lab 15: hydrocarbons
... 3. Check each tube for layers. Add more drops of a particular reagent if you can’t determine the solubility with the amount given. Record your observations about the solubility of each hydrocarbon in hexane (a typical hydrocarbon solvent). 4. Dispose of hydrocarbons in the designated waste container ...
... 3. Check each tube for layers. Add more drops of a particular reagent if you can’t determine the solubility with the amount given. Record your observations about the solubility of each hydrocarbon in hexane (a typical hydrocarbon solvent). 4. Dispose of hydrocarbons in the designated waste container ...
chapter twenty-one transition metals and coordination chemistry
... The crystal field diagrams are different because the geometries of where the ligands point is different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 2 ...
... The crystal field diagrams are different because the geometries of where the ligands point is different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 2 ...
ALKANES – STRUCTURE, PROPERTIES, AND SYNTHESIS
... Predict the relative stabilities of conformations of alkanes and cycloalkanes, and draw and describe the most stable conformations in these systems. Also, give or identify the types of strain present in different conformations in these systems, and use this information to explain relative stabilitie ...
... Predict the relative stabilities of conformations of alkanes and cycloalkanes, and draw and describe the most stable conformations in these systems. Also, give or identify the types of strain present in different conformations in these systems, and use this information to explain relative stabilitie ...
ExamView - 2011-2012 AP Chemistry of Life Unit Exam.tst
... 40) Which of the following statements is true for the class of biological molecules known as lipids? A) They are insoluble in water. B) They are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate. C) They contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates. D) They are made by dehydration reactions. E) ...
... 40) Which of the following statements is true for the class of biological molecules known as lipids? A) They are insoluble in water. B) They are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate. C) They contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates. D) They are made by dehydration reactions. E) ...
Chapter 8 "Ionic versus Covalent Bonding"
... energy(U)3, the enthalpy change that occurs when a solid ionic compound is transformed into gaseous ions. For covalent compounds, this energy is called the bond energy4, which is the enthalpy change that occurs when a given bond in a gaseous molecule is broken. 3. Each chemical bond is characterized ...
... energy(U)3, the enthalpy change that occurs when a solid ionic compound is transformed into gaseous ions. For covalent compounds, this energy is called the bond energy4, which is the enthalpy change that occurs when a given bond in a gaseous molecule is broken. 3. Each chemical bond is characterized ...
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry
... When a C atom is single-bonded to another C atom, the bond is a strong covalent bond that is difficult to break. Thus, the sites in organic molecules that contain C2C bonds are not reactive. However, double or triple bonds between C atoms are more reactive. The second and third bonds formed in a mul ...
... When a C atom is single-bonded to another C atom, the bond is a strong covalent bond that is difficult to break. Thus, the sites in organic molecules that contain C2C bonds are not reactive. However, double or triple bonds between C atoms are more reactive. The second and third bonds formed in a mul ...
10.1 Intro to Organic Chemistry 10.1 Organic Chemistry
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
Intermolecular forces and molecules
... boiling point. Do electronegativity differences account for this difference? Due to the molecule geometry, the bond dipoles in each cancel. In this case, differences in molar mass (polarizability) account for the variation in boiling point. Having noted that molar mass affects van der Waals forces, ...
... boiling point. Do electronegativity differences account for this difference? Due to the molecule geometry, the bond dipoles in each cancel. In this case, differences in molar mass (polarizability) account for the variation in boiling point. Having noted that molar mass affects van der Waals forces, ...
Amines
... • The basicity of the amines depends on the ability of the lone pair none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) sub ...
... • The basicity of the amines depends on the ability of the lone pair none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) sub ...
