chap17_f03_phints
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. HINT: A star appears fainter if it is located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived bright ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. HINT: A star appears fainter if it is located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived bright ...
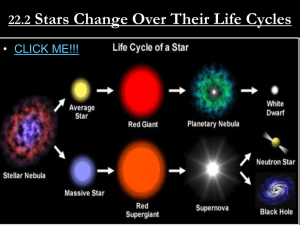
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
... viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
Stars
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
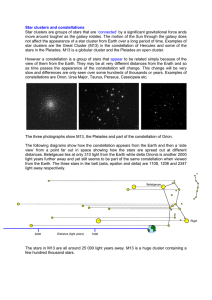
Star clusters and constellations
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
September Evening Skies
... Two open or galactic clusters are noted: M7 between the Teapot and tail of Scorpius, and the Double Cluster in Perseus. Two globular clusters, more compact concentrations of hundreds of thousands of stars, can be found: M13 in Hercules and M22 in Sagittarius. M8 in Sagittarius is the Lagoon Nebula, ...
... Two open or galactic clusters are noted: M7 between the Teapot and tail of Scorpius, and the Double Cluster in Perseus. Two globular clusters, more compact concentrations of hundreds of thousands of stars, can be found: M13 in Hercules and M22 in Sagittarius. M8 in Sagittarius is the Lagoon Nebula, ...
The Constellation Microscopium, the Microscope Microscopium is a
... brightest star. It is a yellow giant of spectral type G6III. Lying 381 light years away, It depicts the eyepiece of the microscope. Alpha Microscopii is also a yellow giant, though in this case a variable Johann Bode in his Uranographia atlas of star, which ranges between apparent magnitudes 4.88 an ...
... brightest star. It is a yellow giant of spectral type G6III. Lying 381 light years away, It depicts the eyepiece of the microscope. Alpha Microscopii is also a yellow giant, though in this case a variable Johann Bode in his Uranographia atlas of star, which ranges between apparent magnitudes 4.88 an ...
One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the
... information is discovered. Which of the following would NOT be a result of new scientific research and information? A. Binomial nomenclature is assigned to a recently identified plant species. B. An endangered monkey species is put in a reserve for protection from extinction. C. A newly discovered c ...
... information is discovered. Which of the following would NOT be a result of new scientific research and information? A. Binomial nomenclature is assigned to a recently identified plant species. B. An endangered monkey species is put in a reserve for protection from extinction. C. A newly discovered c ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
Figure 10-6 The same star field shown in Figure
... stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. The only way to express these hitherto unsuspected magnitude ...
... stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. The only way to express these hitherto unsuspected magnitude ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
... Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order to be visible to the naked eye? Suppose two stars have ...
... 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order to be visible to the naked eye? Suppose two stars have ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 S ...
... 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 S ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
1 - Pitt County Schools
... Chapter 25 Concept Questions Name:_______________________________Date:___________________ 1. Absolute magnitude: 2. Apparent magnitude: 3. Big band theory: 4. Binary star: ...
... Chapter 25 Concept Questions Name:_______________________________Date:___________________ 1. Absolute magnitude: 2. Apparent magnitude: 3. Big band theory: 4. Binary star: ...
Blank Jeopardy
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
Constellations
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
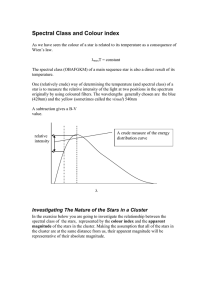
Spectral Class and Colour index
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.