Economics Worksheet: Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve
... The percentage of money that all banks must keep on hand, of all their deposits. ...
... The percentage of money that all banks must keep on hand, of all their deposits. ...
Institution
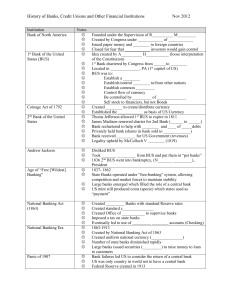
... US mint still produced coins (specie) which states used as “payment” Created _________ Banks with standard Reserve rates Created standard c_______________ Created Office of ___________ to supervise banks Imposed a tax on state banks Eventually led to use of _________ ________ accounts (Checking) ...
... US mint still produced coins (specie) which states used as “payment” Created _________ Banks with standard Reserve rates Created standard c_______________ Created Office of ___________ to supervise banks Imposed a tax on state banks Eventually led to use of _________ ________ accounts (Checking) ...
Federal Reserve System
... • holds member bank reserves and other deposits • makes loans to financial institutions when necessary • provides wire transfer services (ETS) √ Banker to the Federal Government • maintains the Treasury Department’s checkbook • issues and redeems government bonds and other securities √ Supervises an ...
... • holds member bank reserves and other deposits • makes loans to financial institutions when necessary • provides wire transfer services (ETS) √ Banker to the Federal Government • maintains the Treasury Department’s checkbook • issues and redeems government bonds and other securities √ Supervises an ...
MB-ch13-MSProcess
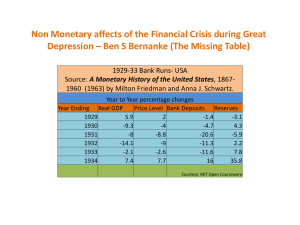
... government securities (Treasury bills, bonds, notes) for two reasons: (i) buying and selling of government securities is one of the CB’s major tool (known as OMO) in controlling the economy’s money supply, and (ii) holding government securities provides a return. 2. Discount loans: The CB makes loan ...
... government securities (Treasury bills, bonds, notes) for two reasons: (i) buying and selling of government securities is one of the CB’s major tool (known as OMO) in controlling the economy’s money supply, and (ii) holding government securities provides a return. 2. Discount loans: The CB makes loan ...
AP Macro Economics Monetary Policy When a commercial bank
... The three main tools of monetary policy are; ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... The three main tools of monetary policy are; ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
2/27 - David Youngberg
... Anatomy of banks a. Assets—uses of funds b. Liabilities—sources of funds c. Capital—bank’s net worth; the cushion d. Assets = Liabilities + Capital Profit making a. Banks make money by turning their liabilities into assets, such as lending out a deposit (a process called asset transformation). b. Re ...
... Anatomy of banks a. Assets—uses of funds b. Liabilities—sources of funds c. Capital—bank’s net worth; the cushion d. Assets = Liabilities + Capital Profit making a. Banks make money by turning their liabilities into assets, such as lending out a deposit (a process called asset transformation). b. Re ...
Bank One
... Homework: In Westlandia, the public holds 50% of M1 in the form of currency, and the required reserve ratio is 20%. 1. Estimate how much the money supply will increase in response to a new cash deposit of $500 by completing the accompanying table. (Hint: The first row shows that the bank must hold $ ...
... Homework: In Westlandia, the public holds 50% of M1 in the form of currency, and the required reserve ratio is 20%. 1. Estimate how much the money supply will increase in response to a new cash deposit of $500 by completing the accompanying table. (Hint: The first row shows that the bank must hold $ ...
Banking and Money Creation
... – Money is a new form of slavery, and distinguishable from the old simply by the fact that it is impersonal—that there is no human relation between master and slave. ...
... – Money is a new form of slavery, and distinguishable from the old simply by the fact that it is impersonal—that there is no human relation between master and slave. ...
Chapter 15 Glossary - Banking and Financial Systems 2013
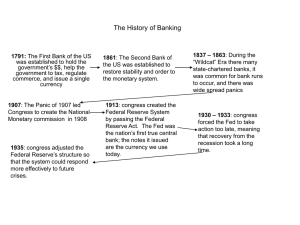
... Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). An independent federal agency established in 1933 that provides deposit insurance up to $250,000 for depositors in insured banks and thrifts in the case of bank failure. Federal Reserve Act. Established the Federal Reserve System; passed in 1913. fiat mo ...
... Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). An independent federal agency established in 1933 that provides deposit insurance up to $250,000 for depositors in insured banks and thrifts in the case of bank failure. Federal Reserve Act. Established the Federal Reserve System; passed in 1913. fiat mo ...
Activity 11 - The Banking System and Monetary Policy
... Assume that the required reserve ratio in the United States is currently 20%. Answer the following questions about the fractional reserve banking system, the money multiplier, and monetary policy. ...
... Assume that the required reserve ratio in the United States is currently 20%. Answer the following questions about the fractional reserve banking system, the money multiplier, and monetary policy. ...
Chapter 16
... 3. A(n) policy increases the money supply. 5. Actions the Fed takes to influence the real GDP and the inflation rate are called policy. 6. Funds over and above Fed requirements make up a bank’s ...
... 3. A(n) policy increases the money supply. 5. Actions the Fed takes to influence the real GDP and the inflation rate are called policy. 6. Funds over and above Fed requirements make up a bank’s ...
Econ2012: Principles of Macroeconomics
... Name____________________________ Class ____________________________ ...
... Name____________________________ Class ____________________________ ...