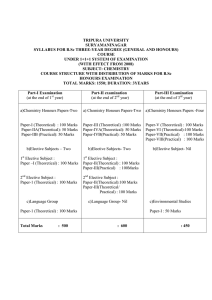
TRIPURA UNIVERSITY SURYAMANINAGAR SYLLABUS FOR B.Sc THREE-YEAR DEGREE (GENERAL AND HONOURS) COURSE
... g) One Compulsory question (Q.No.1) is to be set with six(short/ multiple choice/ both) questions of 1 mark each from two units, of which three are to be answered. h) Two questions of 15 marks each are to be set from each unit, out of which one question is to be answered. Each question of 15 marks m ...
... g) One Compulsory question (Q.No.1) is to be set with six(short/ multiple choice/ both) questions of 1 mark each from two units, of which three are to be answered. h) Two questions of 15 marks each are to be set from each unit, out of which one question is to be answered. Each question of 15 marks m ...
Sodium acetate method for determining CEC of cadmium
... 3.6%. Organic matter was the main contributor to CEC; but in this investigation, the organic bonding fraction represented only 2.3%. Most of the Cd that was bound to organic matter was plausibly extracted in the exchangeable fraction. Figures 1 and 2 present the distributions of each fraction of Cd ...
... 3.6%. Organic matter was the main contributor to CEC; but in this investigation, the organic bonding fraction represented only 2.3%. Most of the Cd that was bound to organic matter was plausibly extracted in the exchangeable fraction. Figures 1 and 2 present the distributions of each fraction of Cd ...
A Direct Access to 3-(2-Oxoalkyl)indoles via
... for C-C bond formation. More recently, we have found that AlCl3-induced acylation could be utilized as a novel route to 3-(2-oxoalkyl)indoles 3 by reacting 3-methylindole 1 with acyl chloride 2 under the Friedel-Crafts reaction condition (Scheme 1). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first ex ...
... for C-C bond formation. More recently, we have found that AlCl3-induced acylation could be utilized as a novel route to 3-(2-oxoalkyl)indoles 3 by reacting 3-methylindole 1 with acyl chloride 2 under the Friedel-Crafts reaction condition (Scheme 1). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first ex ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook
... Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between positive ions and negative ions is called ionic bonding. In a purely ionic bond, the metal atom gives up its electron or electrons to the nonmetal atom. In covalent bonding, a bond forms from the sharing of electron pairs between t ...
... Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between positive ions and negative ions is called ionic bonding. In a purely ionic bond, the metal atom gives up its electron or electrons to the nonmetal atom. In covalent bonding, a bond forms from the sharing of electron pairs between t ...
A Study of the Behavior of Alkyl Side Chains Phenols and Arenes in
... abandoned. Therefore, it was the cyclization alkyl chains of the considered compounds that was preferred. The preference for the cyclization arises also from the fact that alicyclic-aromatic ethers with five- and six-membered alicyclic rings with oxygen and an interconnected aromatic ring (Figure 2) ...
... abandoned. Therefore, it was the cyclization alkyl chains of the considered compounds that was preferred. The preference for the cyclization arises also from the fact that alicyclic-aromatic ethers with five- and six-membered alicyclic rings with oxygen and an interconnected aromatic ring (Figure 2) ...
High-Valent Transition-Metal Alkylidene
... Ti-, Zr-, and Hf-alkylidenes as a function of alkylidene substituent (H, C1, Li, SiH3, CH3, O H ) and metal ligand (H, C1) are summarized in Figures 1-3, respectively. A force field analysis establishes all the geometries shown in these figures as minima. The geometries of the analogous Ti-, Zr-, an ...
... Ti-, Zr-, and Hf-alkylidenes as a function of alkylidene substituent (H, C1, Li, SiH3, CH3, O H ) and metal ligand (H, C1) are summarized in Figures 1-3, respectively. A force field analysis establishes all the geometries shown in these figures as minima. The geometries of the analogous Ti-, Zr-, an ...
Number of students performing at
... occur following either an SN1 or an SN2 mechanism. Based on the structure of each of the alcohols, one can make a prediction on the mechanism of its reaction with HBr, as shown above to the right. The profile, on the other hand, definitely reflects a stepwise reaction, i.e. one that follows an SN1 m ...
