sinn fein response to governments banking inquiry proposals
... continuation of the bank levy; and for the Financial Regulator to ensure that low income groups have equal access to borrowing from all credit institutions in order to ensure that such income groups are not forced to rely on high costs sources of credit (moneylenders). The report looked at bank cha ...
... continuation of the bank levy; and for the Financial Regulator to ensure that low income groups have equal access to borrowing from all credit institutions in order to ensure that such income groups are not forced to rely on high costs sources of credit (moneylenders). The report looked at bank cha ...
Economic History of the US
... Industrial Age…rise of Investment Banks Peculiar to US Big companies raise money from savers directly… …by issuing stocks and bonds Underwriting and trading ...
... Industrial Age…rise of Investment Banks Peculiar to US Big companies raise money from savers directly… …by issuing stocks and bonds Underwriting and trading ...
Banks
... Lowering the interest payments on reserves held at the Fed increases the money supply Increasing the interest payments on reserves held at the Fed decreases the money supply Crisis of 2008 ◦ Before: Fed did not pay interest on reserves ◦ After: Fed has been paying rate about equal to federal funds r ...
... Lowering the interest payments on reserves held at the Fed increases the money supply Increasing the interest payments on reserves held at the Fed decreases the money supply Crisis of 2008 ◦ Before: Fed did not pay interest on reserves ◦ After: Fed has been paying rate about equal to federal funds r ...
Lesson: The Great Depression
... were many local or state banks •The Bank Panic of 1857 had little to no effect ...
... were many local or state banks •The Bank Panic of 1857 had little to no effect ...
Homework Assignment:
... M1; currency, traveler’s checks, demand deposits, other checkable deposits M2; M1 plus savings deposits, small time deposits, money market mutual funds M3, M2 plus large time deposits, repurchase agreements, Eurodollars, and institution only money market mutual fund balances ...
... M1; currency, traveler’s checks, demand deposits, other checkable deposits M2; M1 plus savings deposits, small time deposits, money market mutual funds M3, M2 plus large time deposits, repurchase agreements, Eurodollars, and institution only money market mutual fund balances ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... which represent the core bank products. Many of these competitors target large firms with the largest loans and deposits. Many banks have similarly decided not to take as much credit risk. As such, they originate loans then securitize them. Securitization effectively moves the loans off bank balance ...
... which represent the core bank products. Many of these competitors target large firms with the largest loans and deposits. Many banks have similarly decided not to take as much credit risk. As such, they originate loans then securitize them. Securitization effectively moves the loans off bank balance ...
Beyond Banking South Asia Expereinces
... no access to savings or credits – 59% SME have no loan or overdraft – Source IFC statistics -Unbanked and under banked Drift towards Class Banking – from Mass Banking – Limited Credit flow SME’s- Banking Industry Consolidations in Urban areas Focus on FEE based income – Moving away from financia ...
... no access to savings or credits – 59% SME have no loan or overdraft – Source IFC statistics -Unbanked and under banked Drift towards Class Banking – from Mass Banking – Limited Credit flow SME’s- Banking Industry Consolidations in Urban areas Focus on FEE based income – Moving away from financia ...
What Counts as Money
... Changes in either required reserve ratio or discount rate could set off the process of deposit creation or deposit destruction in much the same way outlined in this chapter In reality, neither of these policy tools is used very often ...
... Changes in either required reserve ratio or discount rate could set off the process of deposit creation or deposit destruction in much the same way outlined in this chapter In reality, neither of these policy tools is used very often ...
Central bank - WordPress.com
... SLR in a way ensures the solvency of commercial banks. By determining SLR,RBI, in a way, compels the commercial banks to invest in government securities like government bonds. ...
... SLR in a way ensures the solvency of commercial banks. By determining SLR,RBI, in a way, compels the commercial banks to invest in government securities like government bonds. ...
Occupant Load
... The critical feature of this model is that currently the economy’s money supply is created by banks, through debt, rather than being created debt-free by the government. Our analytical and simulation results fully validate Fisher’s (1936) claims. The Chicago Plan could significantly reduce business c ...
... The critical feature of this model is that currently the economy’s money supply is created by banks, through debt, rather than being created debt-free by the government. Our analytical and simulation results fully validate Fisher’s (1936) claims. The Chicago Plan could significantly reduce business c ...
1 An extended credit boom
... (a) Five-year rolling average of annualised volatility of quarter-on-quarter growth rate. 2008 data are to Q2. ...
... (a) Five-year rolling average of annualised volatility of quarter-on-quarter growth rate. 2008 data are to Q2. ...
ExamView Pro - Untitled.tst
... b. coins are more portable d. coins are more limited in supply ____ 12. What happens during a bank run? a. The government orders a bank to close. b. States charter more banks than needed. c. The price of gold suddenly increases. d. More customers withdraw money than the bank has on hand. ____ 13. Wh ...
