscopy is commonly used by crime labs t ...
OR Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
... Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a starting material and a fuel additive; it is produced in large quantities by catalytic reduction ...
... Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a starting material and a fuel additive; it is produced in large quantities by catalytic reduction ...
Chapter
... Types of Formula Structural Formula • Structural Formula describe the kinds of elements found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment – they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess a ...
... Types of Formula Structural Formula • Structural Formula describe the kinds of elements found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment – they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess a ...
A study of the structure and bonding of small aluminum oxide
... Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed laser beam ~532 nm 10–20 mJ, 10 Hz! is focused down to a 1 mm diameter spot onto a pure aluminum target, producing a plasma containing aluminum atoms in both charged and neutra ...
... Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed laser beam ~532 nm 10–20 mJ, 10 Hz! is focused down to a 1 mm diameter spot onto a pure aluminum target, producing a plasma containing aluminum atoms in both charged and neutra ...
Organic Chemistry I-2 Ans Chapter 7 Free Radical Answers 1
... 6. Give the product of the reaction of excess benzene with each of the following reagents: a. isobutyl chloride + AlCl3 b. neopentyl chloride + AlCl3 c. propene + HF d. dichloromethane + AlCl3 ...
... 6. Give the product of the reaction of excess benzene with each of the following reagents: a. isobutyl chloride + AlCl3 b. neopentyl chloride + AlCl3 c. propene + HF d. dichloromethane + AlCl3 ...
and x
... are not always two separate sets of numbers. There may be numbers that are solutions of both parts of the compound inequality. ...
... are not always two separate sets of numbers. There may be numbers that are solutions of both parts of the compound inequality. ...
Structural principles for minerals and inorganic
... essentially higher than the bond valences between A and atoms from other structural units. According to their size, anion-centered tetrahedra may be subdivided into large and small tetrahedra, formed from cations with ionic radii near to 1.0 Å (e.g., Pb2+, Bi3+, and REE3+) and 0.5–0.7 Å (e.g., Cu2+ ...
... essentially higher than the bond valences between A and atoms from other structural units. According to their size, anion-centered tetrahedra may be subdivided into large and small tetrahedra, formed from cations with ionic radii near to 1.0 Å (e.g., Pb2+, Bi3+, and REE3+) and 0.5–0.7 Å (e.g., Cu2+ ...
History, Introduction, and Kinetics of Ion Exchange Materials
... are exchanged for different ions of similar charge in solution. The exchanger must have an open network structure, either organic or inorganic, which carries the ions and which allows ions to pass through it. An ion exchanger is a water-insoluble substance which can exchange some of its ions for sim ...
... are exchanged for different ions of similar charge in solution. The exchanger must have an open network structure, either organic or inorganic, which carries the ions and which allows ions to pass through it. An ion exchanger is a water-insoluble substance which can exchange some of its ions for sim ...
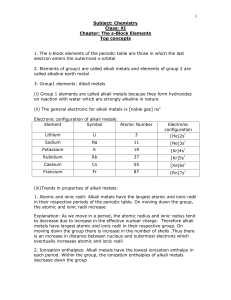
The s-Block Elements Top concepts 1. The s-block
... (iii) Trends in properties of alkaline metals and their comparison with alkali metals: 1. Atomic and ionic radii: Atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals increases down the group and are smaller than the corresponding members of the alkali metals Explanation: Alkaline earth metals have a hig ...
... (iii) Trends in properties of alkaline metals and their comparison with alkali metals: 1. Atomic and ionic radii: Atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals increases down the group and are smaller than the corresponding members of the alkali metals Explanation: Alkaline earth metals have a hig ...
Molecular Asymmetry in Prebiotic Chemistry: An Account from
... indicate a fundamental distinction between abiotic and biological chemical processes in their gaining of molecular complexity. To say it with the words of Shakespeare, therefore, a meteoritic organic input of thousands H, C, N, O containing molecules would have offered “too much of a good thing” for ...
... indicate a fundamental distinction between abiotic and biological chemical processes in their gaining of molecular complexity. To say it with the words of Shakespeare, therefore, a meteoritic organic input of thousands H, C, N, O containing molecules would have offered “too much of a good thing” for ...
