The Federal Reserve System
... to keep a fraction of their deposits in legal reserves • Legal reserves- coins and currency that must be kept in the vault, and deposits in the fed district banks. • Reserve requirement rule stating the percentage of total deposits that the bank must have in legal reserves ...
... to keep a fraction of their deposits in legal reserves • Legal reserves- coins and currency that must be kept in the vault, and deposits in the fed district banks. • Reserve requirement rule stating the percentage of total deposits that the bank must have in legal reserves ...
22-Nov-2012 - Public Banking
... Cheap credit lines to state and local government agencies. Low-interest loans for designated local projects. Redirects credit away from speculation toward local lending; mandate to serve the public interest. • Underwrites municipal bonds, avoiding high cost of fees, “insurance” (swaps), and bond mar ...
... Cheap credit lines to state and local government agencies. Low-interest loans for designated local projects. Redirects credit away from speculation toward local lending; mandate to serve the public interest. • Underwrites municipal bonds, avoiding high cost of fees, “insurance” (swaps), and bond mar ...
Financial Institutions Unit 6
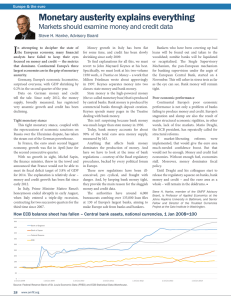
... Loanable funds Demand for loanable funds Supply of loanable funds Savings (related to loanable funds) (Financial) investment ...
... Loanable funds Demand for loanable funds Supply of loanable funds Savings (related to loanable funds) (Financial) investment ...
Lecture28(Ch24)
... Third key idea in the story: The Fed can control the amount of bank reserves in the economy • How? (Recall that bank reserves are simply deposits that banks have at the Fed) • By buying and selling “things” and paying or getting paid with the reserves, the Fed can determine the total amount of rese ...
... Third key idea in the story: The Fed can control the amount of bank reserves in the economy • How? (Recall that bank reserves are simply deposits that banks have at the Fed) • By buying and selling “things” and paying or getting paid with the reserves, the Fed can determine the total amount of rese ...
Econ 204 Practice Qu..
... a. Money demand is sometimes called the liquidity preference function. b. An increase in interest rates will move left along the money demand curve c. An increase in output will shift the money demand curve to the right d. A decrease in price levels will shift the money demand curve to the left e. N ...
... a. Money demand is sometimes called the liquidity preference function. b. An increase in interest rates will move left along the money demand curve c. An increase in output will shift the money demand curve to the right d. A decrease in price levels will shift the money demand curve to the left e. N ...
Policy Actions to Mitigate Bank
... gains and socializing losses. Participants in no other industry get as self-righteously angry when public officials – particularly, central bankers – fail to come at once to their rescue when they get into (well-deserved) trouble.” (Martin Wolf, Financial Times, Jan 15, 2008). ...
... gains and socializing losses. Participants in no other industry get as self-righteously angry when public officials – particularly, central bankers – fail to come at once to their rescue when they get into (well-deserved) trouble.” (Martin Wolf, Financial Times, Jan 15, 2008). ...
I
... by central banks. Bank money is produced by commercial banks through deposit creation. Keynes spends many pages in the Treatise dealing with bank money. This isn’t surprising because bank money was much larger than state money in 1930. Today, bank money accounts for about 90% of the total euro area ...
... by central banks. Bank money is produced by commercial banks through deposit creation. Keynes spends many pages in the Treatise dealing with bank money. This isn’t surprising because bank money was much larger than state money in 1930. Today, bank money accounts for about 90% of the total euro area ...
Company Name - University of Wisconsin–La Crosse
... are financial assets that can’t be directly used as a medium of exchange but can readily be converted into cash or checkable bank deposits. ...
... are financial assets that can’t be directly used as a medium of exchange but can readily be converted into cash or checkable bank deposits. ...
Class 3 9/6 Money & Banking Power Point Presentaton
... must keep 10% of deposits on reserve and can lend the other 90%. In theory, $1 deposited in a Bank with a 10% RR results in the creation of another $10 in credit through the “multiplier effect” [$1/0.1 = $10]. ...
... must keep 10% of deposits on reserve and can lend the other 90%. In theory, $1 deposited in a Bank with a 10% RR results in the creation of another $10 in credit through the “multiplier effect” [$1/0.1 = $10]. ...
starting over safely: rebuilding banking systems
... • GDP growth tends to be adversely affected – But could be misleading to interpret as causal ...
... • GDP growth tends to be adversely affected – But could be misleading to interpret as causal ...
Chapter 8
... Work through the sequence of changes in excess reserves, the interest rate, loan making, the money supply, total spending, and economic activity for an increase and a decrease in excess reserves. ...
... Work through the sequence of changes in excess reserves, the interest rate, loan making, the money supply, total spending, and economic activity for an increase and a decrease in excess reserves. ...
Economic Firefight – An Inside View
... part of banks’ funding, not risk capital. owned by pension funds, insurance companies, credit unions, multinational companies, and other long-term providers of funds. Same investors that buy Government debt. covered by the Bank Guarantee. legally entitled to same treatment as deposits. ...
