Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... star a large celestial body that is composed of gas and that emits light. Nuclear fusion is the combination of light atomic nuclei to form heavier atomic nuclei Astronomers learn about stars by analyzing the light that the stars emit. ...
... star a large celestial body that is composed of gas and that emits light. Nuclear fusion is the combination of light atomic nuclei to form heavier atomic nuclei Astronomers learn about stars by analyzing the light that the stars emit. ...
Main Sequence Stars
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram Study Guide
... Most stars are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. ...
... Most stars are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. ...
ASTRONOMY
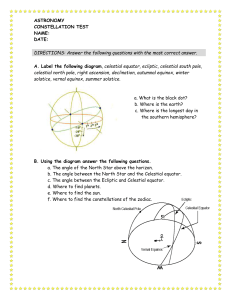
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
Chapter 8 lesson 4 Notes
... Stars form when matter comes together and starts to give off energy. ...
... Stars form when matter comes together and starts to give off energy. ...
Chapter 21 power point - Laconia School District
... Radio telescope • A device used to detect radio waves from objects in space. ...
... Radio telescope • A device used to detect radio waves from objects in space. ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
Stars and Constellations
... • They are formed in space in large clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. • Atoms inside the nebula accelerate inward due to the force of gravity and they collide rapidly with each other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise ...
... • They are formed in space in large clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. • Atoms inside the nebula accelerate inward due to the force of gravity and they collide rapidly with each other, causing the center of the nebula to become very dense and hot, causing the temperature of the protostar to rise ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • Stars are classified using three main characteristics: – Size – Temperature – Brightness ...
... • Stars are classified using three main characteristics: – Size – Temperature – Brightness ...
The Sun and the Stars
... total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s) • When discussion stars we always compare with the sun, some stars are about 10 000 times less luminous than the Sun or up to 30 000 times more luminous. ...
... total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s) • When discussion stars we always compare with the sun, some stars are about 10 000 times less luminous than the Sun or up to 30 000 times more luminous. ...
stars and constellations
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... • Hipparcos classified the stars visible to the naked eye into six different brightness classes called magnitudes • Hipparcos chose to categorize the brightest stars as magnitude 1, and the faintest as magnitude 6 (smaller numbers are brighter stars) • The magnitude system of Hipparcos is still in u ...
... • Hipparcos classified the stars visible to the naked eye into six different brightness classes called magnitudes • Hipparcos chose to categorize the brightest stars as magnitude 1, and the faintest as magnitude 6 (smaller numbers are brighter stars) • The magnitude system of Hipparcos is still in u ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... CASSIOPEIA LACERTA moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
... CASSIOPEIA LACERTA moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
Worksheet 4.1 Coordinates and Star Maps
... b. What is its abbreviated name (Greek letter and constellation abbreviation)? Alpha CMa c. What is its RA and Dec? RA: 6hr 45min Dec: -16 degrees 3. If Earth’s axis were tilted by 33.5º rather than the actual 23.5º, what would be the declination of the … a. Vernal Equinox? 20 degrees ...
... b. What is its abbreviated name (Greek letter and constellation abbreviation)? Alpha CMa c. What is its RA and Dec? RA: 6hr 45min Dec: -16 degrees 3. If Earth’s axis were tilted by 33.5º rather than the actual 23.5º, what would be the declination of the … a. Vernal Equinox? 20 degrees ...
Nebula - NICADD
... Emission Nebulae • Gas clouds can be heated by nearby stars. – Emits own light – H II region ...
... Emission Nebulae • Gas clouds can be heated by nearby stars. – Emits own light – H II region ...
BAS - Monthly Sky Guide
... just a few catalogued deep sky objects within reach of amateur telescopes – a quick look at a few globular clusters can tick this constellation off an observer’s list. However Corona Borealis, “the Northern Crown”, is a little more interesting with a scattering of distance faint galaxies. ...
... just a few catalogued deep sky objects within reach of amateur telescopes – a quick look at a few globular clusters can tick this constellation off an observer’s list. However Corona Borealis, “the Northern Crown”, is a little more interesting with a scattering of distance faint galaxies. ...
New Directions in Star Cluster Research
... Astrophysics (physics of stars) Is not an experimental science - we cannot devise and conduct experiments in order to test theories Theory is validated by observations Evidence often derived from past events Information we can gather is very restricted - apparent brightness (depends on distance), l ...
... Astrophysics (physics of stars) Is not an experimental science - we cannot devise and conduct experiments in order to test theories Theory is validated by observations Evidence often derived from past events Information we can gather is very restricted - apparent brightness (depends on distance), l ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.