An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). There are 88 officially r ...
... night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the celestial sphere as defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). There are 88 officially r ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... • How bright a star looks depends on: – How far it is from Earth – How bright the star actually is ...
... • How bright a star looks depends on: – How far it is from Earth – How bright the star actually is ...
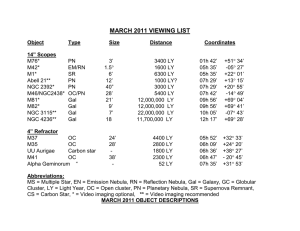
March
... M1 The Crab Nebula in the constellation Taurus (TAW-rus) is the brightest and most famous supernova remnant in the sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 da ...
... M1 The Crab Nebula in the constellation Taurus (TAW-rus) is the brightest and most famous supernova remnant in the sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 da ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... Which ones cannot be seen without the aid of a telescope? Which two planets are seen only near the hours of sunrise or sunset? 16. Where and in what way does the Bible refer to Orion, the Pleiades, and Arcturus? ...
... Which ones cannot be seen without the aid of a telescope? Which two planets are seen only near the hours of sunrise or sunset? 16. Where and in what way does the Bible refer to Orion, the Pleiades, and Arcturus? ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Early peoples observed bright stars and grouped them into constellations (88) Ancient Greeks established classification system based on star brightness ...
... Early peoples observed bright stars and grouped them into constellations (88) Ancient Greeks established classification system based on star brightness ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Characteristics of Stars
... luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
Review_game_and_answers
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. Completion: 1. Gather in groups of 3 (one for each mass type) 2. Share each flip book explaining the stages to the other two 3. Complete the worksheet provided. Life Cycle of Stars ...
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. Completion: 1. Gather in groups of 3 (one for each mass type) 2. Share each flip book explaining the stages to the other two 3. Complete the worksheet provided. Life Cycle of Stars ...
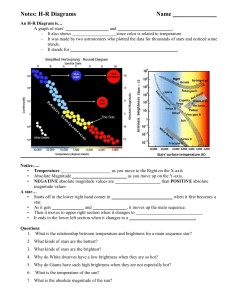
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... 6. The star Fomalhaut is visible in the evening now, and will be more prominent later in the fall. Its apparent magnitude is 1.15. Is it brighter or fainter than Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a ...
... 6. The star Fomalhaut is visible in the evening now, and will be more prominent later in the fall. Its apparent magnitude is 1.15. Is it brighter or fainter than Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.