Stains for Developing TLC Plates
... teaching lab. Typical examples of functional groups which may be visualized through this method are aromatic groups, α,β-unsaturated carbonyls, and any other compounds containing extensively π-conjugated systems. While exposing these TLC plates to UV light, you will notice that the silica gel will f ...
... teaching lab. Typical examples of functional groups which may be visualized through this method are aromatic groups, α,β-unsaturated carbonyls, and any other compounds containing extensively π-conjugated systems. While exposing these TLC plates to UV light, you will notice that the silica gel will f ...
Stains for Developing TLC Plates ()
... the visualization of the components of a reaction mixture. This is true primarily because most organic compounds are colorless. Frequently, the organic compounds of interest contain a chromophore which may be visualized by employing either a short or a long wave UV lamp. These lamps may be found as ...
... the visualization of the components of a reaction mixture. This is true primarily because most organic compounds are colorless. Frequently, the organic compounds of interest contain a chromophore which may be visualized by employing either a short or a long wave UV lamp. These lamps may be found as ...
Sequential nonadiabatic excitation of large molecules and ions
... proportional to the distance over which the charge is transferred. Thus, in the case of a diatomic molecule, the transition dipole moment grows with the internuclear separation R; in the limit of large R, it asymptotically approaches eR/2 关26兴. The role of 兩CT典 states in the dissociation dynamics of ...
... proportional to the distance over which the charge is transferred. Thus, in the case of a diatomic molecule, the transition dipole moment grows with the internuclear separation R; in the limit of large R, it asymptotically approaches eR/2 关26兴. The role of 兩CT典 states in the dissociation dynamics of ...
13-4 Ligands in Organometallic Chemistry
... Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Organometallic chemistry combines aspects of inorganic chemistry and organic chemistry. Organometallic compounds find practical use in stoichiometric and catalytically active compounds. Electron ...
... Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Organometallic chemistry combines aspects of inorganic chemistry and organic chemistry. Organometallic compounds find practical use in stoichiometric and catalytically active compounds. Electron ...
Reprinted from The Journal of Physical Chemistry, lgg5, 99
... parallel to the graphite surface. (On gold. by contrast, alkanethiolatesare chemisorbedon the surfacethrough a S-Au bond, and the alkyl chainsorient at an angle 30' fiom the normal to the gold surface.rr) The parallel orientationof the alkanethiols on graphite suggeststhat they are physisorbed on th ...
... parallel to the graphite surface. (On gold. by contrast, alkanethiolatesare chemisorbedon the surfacethrough a S-Au bond, and the alkyl chainsorient at an angle 30' fiom the normal to the gold surface.rr) The parallel orientationof the alkanethiols on graphite suggeststhat they are physisorbed on th ...
M.Sc. II - Punjabi University
... vibrations, selection rules, force constant, vibration in polyatomic molecules, effects giving rise to absorption bands, Group vibrations, limitation of group vibration concept. Raman Spectroscopy : Introduction, selection rules, polarised and depolarised Raman lines, significance of nomenclature us ...
... vibrations, selection rules, force constant, vibration in polyatomic molecules, effects giving rise to absorption bands, Group vibrations, limitation of group vibration concept. Raman Spectroscopy : Introduction, selection rules, polarised and depolarised Raman lines, significance of nomenclature us ...
$doc.title
... • The C=O group is strongly electron-‐withdrawing, making the N a very weak base • AddiHon of a proton occurs on O but this destroys the double bond character of C=O as a requirement of stabiliza ...
... • The C=O group is strongly electron-‐withdrawing, making the N a very weak base • AddiHon of a proton occurs on O but this destroys the double bond character of C=O as a requirement of stabiliza ...
Introduction to Nanochemistry
... Spectrophotometry and Colorimetry Theory of spectrophotometry and colorimetry, Beer's law, Deviation from Beer's law, absorptivity, Photometric accuracy. Spectrophotometric titrations and titration curves and applications to quantitative analysis. Solvent extraction : Distribution constant and distr ...
... Spectrophotometry and Colorimetry Theory of spectrophotometry and colorimetry, Beer's law, Deviation from Beer's law, absorptivity, Photometric accuracy. Spectrophotometric titrations and titration curves and applications to quantitative analysis. Solvent extraction : Distribution constant and distr ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.