Constellation Information
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
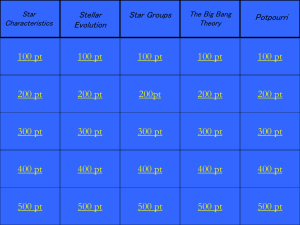
Stars and Moon Summative Review
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
Slide 1
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... passes through our atmosphere, its path is deviated (refracted) multiple times before reaching the ground. Stars that are near to the horizon will scintillate much more than stars high overhead since you are looking through more air (often the refracted light will display individual colors). In spac ...
... passes through our atmosphere, its path is deviated (refracted) multiple times before reaching the ground. Stars that are near to the horizon will scintillate much more than stars high overhead since you are looking through more air (often the refracted light will display individual colors). In spac ...
Stars Part 2 - westscidept
... Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 light years away. There are thousands of close ...
... Earth is called apparent magnitude. • A dim star might look bright to us on Earth if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 light years away. There are thousands of close ...
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
Apparent brightness
... Distinguish between luminosity and brightness and explain how stellar luminosity is determined. Explain how stars are classified according to their colors, surface temperatures and spectral characteristics, and tell why such a classification is useful. State how an H-R diagram is constructed, ...
... Distinguish between luminosity and brightness and explain how stellar luminosity is determined. Explain how stars are classified according to their colors, surface temperatures and spectral characteristics, and tell why such a classification is useful. State how an H-R diagram is constructed, ...
Cat`s EyE - Chandra X
... HOW: The spectacular filamentary structures in planetary nebulas come from the outer layers that have been shed by the dying star then sculpted by intense radiation from the hot central star (bright white dot in middle) that will eventually become a white dwarf. WHY: It is important to understand th ...
... HOW: The spectacular filamentary structures in planetary nebulas come from the outer layers that have been shed by the dying star then sculpted by intense radiation from the hot central star (bright white dot in middle) that will eventually become a white dwarf. WHY: It is important to understand th ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
name - New York Science Teacher
... TASK# 1: MAGNITUDE & BRIGHTNESS You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on ...
... TASK# 1: MAGNITUDE & BRIGHTNESS You will begin by learning how to identify stars by their magnitude (brightness), color, and temperature, and spectral class. PART 1: Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on ...
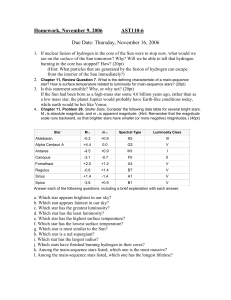
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.