Star Classification
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
Orion
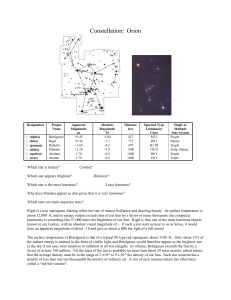
... in the sky, visible to the naked eye, and rewarding in telescopes of every size, from the smallest glasses to the greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellati ...
... in the sky, visible to the naked eye, and rewarding in telescopes of every size, from the smallest glasses to the greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellati ...
August Evening Skies
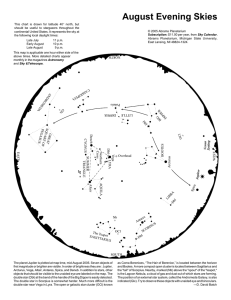
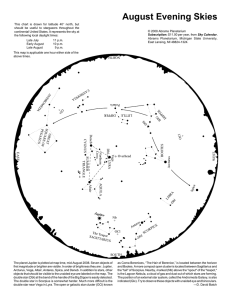
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
Review Day
... burning at about 15 million degrees F Radiation Zone: Heat travels outward through the zone to the next layer. Convection Zone: Area where currents of heated materials transfer heat to the exterior and carry cooler area in. ...
... burning at about 15 million degrees F Radiation Zone: Heat travels outward through the zone to the next layer. Convection Zone: Area where currents of heated materials transfer heat to the exterior and carry cooler area in. ...
Ch 29 Sun and Solar Activity
... atmosphere, disrupt longrange radios, satell. & radar • solar flame animation ...
... atmosphere, disrupt longrange radios, satell. & radar • solar flame animation ...
Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... a. Explosion; atoms form; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point. b. All matter concentrated at a single point; explosion; atoms form; stars form. c. Explosion; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point; atoms form. d. Stars form; atoms form; all matter concentrated at a s ...
... a. Explosion; atoms form; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point. b. All matter concentrated at a single point; explosion; atoms form; stars form. c. Explosion; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point; atoms form. d. Stars form; atoms form; all matter concentrated at a s ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram ...
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram ...
SNC1PL Celestial Objects and Constellations
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
Constellations and Asterisms
... the shapes of microscopes and telescopes. As you can probably infer, these sets are so drastically different in shape from each other reflecting who was looking up into the sky. The early constellations were most likely seen by the naked eye by cultures wanting to see these creatures mapped in the s ...
... the shapes of microscopes and telescopes. As you can probably infer, these sets are so drastically different in shape from each other reflecting who was looking up into the sky. The early constellations were most likely seen by the naked eye by cultures wanting to see these creatures mapped in the s ...
Observing Information for Waddesdon, 4th October 2014
... The youngest major crater, maybe only 100 million years old. Has an extensive ray system covering much of the visible side of the Moon. 86Km in diameter. Clavius An impressive crater in the Southern highlands. 225Km in diameter. Has a string of craters across it that form a curved line with the crat ...
... The youngest major crater, maybe only 100 million years old. Has an extensive ray system covering much of the visible side of the Moon. 86Km in diameter. Clavius An impressive crater in the Southern highlands. 225Km in diameter. Has a string of craters across it that form a curved line with the crat ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... b. apparent magnitude – how bright a star APPEARS to be from the point of view of the observer. c. absolute magnitude – how bright a star REALLY is 2) As you move up the Y axis on the diagram, what happens to brightness? ...
... b. apparent magnitude – how bright a star APPEARS to be from the point of view of the observer. c. absolute magnitude – how bright a star REALLY is 2) As you move up the Y axis on the diagram, what happens to brightness? ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
chapter 18
... Astronomers measure stellar distances in three different units. The smallest of these is a) the light-year. b) the absolute magnitude. c) the astronomical unit. d) the parsec. ...
... Astronomers measure stellar distances in three different units. The smallest of these is a) the light-year. b) the absolute magnitude. c) the astronomical unit. d) the parsec. ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
Understanding Stars
... Globules condense from a nebula to form a stellar nursery The stellar nurseries are big enough to form many stars – Star clusters: open or globular Spectroscopy Every element has it’s own unique spectrum – Use this to identify the composition of a gas • Chromosphere or corona Extremely dense things ...
... Globules condense from a nebula to form a stellar nursery The stellar nurseries are big enough to form many stars – Star clusters: open or globular Spectroscopy Every element has it’s own unique spectrum – Use this to identify the composition of a gas • Chromosphere or corona Extremely dense things ...
proposed october viewing list
... best with the 4” refractor at low magnification. It contains more than 2900 stars and is estimated to be about 250 million years old. M11 is receding from us at a speed of 27 km/s. M17 The Omega, or Swan, Nebula in the constellation Sagittarius (Sah-jih-TAIR-ee-us ) is an emission nebula caused to r ...
... best with the 4” refractor at low magnification. It contains more than 2900 stars and is estimated to be about 250 million years old. M11 is receding from us at a speed of 27 km/s. M17 The Omega, or Swan, Nebula in the constellation Sagittarius (Sah-jih-TAIR-ee-us ) is an emission nebula caused to r ...
Light from stars part II
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • Refined in the 19th Century when instruments became precise enough to accurately measure brightness • Modern scale is defined so that 6th magnitude stars are exactly 100 times brighter than 1st magnitude stars • This means stars that differ in magni ...
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • Refined in the 19th Century when instruments became precise enough to accurately measure brightness • Modern scale is defined so that 6th magnitude stars are exactly 100 times brighter than 1st magnitude stars • This means stars that differ in magni ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Light years: used to measure distance to stars and galaxies – Distance that light travels in one year – 300,000 km/s = speed of light – 9.5 trillion km in one year – Sun in 8 light minutes from Earth – Proxima Centauri: closest star to Earth (other than the sun) is 4.2 light years away Sirius (brigh ...
... Light years: used to measure distance to stars and galaxies – Distance that light travels in one year – 300,000 km/s = speed of light – 9.5 trillion km in one year – Sun in 8 light minutes from Earth – Proxima Centauri: closest star to Earth (other than the sun) is 4.2 light years away Sirius (brigh ...
Magnitude Scale
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.