... occur following either an SN1 or an SN2 mechanism. Based on the structure of each of the alcohols, one can make a prediction on the mechanism of its reaction with HBr, as shown above to the right. The profile, on the other hand, definitely reflects a stepwise reaction, i.e. one that follows an SN1 m ...
Fulltext PDF
... coordinate donation of an electron pair from the carbene carbon atom and CO ligands. Competition for the d-electrons of the metal takes place between bonding ligands such as CO, and the empty p-orbital on carbon. This in turn, is stabilized by overlap with electron pairs on the heteroatom substitu ...
... coordinate donation of an electron pair from the carbene carbon atom and CO ligands. Competition for the d-electrons of the metal takes place between bonding ligands such as CO, and the empty p-orbital on carbon. This in turn, is stabilized by overlap with electron pairs on the heteroatom substitu ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds • Unlike in alkenes and alkynes, electrons do not sit between two atoms. • Electrons are delocalized; this stabilizes aromatic compounds. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
Answers
... oxidized further to the caboxylic acid while propanone is not easily oxidized. The Tollens’ Test for aldehydes makes use of this difference in properties. (Tollens’ reagent is made by adding sodium hydroxide to silver nitrate solution to give a precipitate of silver hydroxide and then redissolving t ...
... oxidized further to the caboxylic acid while propanone is not easily oxidized. The Tollens’ Test for aldehydes makes use of this difference in properties. (Tollens’ reagent is made by adding sodium hydroxide to silver nitrate solution to give a precipitate of silver hydroxide and then redissolving t ...
intestazione repositorydell`ateneo Layer charge and heavy metals
... charge (montmorillonite and vermiculite); iii) a comparison between our results and literature data. This study will also be supported by several different experimental techniques such as chemical and thermal analyses, X-ray powder diffraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Based on our data Cd ...
... charge (montmorillonite and vermiculite); iii) a comparison between our results and literature data. This study will also be supported by several different experimental techniques such as chemical and thermal analyses, X-ray powder diffraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Based on our data Cd ...
chapter19
... trisubstituted alkenes but not tetrasubstituted alkenes The reaction yields a pure alkene of known structure For comparison, addition of CH3MgBr to cyclohexanone and dehydration with, yields a mixture of two alkenes ...
... trisubstituted alkenes but not tetrasubstituted alkenes The reaction yields a pure alkene of known structure For comparison, addition of CH3MgBr to cyclohexanone and dehydration with, yields a mixture of two alkenes ...
Organic Chemistry
... nature of their motion. Now, however, I saw how, frequently, two smaller atoms united to form a pair; how a larger one embraced the two smaller ones; how still larger ones kept hold of three or even four of the smaller; whilst the whole kept whirling in a giddy dance. I saw how the larger ones forme ...
... nature of their motion. Now, however, I saw how, frequently, two smaller atoms united to form a pair; how a larger one embraced the two smaller ones; how still larger ones kept hold of three or even four of the smaller; whilst the whole kept whirling in a giddy dance. I saw how the larger ones forme ...
Phenol
... 7) Synthesis of Phenolic aldehydes (Reimer-Tiemann reaction): Treatment of Phenol with chloroform and aqueous hydroxide introduces an aldehyde group, –CHO, into the aromatic ring, generally ortho to the –OH. This reaction is known as the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. ...
... 7) Synthesis of Phenolic aldehydes (Reimer-Tiemann reaction): Treatment of Phenol with chloroform and aqueous hydroxide introduces an aldehyde group, –CHO, into the aromatic ring, generally ortho to the –OH. This reaction is known as the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. ...
Table of Contents - slccscience`s Home Page
... elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a separate discipline, but there is a very good reason for this. There are about 1.5 million known inorganic co ...
... elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a separate discipline, but there is a very good reason for this. There are about 1.5 million known inorganic co ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.