... part of banks’ funding, not risk capital. owned by pension funds, insurance companies, credit unions, multinational companies, and other long-term providers of funds. Same investors that buy Government debt. covered by the Bank Guarantee. legally entitled to same treatment as deposits. ...
Money and Monetary Policy
... Money Creation Recall: deposit-takers receive deposits from savers and lend to borrowers, while keeping some cash reserves on hand for withdrawals by deposits By charging higher interest rates to lenders than they pay to depositors, deposit-takers make profit In a sense through this process, ch ...
... Money Creation Recall: deposit-takers receive deposits from savers and lend to borrowers, while keeping some cash reserves on hand for withdrawals by deposits By charging higher interest rates to lenders than they pay to depositors, deposit-takers make profit In a sense through this process, ch ...
Money, Prices, and the Federal Reserve
... Banks and the Creation of Money We will show the changes in assets and liabilities of a bank in response to deposit and loan activities. Deposits into checking accounts are liabilities of a bank. Cash is an asset. Assets = Liabilities for a Balance Sheet to be in balance. ...
... Banks and the Creation of Money We will show the changes in assets and liabilities of a bank in response to deposit and loan activities. Deposits into checking accounts are liabilities of a bank. Cash is an asset. Assets = Liabilities for a Balance Sheet to be in balance. ...
Proceedings of 4th Global Business and Finance Research Conference
... Performance in E-Business under Sanction Conditions Omid Pour Mirza and Arezou Pour Mirza The purpose of the present study is to find out the CRM functioning and effectiveness in private banking sectors of Iran, as perceived by the customers. It also attempts to find the relationship between percept ...
... Performance in E-Business under Sanction Conditions Omid Pour Mirza and Arezou Pour Mirza The purpose of the present study is to find out the CRM functioning and effectiveness in private banking sectors of Iran, as perceived by the customers. It also attempts to find the relationship between percept ...
Unit 4 Test Review Savings, Investment and the Financial System 1
... b. If the current interest rate was above equilibrium, what would eventually happen to interest rates? c. If the current interest rate was below equilibrium, what would eventually happen to interest rates? Banking and Money Creation 20. Why is there a money multiplier and what is its formula? Why in ...
... b. If the current interest rate was above equilibrium, what would eventually happen to interest rates? c. If the current interest rate was below equilibrium, what would eventually happen to interest rates? Banking and Money Creation 20. Why is there a money multiplier and what is its formula? Why in ...
Type Programme Name or Title Here
... The changing nature of the financial sector – who will carry the risks? • Financial services – growth in intermediaries carrying very low balance sheet risk, low threat to national economy and security • But which institutions will take on balance sheet risks? Which countries can afford this? • Ris ...
... The changing nature of the financial sector – who will carry the risks? • Financial services – growth in intermediaries carrying very low balance sheet risk, low threat to national economy and security • But which institutions will take on balance sheet risks? Which countries can afford this? • Ris ...
Topic Outline - Matthew H. Shapiro
... Central Bank and the Money Supply Name of the USA central bank: ...
... Central Bank and the Money Supply Name of the USA central bank: ...
Slide 1 - Bank of America Merrill Lynch
... With respect to investments in money market mutual funds, you should carefully consider a fund’s investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses before investing. Although money market mutual funds seek to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, it is possible to lose money by ...
... With respect to investments in money market mutual funds, you should carefully consider a fund’s investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses before investing. Although money market mutual funds seek to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, it is possible to lose money by ...
Chapter 14 Review Questions
... for them by drawing checks. As a result, commercial bank reserves will: A) increase by $10 billion. B) remain unchanged. C) decrease by $2 billion. D) increase by $2 billion. 10. If the Fed were to increase the legal reserve ratio, we would expect: A) lower interest rates, an expanded GDP, and depre ...
... for them by drawing checks. As a result, commercial bank reserves will: A) increase by $10 billion. B) remain unchanged. C) decrease by $2 billion. D) increase by $2 billion. 10. If the Fed were to increase the legal reserve ratio, we would expect: A) lower interest rates, an expanded GDP, and depre ...
2011 result: Shareholders restate confidence in Zenith`s management
... December, 2011, saying that it attested to the doggedness of the management team. A cross section of the shareholders that spoke with Vanguard noted that the result indicates the determination of the board and management to ensure that the bank retains its leadership position in the industry. They a ...
... December, 2011, saying that it attested to the doggedness of the management team. A cross section of the shareholders that spoke with Vanguard noted that the result indicates the determination of the board and management to ensure that the bank retains its leadership position in the industry. They a ...
Central Banks
... drawn on, the details of the facilities through which US dollar liquidity would be provided to the Canadian financial system would depend on the specific market circumstances at that time. The Bank of Canada is closely monitoring global market developments and is committed to providing liquidity a ...
... drawn on, the details of the facilities through which US dollar liquidity would be provided to the Canadian financial system would depend on the specific market circumstances at that time. The Bank of Canada is closely monitoring global market developments and is committed to providing liquidity a ...
Slide 1
... priced in €, eliminate hedging costs XOF is a managed currency. The importer’s bank (wherever situated in WAEMU) must wait for BCEAO to release FX. Banks can help here ...
... priced in €, eliminate hedging costs XOF is a managed currency. The importer’s bank (wherever situated in WAEMU) must wait for BCEAO to release FX. Banks can help here ...