... b. coins are more portable d. coins are more limited in supply ____ 12. What happens during a bank run? a. The government orders a bank to close. b. States charter more banks than needed. c. The price of gold suddenly increases. d. More customers withdraw money than the bank has on hand. ____ 13. Wh ...
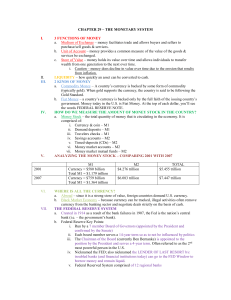
CHAPTER 29 – THE MONETARY SYSTEM 3 FUNCTIONS OF
... to slow it down, it will sell treasury bonds from its portfolio to the public in the nation’s bond markets. Selling bonds, in essence, acts as a vacuum cleaner, sucking money out of the economy. 2. When the FED wants to put money into circulation to speed up the economy, it will go into the bond mar ...
... to slow it down, it will sell treasury bonds from its portfolio to the public in the nation’s bond markets. Selling bonds, in essence, acts as a vacuum cleaner, sucking money out of the economy. 2. When the FED wants to put money into circulation to speed up the economy, it will go into the bond mar ...
a. projected excess reserves of the banking system
... Private sector reserves include Foreign Currency Denominated Accounts (FCDAs) and ADBs own forex positions million per month is used in this calculation ...
... Private sector reserves include Foreign Currency Denominated Accounts (FCDAs) and ADBs own forex positions million per month is used in this calculation ...
Slides 2
... reduce monitoring effort vis-à-vis borrowers Worse in banking than in other industries Opacity and long-term maturity of banking assets ...
... reduce monitoring effort vis-à-vis borrowers Worse in banking than in other industries Opacity and long-term maturity of banking assets ...
the impact of government policy and regulation on banking
... The Glass-Steagall Act, passed by the U.S. Congress in 1933, was one of the most comprehensive pieces of banking legislation in American history. It created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation to insure smaller-size bank deposits, imposed interest-rate ceilings on bank deposits, broadened the ...
... The Glass-Steagall Act, passed by the U.S. Congress in 1933, was one of the most comprehensive pieces of banking legislation in American history. It created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation to insure smaller-size bank deposits, imposed interest-rate ceilings on bank deposits, broadened the ...
Banks
... • a medium of exchange ü In economics, money is a broad term that refers to any financial instrument that can fulfill the functions of money ü Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a particular country or so ...
... • a medium of exchange ü In economics, money is a broad term that refers to any financial instrument that can fulfill the functions of money ü Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a particular country or so ...
Diamond Bank Plc Audited Financial Results for the year ended 31st
... banking app, “Diamond Mobile” currently has over 1 million active subscribers on its platform. Diamond Bank has over the years leveraged on its underlying resilience to grow its asset base and to successfully retain its key business relationships. It has also played a leading role in partnering with ...
... banking app, “Diamond Mobile” currently has over 1 million active subscribers on its platform. Diamond Bank has over the years leveraged on its underlying resilience to grow its asset base and to successfully retain its key business relationships. It has also played a leading role in partnering with ...
A Look at Banking Deregulation and its Effects on the U.S.
... Found no significant cost savings, on average, attributed to mergers Submit that when banks do become more profitable after mergers it may be due to product mix, as opposed to cost efficiencies ...
... Found no significant cost savings, on average, attributed to mergers Submit that when banks do become more profitable after mergers it may be due to product mix, as opposed to cost efficiencies ...
Money - Dpatterson
... .1. affects the money supply (the point of monetary policy) 2. if the Federal Reserve Bank wants to reduce the money supply – tight money– it will raise reserve requirements. 3. if it wants to increase money supply and have easy money, it will reduce the reserve requirement. ...
... .1. affects the money supply (the point of monetary policy) 2. if the Federal Reserve Bank wants to reduce the money supply – tight money– it will raise reserve requirements. 3. if it wants to increase money supply and have easy money, it will reduce the reserve requirement. ...
Notes for Chapter 13 - FIU Faculty Websites
... its components are actively used and widely accepted for making payments. Credit Cards are not part of any money supply. Credit cards are just that, a credit account. An account you are borrowing from, and there for is not a payment. Only when you pay your bill with cash or your checking account are ...
... its components are actively used and widely accepted for making payments. Credit Cards are not part of any money supply. Credit cards are just that, a credit account. An account you are borrowing from, and there for is not a payment. Only when you pay your bill with cash or your checking account are ...
Economics: Module 4 Note Taking Guide
... A decreasing reserve req. = banks keep ______ $ in vault = banks loan _______ $ to people. An increasing reserve req. = banks keep ______ $ in vault = ________ loans available to people. Open Market Operations ______________________________________________________________________ Buy bonds = FED ___ ...
... A decreasing reserve req. = banks keep ______ $ in vault = banks loan _______ $ to people. An increasing reserve req. = banks keep ______ $ in vault = ________ loans available to people. Open Market Operations ______________________________________________________________________ Buy bonds = FED ___ ...